Contributing to Extinction: The Petting Scam.
THE BIG CAT DEBATE PART III
“Conservation is not Petting Cubs or Promoting the Petting Industry”
Over the past week and a half we have been investigating some nine conservation organisations and companies aligned to them organisations within South Africa. As of yesterday we began to make public them questions which were legitimate and fully above board. We have given two related companies known as Your Cheetah Spot and Ukutula Game Lodge over twenty four hours to answer the questions set out here on Facebook within this article. Any professional organisation that isn’t involved within the direct petting or game hunting of threatened species one would then think such questions would quite easily be answerable to place public faith into the domain. Unfortunately within the past hour it seems otherwise.
Your Cheetah Spot a photography and alleged merchandise company, and what appears to be an organisation that is directly aligned with the promotion of petting cubs has not only failed to answer more than straightforward questions, but has evaded them by attacking us with silly nonsense seen hereto. Now we weren’t pointing fingers, nor was we accusing which can be read in all of our posts on Facebook hereto.
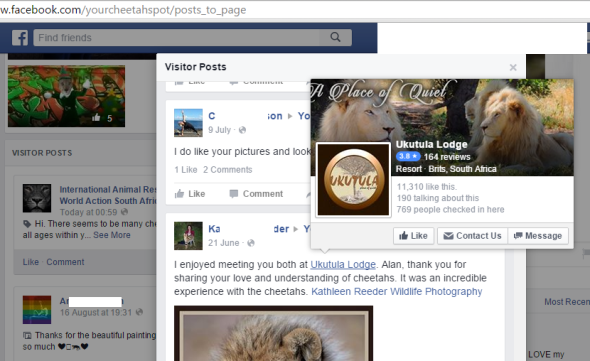
While we respect that Your Cheetah Spot is indeed a company their main Facebook imagery and online articles states otherwise. In the image below one can clearly see that the Your Cheetah Spot company is in someway aligned with the recently brought into question Ukutula Game Lodge, that appears to have some two or more Facebook pages online. International Animal Rescue Foundation Africa is a company and not charitable. Meaning that we work for our money. From 2012 to 2015 we have become increasingly suspicions in relation to over ninety South African organisations being “conservation and hunting”.
We equated that over R8.9 BILLION (ZAR) has been pumped into all of the ninety hunting and conservation organisations. However we’ve seen little if any conservation work, reduction in species threat status, reduction in anti poaching or increase of any species they are directly working with in the wild. As we are not a charity but indeed a giver 1/2 of these organisations fell within our (Funding African and Asian Wildlife Survival) program. While we have not provided monetary income to Your Cheetah Spot or Ukutula Game Lodge, we have directly and indirectly promoted their services or organisation[s] (2013-2014). That in turn has technically brought our company into disrepute in regards to malpractice and public misinformation, furthermore it was somewhat more embarrassing that members of the public also pointed this out to us too, and not forgetting some twelve key conservation experts.
The image below shows that both Your Cheetah Spot and Ukutula Game Lodge are related in one way or the other.
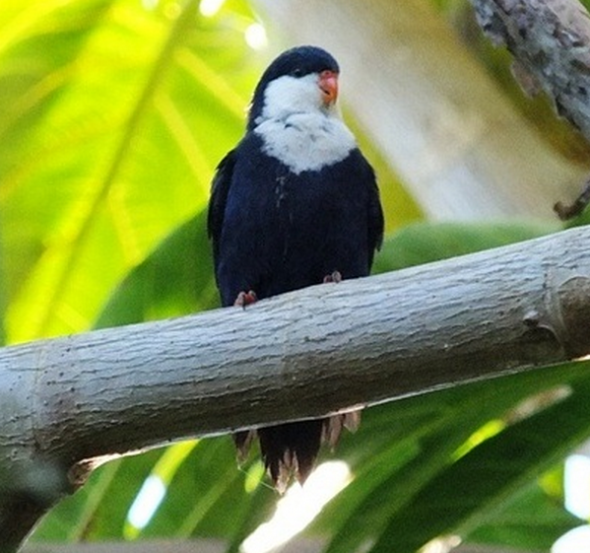
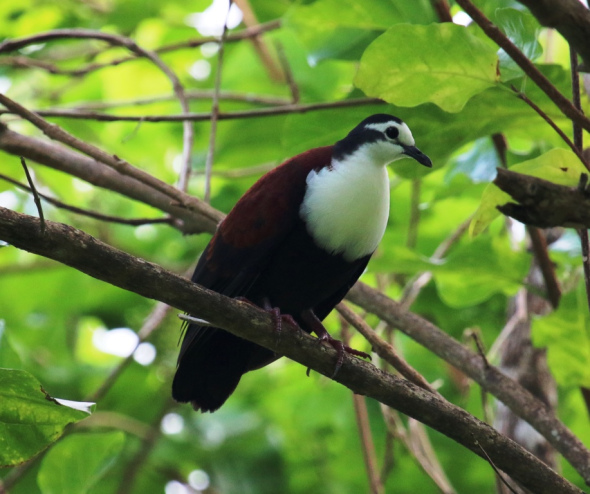
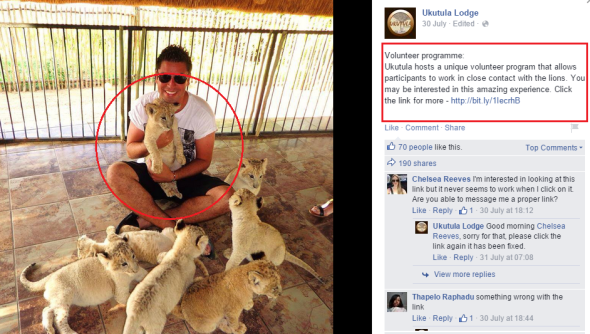
Ukutula Lodge does go under other names of Facebook too such as Ukutula Game Lodge Etc. On viewing Your Cheetah Spot company we were somewhat concerned with the vast amount of small cubs that are in our eyes being petted by the public, or by the staff in general from which we believe is at the Ukutula Game Lodge. Please view the images below. Please also note that it has been alleged that some of these animals are “sick and unwell” and cannot be released into the wild. We our now bringing that into question.
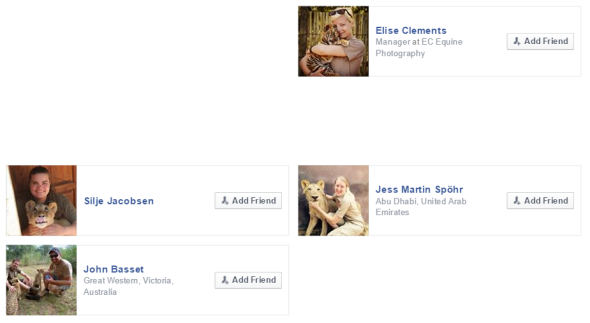
The male in the image above is known as a wildlife photographer and conservation researcher, of which he also with his students, friends and family helps at the Cheetah Research Center, while meeting up with members of the public at the Ukutula Game Lodge or Ukutula Lodge. When putting questions to Scottish born Alan Strachan and the user on the Your Cheetah Spot Facebook page we was then made aware of the current unprofessional behavior of Ukutula Game Lodge. Its at this very lodge that our suspicions have yet again arisen, of which you can view in the images below.
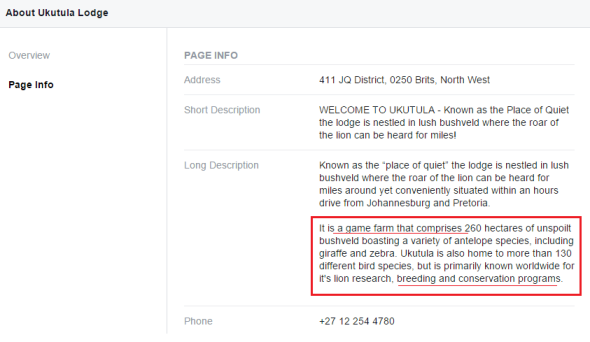
Interestingly when viewing more data on Ukutula Game Lodge we were somewhat perplexed as to how many big cats this farm is currently holding of which it states “is research”. Even more worrying is that the vast majority of these cats are/or were all cubs, all of which are being bred on a “game farm”. Please view the data below.
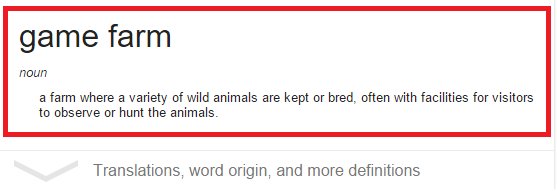
Now just to remind the millions of readers that tune into our environmental investigations news site what a game farm is, we have made it very simple to read and understand for you to come to your own conclusions. Please see the image below.
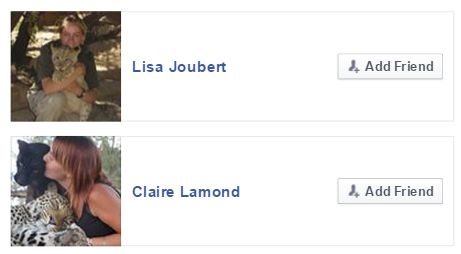
A further suspicion that was then immediately raised by the External Affairs investigative team was the vast majority of friends on Mr Strachan’s Facebook friends list that are all (holding or petting) cubs, yet there seems to be no mothers in sight, please see the image below.
The list is pretty endless of which you can view more here
Any good professional conservation teacher, conservation organisation, research center, or reserve would not under any circumstances allow the direct petting of any big cat cubs. The potential for virus and disease to emerge and not forgetting the removal of the cats natural hunting instincts would severely be detrimental to the animals health. So on viewing the two parties being that The Ukutula Game Lodge and Your Cheetah Spot company that boasts years of experience then why are we seeing such behavior? Furthermore on questioning Your Cheetah Spot company they categorically stated that they hadn’t released any animals in to wild since [2007]. Yet they also stated to the CEO that they were just a simple photography and gift company.
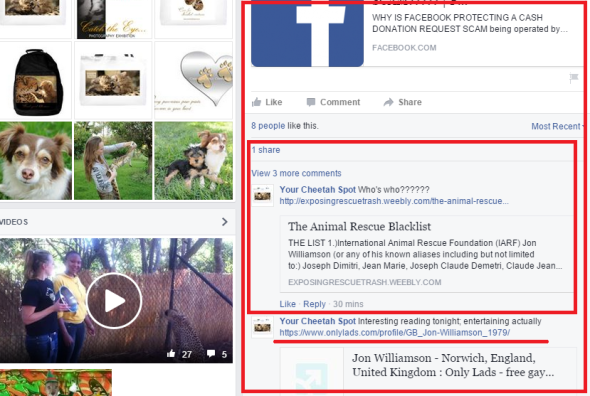
International Animal Rescue Foundation Africa asked some nine very basic and straight forward easy to answer questions. The organisation has waited and waited, the questions were stern but not abusive. However it would appear that on asking such straightforward questions “Your Cheetah Spot company” has not only become abusive but have shown just how hateful of homosexuals they are (again clutching at straws and trying to turn the table onto us). See the screen shots below.
So when basic very polite questions are asked not only are we spat at with trolling nonsense from hunters and deluded pseudo activists whom have created these articles in the image above, the Chief Executive Officer is then spat more abuse at insinuating that he is gay and obviously goes under many other names too. And as yet, still there is no answers to our questions.
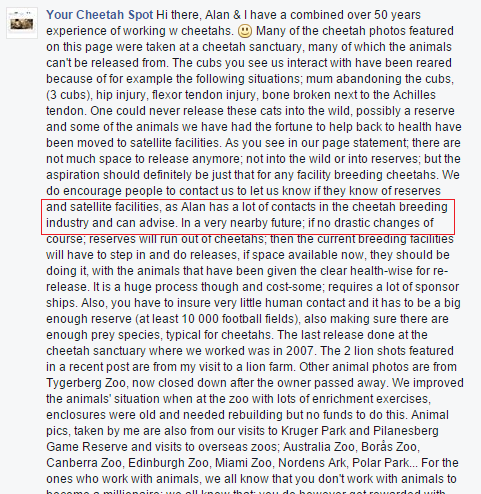
Linda whom runs the Facebook page Your Cheetah Spot stated that the vast majority of these animals cannot be released back into the wild. The kind lady also stated that many animals are sick or injured. Furthermore Linda stated that there is not enough room to simply release Cheetahs back into the wild within South Africa. As a more than competent and professional environmental company there is room, and there are also many active reintroduction programs over the border. In our own opinion these animals are not being released as then that would mean a loss of revenue. Furthermore if these animals are being bred for science, what happens to them after the research is up. Lastly as you may all remember Cecil? Cecil was one of many Lions that the Oxford University Lion Research Center studied, oddly IN THE WILD!
Reintroduction programs have been very operational within Swaziland for some years. Furthermore South Africa is not detached from the continent. Bordering you have Botswana, Namibia, Zimbabwe, Mozambique and finally Lesotho with Swaziland in the far right. So the excuse that these “many small cubs” that are new born and are most certainly not sick, old, injured (in most cases) cannot be reared in accordance to a professional captive breeding program is utter nonsense. Just to remind you - Linda whom is aligned with the You Cheetah Spot company stated that the last release was back in 2007 of any Cheetahs which we do believe was in the KWN.
A further concern is that Linda stated Alan Strachan (experienced photographer and author) has many contacts within the Cheetah Breeding theater, see image below.
The comment above is just a contradiction of what is being viewed at the Ukutula Game Lodge of which Alan Strachan visits regularly such as “you have to make sure that there is very little contact with humans” “The last prey release was back in 2007”. If these contradictions do not spring up red flags to you then they should. Swaziland has been the center for many Cheetah releases over the years as listed on the International Union for the Conservation of Nature’s website. Furthermore the sheer fact that in the vast majority of Mr Strachan’s images on his Facebook profile that depict “cub petting” and on their very own Facebook page is also somewhat concerning.
THE LIES BREEDING AND RESEARCH CENTERS TELL YOU
Below is a list of common lies or misinformation breeding, research and farming centers will try their utmost best to tell you. However at the end of the day its down to you to undertake your own research. Why are there so many cubs, why have there never been any releases of animals into the wild, why are there never no mothers seen with the cubs, why did the breeder or the supporter of a breeder state that these animals cannot be released back into the wild in South Africa..The simple answer to that question would be (mass loss of profit). Again we’re not putting words into your mouths, we are though asking you to please open your eyes, question, look around.
Breeders who charge the public to pet and take photos with young tiger, lion, cheetah or leopard cubs tell venues and customers some or all of the following ‘misinformation which is’:
1) That the exhibitors are “rescuers” and operate “sanctuaries”
2) That the cubs have a good life while being used to make money:
a) They enjoy being carted around the country in a semi and repeatedly awakened and handled by dozens of people all day
b) That blowing in the cubs face “calms” them down
c) That dangling them by holding under their front arms and bouncing them up and down “resets” them cubs at the mall
Cubs at the mall always = cub abuse
d) That close up photos with flash does not harm the cubs
3) That it is safe for the cubs and for humans, and legal, to allow contact with cubs from when they are only a few weeks old to when they are six months or more old.
4) That the exhibitor must keep constantly breeding and using the cubs to make money because that is the only way he can support the adult animals he keeps.
5) That the exhibitor is doing this to promote conservation in the wild.
6) That the exhibitor is teaching people not to have exotic animals as pets
And the biggest lie of all:
7) That the cubs will have good homes after they get too big to be used to make money from petting.
The images and evidence that is seen on one of the nine alleged conservation organisations that are either directly or indirectly involved in the promoting of petting or in this case “science and research”. Have shown little evidence of anyone of these animals actually being released into their native wild.
We DO NOT buy the excuse that states there is little room in South Africa to release these animals back into their native wild. Africa is a continent and South Africa is most certainly not detached from neighboring countries. South Africa borders Botswana, Namibia, Zimbabwe, Mozambique, Lesotho and Swaziland. Swaziland is one country of particular interest as many Cheetah reintroduction programs are happening within this country. The Cheetah Spot company also made public that Mr Strachen has many contacts with “Cheetah breeders” so why are we not seeing reintroduction, but more ‘petting’ of which these images are directly promoting the petting industry which in turn directly promotes the canned and non-canned hunting industry.
If you would like to know more about felid petting one can view the link here supplied by the Big Cat Rescue.
So as our questions haven’t been answered then we’ll reprint them here in a more orderly and professional fashion. On hitting the publish button the news letter will be sent to over 2,000 subscribers and over 6.1 million supporters respectfully.
- What relation does Mr Strachan and Your Cheetah Spot company have in relation to the Ukutala Game Lodge?
- Why are there so many cubs being shown on the Ukutala Game Lodge and Your Cheetah Spot company that are not unwell but more than healthy?
- Why are there so many cubs with no mothers being petted at the Ukutala Game Lodge, and where are their mothers?
- What happens to the cubs being shown on the Your Cheetah Spot company and Ukutala Lodge when you have reached maximum holding capacity?
- From reading, Your Cheetah Spot company states its nothing more than a photography and merchandise company. The company stated that they have only managed to release some Cheetahs into the wild back in 2007. So from 2007 to date you’ve obviously been in contact with more cubs, so how many animals are you holding on this farm, and where are the excess going too, one cannot just continue breeding and not releasing they are obviously going somewhere?
- Are you Ukutula and Your Cheetah Spot company involved in game or canned hunting?
- Why are you “Your Cheetah Spot” company directly encouraging through photography the petting industry but then contradict yourselves by stating that these animals must have the bare minimal human contact?
- Are both Your Cheetah Spot company and Ukutala Game Lodge aware of the health implications to these animals via the direct handling, man-handling and petting of cubs and elders?
- Why does the Your Cheetah Spot company that stated 1. They are just a merchandise company then 2. agreed they are working directly with these animals believe that South Africa is the only country that these animals can be released into?
- Will you Your Cheetah Spot company and Ukutula Game Lodge make public the amount of animals that you have allegedly helped, released into the wild and how many have been deliberately bred?
- Why when questioned did you not answer the questions highlighted but then some 14 hours later placed untrue, derogatory and misleading data into the public domain asking people to share. When all we did was obtain the information from your own sites, your own staff, friends and online data? No professional organisation or individual would behave in that manner?
- How much money are Your Cheetah Spot Company directly making from petting big cats and cubs?
- How much money are Ukutala Game Lodge making from the direct petting of big cats and cubs, and where is this money going too. Why are you also promoting the “interaction with very healthy cubs” to foreign tourists of which is commonly known as a “Lion Petting Farm aka Hunting Industry”?
The next time you want to abuse us you may want to remember that we are not propagating misleading lies about you. The data above has derived directly from you. All we have done is placed that all together, reviewed it and come to the conclusion that from questions 1-13 both of you are in some way directly involved in the petting industry which has direct relations to the hunting industry.
For now we’re going to leave our concerns at this. We will though be going through all organisations and individuals aligned with us and, if found to be exploitation any animals will be removed and exposed by us. Lastly when you have emigrated to our country please respect our natural heritage.
External Affairs Department
externalaffairs@international-animalrescue-foundation.org.uk
Environmental and Animal Abuse Investigations Authority Europa.
EXTERNAL AFFAIRS HEAD OFFICERS:
Jose C. Depre: Chief Executive Officer.
Johan Le roux: Anti Poaching / Illegal Animal Parts Trade Head Investigator.
Michal Jooste: Endangered Species Watch.
Pitier Van rens den: Chief Environmental Officer and Emergency Rescue.
Endangered Species Monday: Archaius tigris
Endangered Species Monday: Archaius tigris
This Mondays Endangered Species watch Post (ESP) I document on yet another African species of wildlife that hunting revenue is not helping to preserve. The Tiger Chameleon was identified back in 1820 by Dr Heinrich Kuhl (September 17, 1797 – September 14, 1821) was a German naturalist and zoologist. Kuhl was born in Hanau. He became assistant to Coenraad Jacob Temminck at the Leiden Rijksmuseum van Natuurlijke Historie. (Image: Credited to Henrick Bringsoe, A tigris).
In 1817 he published a monograph on bats, and in 1819 he published a survey of the parrots, Conspectus psittacorum. He also published the first monograph on the petrels, and a list of all the birds illustrated in Daubenton’s Planches Enluminées and with his friend Johan Coenraad van Hasselt (1797–1823) Beiträge zur Zoologie und vergleichenden Anatomie (“Contributions to Zoology and Comparative Anatomy”) that were published at Frankfurt-am-Main, 1820.
Commonly known as the Tiger Chameleon or Seychelles Tiger Chameleon the species is currently listed as [endangered] which is not uncommon as like many Chameleons within the Seychelles their range is shrinking by the year or being overrun by invasive botanical species.
Endemic to the Seychelles the species has been listed as endangered since 2006 of which populations trends are unknown. Much documentation often cites the species at “comparatively” low density, however one must not take this as factual until a true population count is seen. It has been alleged that for every [five hectares] there is possibly 2.07 individuals which isn’t good ‘if true’ since the island is only 455 km2.
From what we know the species remains undisturbed where there aren’t invasive Cinnamon trees identified as the Cinnamomum verum. However where C. verum is spreading the Tiger Chameleons habitat is under threat from this invasive plant. There is a negative correlation between Chameleon density and the presence of cinnamon, suggesting this invasion is detrimental to chameleon populations. Negative correlation is a relationship between two variables such that as the value of one variable increases, the other decreases.
The Tiger Chameleon’s main endemic range on the Seychelles islands is Mahé, Silhouette and Praslin. A historical record from Zanzibar (Tanzania) is erroneous. It occurs from sea level to 550 m asl, in areas of the islands that have either primary or secondary forest, or in the transformed landscape if there are trees and bushes present. Although they are currently estimated to have a restricted distribution on each island (following survey transects conducted by Dr Gerlach if anecdotal observations from transformed landscapes (e.g. degraded areas outside the areas surveyed) are valid, then the distribution would be larger than mapped at present.
To date the only [non-active] conservation actions that I am aware of are within the Vallee de Mai on Praslin which is currently not a protected national park. Fortunately the species is protected to some degree in the Morne Seychelles, Praslin and Silhouette National Parks. The primary threat within non-protected areas is as explained invasive Cinnamon which seems to be posing similar threats to both small reptilians, insects and birds on the islands and mainland Madagascar.
While the species has been in the past used as a trade animal it was alleged that there were no Cites quotes since 2000 - 2014. However from 1997 - 2013 a total of twelve live specimens were legally exported [despite the species threatened at risk status]. Cites allowed the twelve species to be exported for use within the pet trade which I myself find somewhat confusing. Two specimens were exported to Germany in 1981 with the remainder [10] sent to Spain. I am a little perplexed as to why these twelve specimens were legally exported, furthermore I have found no evidence or follow up data that would satisfy me in believing this export was even worthwhile for the species currently losing ground within their natural habitat.
From 1981 -2010 a further 98 dead specimens were legally exported for scientific zoological projects. Then in 1982 a single live specimen was legally exported with Cites permit for experimental purposes. While I cannot [again] locate any evidence or reason as to why this single specimen was exported alive - I must make it clear that Cites is sympathetic to Huntington Life Science’s and various other animal experimental laboratories. However this doesn’t prove that Cites has exported to anyone of these experimental research centers, it is merely my assumption.
Image: Archaius tigris
No other trade is reported out of the Seychelles, although re-export of specimens imported to Germany and Spain has been reported to Switzerland and South Africa, respectively (UNEP-WCMC 2014). This species is present and available in limited quantities in the European pet trade, and illegal trade and/or harvest may occur on a limited basis. ‘A’ report handed to myself from an [anonymous 2014] officer from the office of UNEP states that a population of some 2,000 specimens has been recorded [2014] however there is yet again no census historical data to back these claims/report up. I again must point out that if its proven there are no fewer than [2,000 Tiger Chameleons] remaining in the wild and, Cites is allowing export then Cites is going to come under immense pressure from International Animal Rescue Foundation Africa because exporting live animals for pet trade at such ‘alleged’ depressed populations - is neither helping the species nor supportive of conservation practices.
Threats
The main threat is habitat degradation as a result of the invasion by alien plants species, especially Cinnamomum verum, principally on Mahé and Praslin. Cinnamon is displacing other vegetation, it is present all over the islands and it is the fastest growing, heaviest seeding plant in most areas and is changing the composition of the forests. Currently it makes up 70-90% of trees in Seychelles forests, reaching >95% in some areas. For Archaius tigris, the cinnamon trees provide a normal structure of vegetation, but the invaded forests support a massively diminished insect population, somewhere in the region of 1% of normal abundance. This excludes invasive ants which are the only common invertebrates associated with cinnamon.
In addition, the cinnamon produces a denser canopy than native trees, giving deeper shade which excludes forest floor undergrowth (other than cinnamon seedlings), and this also is a factor in the reduced insect abundance. The Chameleons are found on cinnamon and in cinnamon invaded areas, as long as there is a wide diversity of other plants and a dense undergrowth. In fact, rural gardens can provide habitat for the Chameleons, because these tend to be more diversity in terms of flora, and therefore can support invertebrate fauna.
Dr Jose C. Depre
Environmental and Botanical Scientist.
Endangered Species Friday: Diomedea amsterdamensis - An Ocean of Grief.
Endangered Species Friday: Diomedea amsterdamensis
This Friday’s (ESP) Endangered Species watch Post I dedicate to one of the most stunning and adorable of all plane like birds. Listed as [critically endangered] and identified back in 1983 by South African Dr Jean Paul Roux whom is a Marine Biologist studying Zoology, Systems Biology and Marine Biology at the University of Cape Town, South Africa Jean Paul Roux works full-time at the Department of Biological Sciences, Cape Town. (Image D. amsterdamensis fledglings)
(Image: Birdingblogs.com)
Commonly identified as the Amsterdam Albatross or Amsterdam Island Albatross the species was listed as [critically endangered] back in 2012. This gorgeous bird is endemic to the French Southern Territories of which its populations are continuing to decline at a rapid pace. Populations were estimated at a mere 170 individuals which in turn ranks as the worlds most endangered species of bird. Out of the 170 individuals there are a total of 80 mature individuals consisting of 26 pairs that breed annually.
Between 2001-2007 there were a total of 24-31 breeding pairs annually, which leaves a slightly lower population count today of around 100 mature individuals. Back in 1998 scientists stated that there were no fewer than 50 mature individuals if that. The Amsterdam Albatross doesn’t naturally have a small population however qualified for the category of [critically endangered] due to this reason when identified in 1983. Furthermore pollution, habitat destruction and disease remain pivotal factors that’s decreasing populations furthermore. The video below from MidWay island explains a little more about pollution and birds of this caliber.
Its quite possible that there could be more unidentified groups within the local territory or elsewhere, unfortunately as yet there is no evidence to suggest the Amsterdam Albatross is located anywhere else, however there have been sightings, which do not necessarily count as the species being endemic to countries the bird may have been noted within.
The species breeds on the Plateau des Tourbières on Amsterdam Island (French Southern Territories) in the southern Indian Ocean. An increase of populations was documented via census back in 1984, a year after identification. Marine Biologists have stated that population sizes may have been more larger when its range was more extensive over the slopes of the island.
Meanwhile in South Africa satellite tracking data has indicated the Amsterdam Albatross ranges off the coast of Eastern South Africa to the South of Western Australia in non-breeding pairs. There have been some [possible] sightings over Australia through to New Zealand too. Meanwhile South Africa “may” have its first breeding pair this must not be taken as factual though. Back in 2013 a nature photographer photographed an Amsterdam Albatross off the Western Cape of South Africa which is the very first documented and confirmed sighting [2013].
AN OCEAN OF GRIEF
Breeding is biennial (when successful) and is restricted to the central plateau of the island at 500-600 m, where only one breeding group is known. Pair-bonds are lifelong, and breeding begins in February. Most eggs are laid from late February to March, and chicks fledge in January to February the following year.
Immature birds begin to return to breeding colonies between four and seven years after fledging but do not begin to breed until they are nine years of age. The Amsterdam Albatross exact diet is unknown, but probably consists of fish, squid and crustaceans. During the breeding season, birds forage both around Amsterdam Island and up to 2,200 km away in subtropical waters which is something of interest. During the great Sardine Run many aquatic species consisting of birds, seals, sharks and whales hit the South African oceans hard for sardines. So I am calling on my fellow South African friends to please be on the lookout for this rather elusive bird.
Read more here on the Avian Biology.
Image: Amsterdam Albatross mating ritual, credited to Andrew Rouse.
Diomedea amsterdamensis, is quite a large albatross. When described in 1983, the species was thought by some researchers to be a sub-species of the wandering albatross, D. exulans. Bird Life International and the IOC recognize it as a species, James Clements does not, and the SACC has a proposal on the table to split the species. Please refer to the link above on Avian Biology which will explain more on the bird and its current classification.
More recently, mitchondrial DNA comparisons between the Amsterdam albatross, the wandering albatross Diomedea exulans, the Antipodean albatross D. antipodensis and the Tristan albatross D. dabbenena, provide clear genetic evidence that the Amsterdam albatross is a separate species.
Threats
Degradation of breeding sites by introduced cattle has decreased the species’s range and population across the island. Human disturbance is presumably also to blame. Introduced predators are a major threat, particularly feral cats. Interactions with longline fisheries around the island in the 1970s and early 1980s could also have contributed to a decline in the population.
Today the population is threatened primarily by the potential spread of diseases (avian cholera and Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae) that affect the Indian Yellow-nosed Albatross Thalassarche carteri population 3 km from the colony. Infection risks are very high and increased chick mortality over recent years suggests the population is already affected.
The foraging range of the species overlaps with longline fishing operations targeting tropical tuna species, so bycatch may also still be a threat, and a recent analysis has suggested that bycatch levels exceeding six individuals per year would be enough to cause a potentially irreversible population decline. Having a distribution on relatively low-lying islands, this species is potentially susceptible to climate change through sea-level rise and shifts in suitable climatic conditions. Plastic pollution has also been noted as problematic.
International Animal Rescue Foundation Africa and International Animal Rescue Foundation France are currently working on projects to reduce more plastic within bird habitat that has never been visited by the organisation before. The current plight of bird habitat and plastic pollution within the Pacific ocean needs to be worked on by everyone, furthermore addressed immediately.
To date all twenty two species within the four genera of Albatross are heavily threatened with extinction. There remains no species at present that is listed as [least concern]. The future is indeed very bleak for all 22 species and something we now need to work on and towards to preserve Albatross’s before extinction occurs within a decade for the vast majority of all twenty two species and sub-species.
Thank you for reading.
Please share to make aware the plight of this stunning bird and the remaining twenty two species too.
Dr Jose C. Depre.
Botanical and Environmental Scientist.
A planet without birds is a world not worth living within anymore. Daily I am traumatized and deeply disturbed at viewing the destruction we have caused to these stunning animals and, their natural habitat. I am pained, deeply frustrated and infuriated at international retail companies whom preach good yet practice negligence killing off via plastic pollution our species of birds. Jose Depre
Endangered Species Monday: Vini peruviana.
Endangered Species Monday: Vini peruviana
This Monday’s endangered species watch post (ESP) I document on a rather elusive bird that is rarely spoken about within the conservation theater or among animal rights organisations. Listed as (vulnerable) the species was formally identified by Professor Philipp Ludwig Statius Müller (April 25, 1725 – January 5, 1776) was a German zoologist. (Image V. peruviana, photographer Tara)
Statius Müller was born in Esens, and was a professor of natural science at Erlangen. Between 1773 and 1776, he published a German translation of Professor Linnaeus’s Natursystem. The supplement in 1776 contained the first scientific classification for a number of species, including the dugong, guanaco, potto, tricolored heron, umbrella cockatoo, red-vented cockatoo, and the enigmatic hoatzin. He was also an entomologist.
Despite the birds high population size the Blue Lorikeet-scientifically named as Vini peruviana is under threat from feral cats, accidental introduction of black rats and violent storms that hit the birds native range frequently causing untold damage and catastrophic destruction to the specie habitat. Furthermore the ‘swamp harrier’ remains an all out threat to Blue Lorikeet’s range which has led to wide range species decline. Swamp Harriers predate on the Blue Parikeet mainly due to the birds color.
Endemic to the Cook Islands and French Polynesia, Blue Lorikeet population sizes are declining quite fast of which drastic conservation measures are now required to control feral cats and the accidental introduction of black rats, not forgetting measures to either reduce swamp harriers or introduce a non-endangered prey for the harrier. The last survey which I believe was undertaken sometime back in 2012 showed a ‘global population’ estimated to be at 7,200 to 9,000 individuals. Which is still quite high, however not high enough to stop the species qualifying for the classification of (endangered).
Taking into consideration range and overall total population size (at an estimate) the species falls into the ‘band’ of 2,500 to 9,000 individuals. This equates (exactly) to 1,677-6,666 ‘mature individuals’ rounded to 1,500-7,000 mature individuals. Summarizing; the exact total population size could be as low as 1,500 but no greater than 7,000 mature individuals (which is extremely concerning).
Blue Lorikeet’s have been recorded within twenty of the south-east Polynesia islands, unfortunately on seven of these islands the species has since been declared officially extinct. The species now remains sparsely distributed on some thirteen islands of which is threatened by rats, feral cats and the swamp harrier. We now know the species is situated within the Society Islands (formerly all), the northern atolls of the Tuamotu Archipelago (both French Polynesia), and Aitutaki (Cook Islands).
Image: Blue Lorikeet - Vini peruviana
Within the Society Islands conservation teams estimated that there were some 200-400 individual pairs on the Motu One and Manuae respectively in 1973 , however this may no longer be the case. On the Maupihaa island back in 1999 conservationists that believed the species to be extinct located breeding pairs. In Tuamotus 2006 surveys have shown the following data in relation to population sizes; Kaukura (1,000), Rangiroa (1,000), Arutua (500), Apataki (200) and Tikehau (50).
Meanwhile in Tiamanu Motu in Apataki atoll a minimum 300 individuals were estimated back in 1989 (this sub-population being allegedly smaller than 10 years previously). On Aitutaki, where it was probably introduced, numbers have been estimated at under 500 pairs, 2,400 individuals and 1,000 individuals (2006).
Following the devastation of Cyclone Pat (2010) a further census was undertaken to asses the impacts of freak weather patterns and catastrophic cyclones on the species. Distance sampling surveys on the island of Aitutaki (2011) showed a decrease in population size of exactly 1,400 individuals. That’s quite a substantial decline of individuals caused directly by a single yet destructive cyclone.
Blue Lorikeets depend on coconut palms for nesting and some of its food, and will frequent cultivated areas. They also roost in palm trees, rising at dawn and calling and preening before feeding. They are usually found in small flocks of less than ten birds. They are active birds, feeding on nectar, insects, and ground forage.
Image: Swamp Harrier (Wiki) - . Circus approximans
Threats
The species’s extinction from many islands is most likely due to predation by black rat Rattus rattus and to a lesser extent, feral cats Felis catus. Blue Lorikeet’s have gone extinct from Makatea in the Tuamotus could have been accelerated by a particularly violent hurricane. Its range reduction in the Society Islands correlates with the spread of the introduced Swamp Harrier Circus approximans. The accidental introduction of black rats to the islands where Blue Loirkeet persists is a continuing threat to the species. Listed on Cites Appendix II conservation actions are under way with more projects proposed.
Thank you for reading.
Dr Jose. C. Depre
Botanical and Environmental Scientist.
India: War on Poaching Intensifies.
India: War on Poaching intensifies.
Since early May 2012 the Indian State, Maharashtra government provided all of its rangers a shoot to kill licence directly aimed at “poachers” regardless of age, sex or religion. The shoot to kill order was given of which rangers are immune from prosecution due to high levels of Rhino, Tiger, Lion and, Elephant poaching within the country.
When International Animal Rescue Foundation India became aware of Maharashtra government’s demands they watched and waited for results of which back then were little however, since 2013 rangers have been actively involved in over one hundred and forty nine legal killings with a further eleven so far to date (13th June 2015). The number is believed to be a lot higher. Furthermore as poaching is not just confined to “animals” but also the sacred sandalwood, forestry rangers have been actively engaging sandalwood poachers and smugglers too.
April 4th 2015 forestry rangers and Police came under heavy gunfire in two separate locations within Tamil Nadu, Chittoor. Police and forestry guards tried to apprehend some twenty sandalwood poachers/smugglers of which took off into the sandalwood forests in Andhra Pradesh. The first shoot out saw some saw some nine smugglers shot dead in one area of the sandalwood forest that is unknown to us while a second saw a further eleven smugglers shot dead in what was described as a “heavy exchange” of bullets from both sides within Chittoor in Southern Andhra Pradesh. While some people have stated this action unjust we please ask you to continue to reading (to the bottom) for you to fully understand why the Police and forestry services may have took such action.
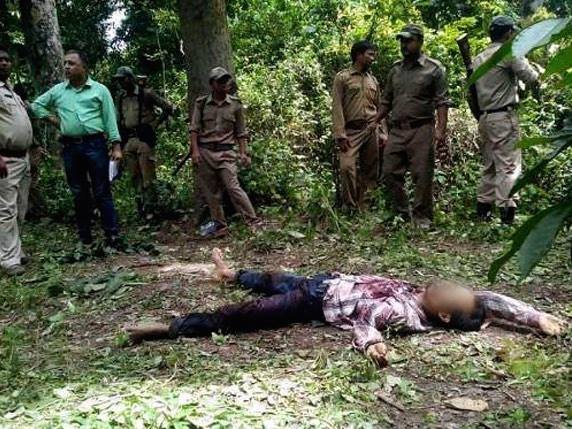
2015 has been quite a busy year thus far for forestry rangers and Police. At the start of the year, 15th January 2015 three Rhino poachers that were directly ordered to lay down their weapons aimed them at forestry guards opening fire. The incident that took place in the Kaziranga National Park, in the remote state of Assam prompted forestry guards to act quickly and professionally to preserve the sacred One Horned Rhino of which they shot the three poachers dead instantly. Fortunately no forestry guards or the Rhino were injured this time.
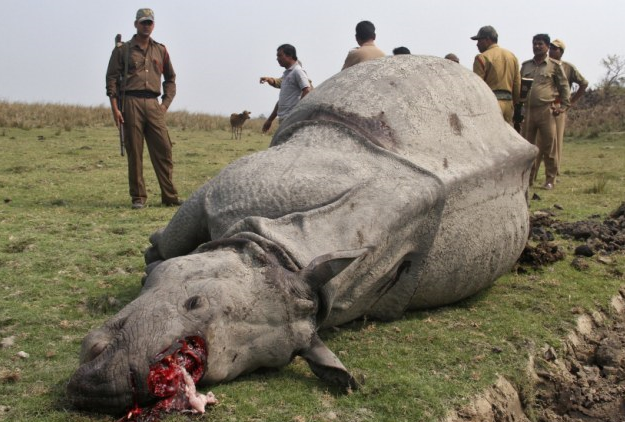
March 2015 a further three ivory poachers that were caught red handed slaughtering an Indian Rhino of which the Indian Rhino lost its life and was left in a pitiful state were shot dead immediately. We’ve included the image of that Rhino below for your information and to grasp why we and India have now had enough of this slaughter and will take the relevant steps required to support our men and women to secure our fauna and flora.
Image: Rhino killed by ivory poachers - poachers shot dead on site.
While poaching continues so does “hunting the poachers too” and so it rightfully should. International Animal Rescue Foundation India supported by its sister Africans Environmental company, began paying five “unnamed” forestry units within the shoot to kill zones larger cash incentives to hunt and take down any mammal or sandalwood poachers. The organisation has come under some fierce criticism from mainly European and American citizens most of which are devout church goers or, believe poverty is the first step that needs to be dealt with.
International Animal Rescue Foundation’s Indian Chief Executive Officer Vasvi Kanal stated “On consulting the Chief Environmental Officer back in 2012 when we were made aware of Maharashtra’s stance we knew we had to do something to support our brave men and women. After a meeting in New Delhi that following summer it was decided we should support the shoot to kill policy to send a a direct message out to poachers that you’ll no longer simply walk into our forests and parks and take what’s not rightfully yours”. Kanal went onto state “The shoot to kill policy had to be endorsed one way or the other and, I thank the Chief Environmental Officer Dr Jose Depre for wiring the funds directly to us that are now placed into the hands of these brave men and women to seek and kill poachers”.
Image: Indian Rhino poacher shot dead on site.
Since the policy was enacted in 2012 in Maharashtra some seven states within India have since followed suite of Maharashtra’s firm stance and, since 2014 we’ve seen a staggering increase of poachers that have been caught trying to kill Rhino, Elephant, Tiger or illegally harvesting sandalwood shot dead on site. Furthermore many Indian press agencies have picked up the organisations support creating debate and stories on the subject that has encouraged more and more female and male citizens to come on board to protect and preserve our natural habitat and sacred heritage.
Soon after Maharashtra’s stance on “all animal and habitat poaching/destruction” took on a new positive twist, Nepal back in 2013 set their Anti Poaching Units into action - to hunt the - hunters. About 10 years ago, when the country was deeply mired in a civil war between government forces and Maoist rebels, there was hardly any focus on wildlife protection in one of Nepal’s most famous parks
The number of army monitoring posts in and around the park was reduced from 30 to seven as soldiers were shifted to anti-insurgency operations. In 2002, about 37 Rhinos were killed by poachers, triggering grave concern over the future of One-Horned Rhinos. Their numbers dropped from an estimated 612 in 2000 to less than 375 in 2005.
“According to our last rhino census in 2011 the number of Rhinos in the park has risen to more than 500,” said Kamal Jung Kunwar, a senior official at the Department of National Parks and Wildlife Conservation.
As the chief of the Anti-Poaching Operation from 2003 to 2007, Mr Kunwar played a key role in the conservation of Rhinos in Chitwan National Park. Spread over an area of more than 930 sq km, the park consists mostly of Sal trees and grasslands. Its flat lowlands are home to a variety of endangered animals like Royal Bengal Tigers, Rhinos, Leopards and Gharial Crocodiles. Crucial re-deployment: The successful conservation effort is attributed to a variety of initiatives, including tough action against poachers, enhanced intelligence and involving villagers living around the park in conservation efforts.
Image: Rhino poacher shot dead.
Meanwhile, while India strides forwards in its tough Anti Poaching operations poachers are still targeting rangers and police leaving their seriously injured on in many cases themselves killed. Deaths continue on both sides and rarely do the press and media overseas bother to print on the bravery of these men and women or, their tragic deaths.
Back in January 2014 poachers killed a female Rhino and a home guard at the Rajiv Gandhi Orang National Park, that Wednesday. Park officials said the home guard, Sushil, was killed during a gun battle with the poachers, who also managed to chop off the Rhino’s horn.
Rifles and ammunition were recovered from the spot. This is the second case of poaching at Orang which has about 100 Rhinos. The last Rhino was killed earlier in December, following which the park authorities announced a cash reward of Rs 50,000 for information on poacher Md Joynaluddin alias Junu. The authorities have also pasted Joynaluddin’s posters at several places in Darrang, Sonitpur, and Morigaon districts.
Back in 2014 a survey was undertaken on the number of rangers that are sadly murdered by poachers and killed by wild animals within the country according to the IBT. The results were shocking of which encouraged International Animal Rescue Foundation India to push more funding into local forestry units around Assam and the Ministry that supports guards financially. India loses more forest/Anti Poaching Guards than any other country on the planet.
Most of the Indian forest security men and women have been killed by poachers and wild animals, states the survey by non-profit organisation International Ranger Federation (IRF). In the past three years, as many as 72 forest rangers died in India, whereas in other countries in Asia, Africa and America, only less than 10 deaths of forest rangers have been reported, The Times of India reported, quoting the survey by IRF which strives to create awareness about forest rangers and security men.
It can be recalled that smugglers of red sanders killed several forest rangers in AP’s Tirumala forests in recent years. Notorious bandit Veerappan has also killed several forest officers and security men till a decade ago. The survey further stated that about 60 percent of the forest rangers’ killings, in the last three years, happened in Asia.
“We are extremely concerned that rangers continue to face high levels of violence and are being murdered at an alarming pace,” said IRF president Sean Willmore.
India lost 24 forest rangers in 2014, 14 in 2013 and 34 in 2012. India tops the list in the deaths of forest rangers during all three years. The report went onto state - That most rangers were killed by wild animals and poachers. Apart from animals and poachers, diseases such as dengue and malaria, forest fires and road accidents have also claimed the lives of rangers, the survey added.
In India, smugglers of wild animals and forest wealth like red sanders do not hesitate to kill rangers, if they are obstructed from committing the crime. In Seshachalam forest of Andhra Pradesh, about 200 smugglers attacked forest rangers and killed two officers in December 2013. The 200 smugglers first rained stones on the ranger sand then attacked them with batons. Rangers in India are often seen unarmed, making them vulnerable to the smugglers’ attacks.
The government of India has been dealing with wildlife poachers with an iron fist in the past one year with 30 poachers being gunned down in the Northeast alone. The number that figured in the data released by the environment ministry is the highest ever in the country. Most of the killings took place in the Kaziranga National Park, Assam. The KNP, Assam is the largest known “active poaching area” hence the largest amount of hits and is custodian to over 1000 endangered Indian one Horned Rhinos.
“The number shows our determination to eliminate wildlife traffickers and poachers. It is a big achievement of the Modi government,” environment minister Prakash Javadekar said recently.
Highly sophisticated arms were recovered from the poachers who killed Rhinos for horns smuggled to South-East Asia through porous Myanmar. Hunting down of poachers in Kharbi Anglong of Assam was undertaken by the Congress-led Assam government to save single-horn rhinos of Kaziranga and nearby areas.
Big cats at huge risk:
Wildlife in other parts of the country isn’t as lucky as the Rhinos. As many as 23 Tigers and 116 Leopards were poached in 2014 across India, with states like Uttarakhand, Maharashtra and Madhya Pradesh reporting a large number of cases.
“These are the cases that have been reported. There might have been cases where the poachers took the whole animal, without leaving a trace,” said Tito Joseph of the Wildlife Protection Society of India. Traffic, a non-government group monitoring wildlife trade, says that there has been no let down in illegal wildlife trade in India. It says the Northeast is turning into a hub of wildlife smuggling.
A report by the National Tiger Conservation Authority also indicates weak wildlife crime management in the country. It states that almost 40% of the forest guards do not have enough equipment to deal with highly organised wildlife crimes. “The states are not providing funds to modernize wildlife crime management,” a senior official said.
Concluding;
Despite some public criticism calling the organisation “dogs” and “disgusting” India’s tough stance on Anti Poaching must continue. International Animal Rescue Foundation India hopes to push a further $15,500 into the cash incentive jar to help equip rangers, police and forest guards. Furthermore the environmental company that has some one people working on the ground in New Delhi will be working with local communities in poverty stricken zones where poachers are known to originate from to help decrease poaching, improve poverty and hopefully decrease killing on both sides.
Lastly I wish to leave you with this video directed at those that believe Indian forestry guards and Anti Poaching Units are randomly picking off innocent people. Please watch the video to the end and undertake your own Google search on those brave men that sadly lost their lives fighting for animal and environmental freedom.
Thank you for reading.
Johan La Roux
Rhino Welfare Project Africa.
Endangered Species Monday: Pseudalopex fulvipes.
Endangered Species Monday - Pseudalopex fulvipes
In this Monday’s endangered species article we focus our attention on the species of fox commonly known as the Darwin fox. Identified by Dr William Charles Linnaeus Martin (1798 - 1864). Dr Martin was an English naturalist.William Charles Linnaeus Martin was the son of William Martin who had published early color books on the fossils of Derbyshire, and who named his son Linnaeus in honor of his interest in the classification of living things.
Listed as CRITICALLY ENDANGERED the species was scientifically identified as Pseudalopex fulvipes endemic to Chile, Los Lagos. Charles Darwin collected the very first evidence of this rather stunning species back in 1834 however was not the primary identifier despite the species name. Since 1989 the fox has been re-monitored to determine its current population sizes and future classification. I am somewhat skeptical that this species will survive into the next five years even with more in-depth wild analysis - the species in my own expert opinion is doomed.
One fox was observed and captured back in 1999 for data and breeding with a further two adults captured back in 2002 in Tepuhueico. That same year it was noted a local as killing a mother and her cubs which amassed to some four Darwin foxes witnessed dead and alive within the wild since revaluation of species began from 1989. Some evidence although (little documented) has confirmed “sightings” of Darwin foxes during the year of 2002 however, these are sketchy reports.
On mainland Chile, Jaime Jiménez has observed a small population since 1975 in Nahuelbuta National Park; this population was first reported to science in the early 1990s. It appears that Darwin’s Foxes are restricted to the park and the native forest surrounding the park. This park, only 68.3 km² in size, is a small habitat island of highland forest surrounded by degraded farmlands and plantations of exotic trees. This population is located about 600 km north of the island population and, to date, no other populations have been found in the remaining forest in between.
Darwin’s Fox was reported to be scarce and restricted to the southern end of Chiloé Island. The comparison of such older accounts (reporting the scarcity of Darwin’s fox), with recent repeated observations, conveys the impression that the Darwin’s Fox has increased in abundance, although this might simply be a sampling bias.
As explained even with a very, very small increase in sightings - populations are declining and sadly we may be reporting in the next year or two an (extinction in the wild) occurring if not a complete extinction overall. Should that happen we’ve lost the entire species for good.
Darwin foxes are said and known to be forest dwelling mammals which could be why environmental surveys are proving to be fruitless. Darwin foxes occur only in southern temperate rainforests. Recent research on Chiloé, based on trapping and telemetry data on a disturbance gradient, indicates that, in decreasing order, foxes use old-growth forest followed by secondary forest followed by pastures and openings. Although variable among individuals, about 70% of their home ranges comprised old-growth forest.
Protected under Chilean law since 1929 the Darwin fox are listed on Cites Appendix II (Convention on International Trade of Endangered Species wild flora and fauna). Conservation actions that are under way in the Nahuelbuta National Park are to increase species populations and establish overall protection within this range. Temuco zoo did hold one single species of which was believed to be held for protective captive breeding however the fox has since died back in 2000.
Threats
Although the species is protected in Nahuelbuta National Park, substantial mortality sources exist when foxes move to lower, unprotected private areas in search of milder conditions during the winter. Some foxes even breed in these areas. This is one of the reasons why it is recommended that this park be expanded to secure buffer areas for the foxes that use these unprotected ranges.
The presence of dogs in the park may be the greatest conservation threat in the form of potential vectors of disease or direct attack. There is a common practice to have unleashed dogs both on Chiloé and in Nahuelbuta; these have been caught within foxes’ ranges in the forest. Although dogs are prohibited in the national park, visitors are often allowed in with their dogs that are then let loose in the park.
There has been one documented account of a visitor’s dog attacking a female fox while she was nursing her two pups. In addition, local dogs from the surrounding farms are often brought in by their owners in search of their cattle or while gathering Araucaria seeds in the autumn. Park rangers even maintain dogs within the park, and the park administrator’s dog killed a guiña in the park. Being relatively naive towards people and their dogs is seen as non-adaptive behaviour in this species’ interactions with humans.
The island population appears to be relatively safe by being protected in Chiloé National Park. This 430 km² protected area encompasses most of the still untouched rainforest of the island. Although the park appears to have a sizable fox population, foxes also live in the surrounding areas, where substantial forest cover remains. These latter areas are vulnerable and continuously subjected to logging, forest fragmentation, and poaching by locals. In addition, being naive towards people places the foxes at risk when in contact with humans. If current relaxed attitudes continue in Nahuelbuta National Park, Chiloé National Park may be the only long-term safe area for the Darwin’s Fox.
No commercial use. However, captive animals have been kept illegally as pets on Chiloé Island.
Current estimates place the species population count at a mere 250 left within the wild.
Thank you for reading.
Please share and lets get this fox the protection it requires through education, awareness and funding.
Links for interest:
Adopt a Darwin Fox.
General Information.
Dr Jose C. Depre.
International Animal Rescue Foundation Africa.
info@international-animalrescue-foundation.org.uk
International Animal Rescue Foundation Africa.
Donate to Say No To Dog Meat today.
Endangered Species Friday: Hispaniolan Solenodon.
Endangered Species Friday: Hispaniolan Solenodon
This Fridays endangered species article we focus on a very peculiar looking animal scientifically named as the Hispaniolan Solenodon pictured above.
Listed as (endangered) the species is endemic to the Dominican Republic and Haiti of which was identified back in 1833 by Dr Johann Friedrich von Brandt (25 May 1802 – 15 July 1879) was a German naturalist.
Dr Brandt was born in Jüterbog and educated at a gymnasium in Wittenberg and the University of Berlin. In 1831 he was appointed director of the Zoological Department at the St Petersburg Academy of Sciences, where he published in Russian. Brandt encouraged the collection of native animals, many of which were not represented in the museum. Many specimens began to arrive from the expeditions of Severtzov, Przhevalsky, Middendorff, Schrenck and Gustav Radde.
At first glance one would be led to believe that the H. solenodon was a type of rodent. The species is in fact a a type of shrew in the family of Solenodontidae identified by Dr Gill in 1872. While they may posses the same characteristics as rodents they do not fall into the super-class of Euarchontoglires that rodents do.
H. solenodon has been classified as (endangered) since early 1982 up to 1996 when a more in depth census undertaken on the species failed to locate any significant evidence of species population increases. To date 29th May 2015 the H. solenodon commonly named as the Haitian Solenodon or Hispaniolan Solenodon remains endangered and is nearing extinction level.
Solenodons which in (Latin means - slotted tooth) are not a creature to be underestimated either as of their pretty nasty venomous bite that does pack a rather large punch. Solenodons are one of very few species of small “rodent like shrews” that’s bite is much worse than its bark.
The solenodon is particularly fascinating because it delivers its poison just as a snake does—using its teeth as a syringe to inject venom into its target. Not a lot is known about these unusual mammals. There are only two solenodon species: One lives on Cuba and the other on Hispaniola (home to Haiti and the Dominican Republic). At night, they dig in the dirt with their Pinocchio snouts and long claws, looking for grub and waiting to disarm their prey—insects, worms, snails and small frogs and reptiles—with a toxic bite.
While their venom is not dangerous to humans we do advise that if handling to please wear a good protective layer of gloves. There have been no reports of humans falling ill or dying from being bitten by a solenodon.
The Haitian solenodon is found in forests and brush country, as well as around plantations. It is mainly nocturnal, hiding during the day in rock clefts, hollow trees, or burrows which it excavates itself. Its diet includes insects and spiders found in soil and leaf litter. Solenodons obtain food by rooting in the ground with their snouts and by tearing into rotten logs and trees with their foreclaws. This species is relatively social, and up to eight individuals may inhabit the same burrow. Litter size is 1 or 2 young. The young are born in a nesting burrow. Young solenodons remain with their mother for several months, which is exceptionally long for insectivores.
Population trends are unfortunately decreasing of which its major threats are listed below for your immediate attention.
Threats
The most significant threat to this species appears to be the continuing demise of its forest habitat and predation by introduced rats, mongoose, cats and dogs, especially in the vicinity of settlements. In Haiti persecution and hunting for food (Samuel Turvey pers. comm.) is a threat, and there is devastating habitat destruction also occurring.
Please view the video below for further information.
Thank you for reading
Dr Jose C. Depre
Chief Environmental & Botanical Officer.
Chief Executive
International Animal Rescue Foundation Africa.
California: Mega-drought looming.
“California mega drought is impending”
DESPITE man-made circulation systems, concrete canals and pipes that bring water from distant mountains to farms and populated areas California is still under an intense three year drought. California’s drought not only affects local citizens but the economy, wildlife and can increase crime and anti-social behavior.
Scientists have already stated a “mega-drought” could be one of the worst in California’s history that’s reduced much Californian landscape to a brown frazzled patch of soil. The people of Los Angeles are not new to drought or lack of rainfall though.
Back in 2011 California recorded a total of 12 inches of rainfall, in 2012 eight inches of rainfall was recorded and, in 2013 a measly (two inches) of rain was recorded for the entire year. Records for the first six months of 2014 recorded a total of one inch of rainfall. 2015 records to date do show a slight improvement although nothing to write home about.
Drought has been recorded within the “California area” since 4000 BC way before the state was founded. Climatologists recently recorded a dry period of some 1,300 years via the use of measuring aged tree stump rings. And, more recently, an extended dry period that began about 1,050 years ago likely helped cause the absolute collapse of intricate Southwest American-Indian societies.
Meanwhile while this three year extended drought is being recorded as “possibly” the worst “mega-drought” in California’s history floods have also took their toll onto the state of America founded in 1850. While the area has been affected by what we consider natural drought since 4000 BC floods have also been noted although these are mostly caused by riverine flooding. Floods of 1825 changed the course of the Los Angeles River from its western outlet into Santa Monica Bay following the course of Ballona Creek to a southern outlet at San Pedro Bay near where it is today. January 1850 floods devastated Sacramento.
Image: 1955-1956 California was hit by some of the worst floods in 90 years.
The Feather River, the Sacramento River’s main tributary in the northern Sierra, rose to 250,000 cubic feet per second and flooded Yuba City and Marysville. The flood destroyed hundreds of buildings (image above) and killed at least 60 people. Such flooding provided support for A. D. Edmonston’s 1951 plan to build the Oroville dam.
December 1861 residents within California witnessed the largest floods since the state was founded in 1850 known as the “Great flood of 1861”. The great flood began December 24th 1861 lasting some forty five days. The “Great flood of 1861” lasted until January 9th to the 12th, 1862. Further flooding events have been noted from 1909, 1933, 1937, 1938, 1939, 1950, 1955, 1964, 1976, 1986, 1995 and 1997.
The most recent recorded flooding event for California was noted December 11th 2014. Documented as “Big Wednesday” Hurricane Marie was blamed for this latest event of flooding. Hurricane Marie‘s center remained well away from land throughout its entire existence, its large size brought increased surf to areas from Southwestern Mexico northward to southern California. Off the coast of Los Cabos, three people drowned after their boat capsized in rough seas.
In Colima and Oaxaca, heavy rains from outer bands caused flooding, resulting in two fatalities. Similar effects were felt across Baja California Sur. Toward the end of August, Marie brought one of the largest hurricane-related surf events to southern California in decades. Swells of 10 to 15 ft (3.0 to 4.6 m) battered coastal areas, with structural damage occurring on Santa Catalina Island and in the Greater Los Angeles Area.
A breakwater near Long Beach sustained $10 million worth of damage, with portions gouged out. One person drowned in the surf near Malibu. Hundreds of ocean rescues, including over 100 in Malibu alone, were attributed to the storm, and overall losses reached $20 million.
While floods have been recorded in California’s history a mega-drought is still threatening many communities, farms and rural populations. International Animal Rescue Foundation’s - Environmental News and Media uncovered startling evidence of “some” farmers now selling their collected water instead of crops as the water is netting more profit at the moment than staple crops are.
“Climate change is not the main aggressive factor here affecting California’s residents and farming communities” Jose Depre stated. “The main problems surrounding California’s drought is the misuse of water and increasing populations”. “People are mostly to blame here and poor water management rather than just “climate change” stated Depre, Chief Environmental Director for International Animal Rescue Foundation, Say No To Dog Meat and Speak up For the Voiceless.Org”.
May 5th 2015 California introduced a newer and tougher water restriction since since the drought of 2012 began. California’s state water board have have approved emergency drought regulations that aim to slash the misuse of water down by some 25%. The measures call for cities and water agencies to reduce water usage by amounts ranging from 8% to 36%. The State Water Resources Control Board drew up the rules to meet Gov. Jerry Brown’s order for a 25% cut in urban water use statewide.
It’s the first time that California has ever put in place mandatory reductions in water use. The plan reflects just how bleak the state’s water picture has become. The snowpack in the Sierra Nevada has shrunk to a record low. Groundwater levels have plummeted across much of California, and in some areas of the Central Valley, the wells of hundreds of families have run dry. Furthermore while families and farming communities are suffering so too are wildlife.
Environmentalists at International Animal Rescue Foundation are now concerned the shortages of water and the impending summer that’s just around the corner will begin to have more than an adverse impact onto local wildlife that are already threatened with drought and wildfires.
While the residents of California can voice their concerns and take the relevant actions to adapt to drought the “silent sufferers” are those non-human species that rely on water to live, feed, bathe and hunt. Many native species of flora and fauna are already being forced to change their routines due to the serious ongoing drought that’s reported to increase this summer 2015. Furthermore the threat of wild fires is only around the corner that will increase pressure on native flora and fauna species furthermore.
75% of Southern California’s water supply derives from the Sierra Nevada Snow Pack. Should this 75% melt Southern California’s wildlife will be placed in extreme danger of death. Human civilization will undoubtedly suffer while the economy, businesses and organisations will feel more than hot pressure. Crime and unemployment will rise too followed by murder and gang related crimes.
From January 1 through to January 25th of this year CalFire responded to 406 wildfires. But in that same time period for the past five years, the average was just 69 wildfires. Meteorologists don’t expect much rain in 2015 during the usually wet spring months, so the heightened fire danger is expected to continue straight into the summer.
One of the very worst recorded wildfires to hit California for “2015” was recorded this February that saw some 50-75 km winds fanning wild fires leading to over five hundred residents being forced to evacuate the two small California towns at the eastern base of the Sierra Nevada. Brown said even rain wasn’t enough to put out the fire because a three-year drought across California created extremely dry timber brush that fueled the flames.
Should the three year drought continue its course of destruction thus seeing wildfires occur the effects onto local wildlife would be catastrophic and something that we do not think the locals are prepared for. Wildfires displace animals, displacement means some if not many of these animals caught up in wildfires can unfortunately end up in human populated areas which can cause some concern especially if larger predatory animals are displaced.
Image: Wild roundfire - 2015 California.
International Animal Rescue Foundation has voiced its concerns regarding drought and black bears that could/will begin to breach California’s human populated areas in search of food. Black bears are very adaptive and very mobile, so they will usually be able to take care of their daily needs in a drought situation. But then they’re coming down to the lake to drink a lot, coming down for food. If the drought persists, it greatly increases the odds of a negative interaction with people. When or if this happens we’ll most likely see hunters brought in to control the species to keep populations intact or even possibly a temporary cull of black bears to reduce human species conflict.
Quote: “It was a surprise to see a bear in this part of the neighborhood”
Farm animals are also affected by California’s “unusual drought” of which residents have reported sightings of cattle and smaller animals within their back gardens. Migrations and hibernation’s are also being thrown of course due to the drought. One commonly known species, the Monarch Butterfly has been seriously affected by the drought of which its populations are decreasing.
Monarch butterfly numbers are falling, in part due to lack of food and the changing weather patterns along their migration route. The butterflies’ winter destination is Mexico; they travel thousands of miles south from Canada and the United States. Some settle along the warmer parts of the California coast, like Pacific Grove, near Monterey.
The larvae (caterpillars) of monarch butterflies eat “only” milkweed. The larvae stage is the only stage of the monarch butterfly that feeds on milkweed; there is something in milkweed that allows the caterpillar to grow and keep all of the vitamins needed to transform into a beautiful butterfly. In turn, the adult butterflies consume all sorts of different foods including nectar, water and even liquids from some of the fruits we consume.
Image: Monarch butterflies decline since records began in 1993
California’s drought has pretty much affected the vast majority of fresh and lush fruit trees that the monarch butterfly requires to thrive on. The World Wildlife Fund for Nature concluded last year in the Sierra Madre of Mexico saw the lowest population count of monarch butterflies since 1993 of which California’s drought was being blamed for.
Newts are staying in hibernation for longer periods too which is not considered normal. Newts would normally be seen out and about now. In Ben Lamond both newts, toads and frogs are literally being overcome by drought that’s seen devastating declines and deaths. While most amphibious creatures dig deep into the soil to take evasive action from such harsh environmental events sadly, the evasive actions taken are not helping to reduce the number of newt, frog and, toad deaths all of which are critically important species of fauna that are required to keep insect populations intact.
When early settlers arrived in California they drained Some 90% of California’s wetlands to create farmland and goldmines of which has had an adverse effect to amphibious species of fauna. Ecologists are trying though to reverse this trend that would help to increase amphibious species. Many amphibians breed and lay their eggs in wetlands. After their aquatic young develop they can survive on land, but they must return to a wetland to create the next generation. With such harsh drought increasing in its third consecutive year many amphibian creatures will be wiped out.
Image: Ben Lamond newt rescued from its natural habitat that has since dried up
Things do work out better for native amphibians though if a wetland dries up for “part of the year”. When it comes to amphibians’ predator control, drought can be a good thing, and timing is everything. While most of the three year drought period has dried up substantial amounts of wetland California’s native frog, toad and newt species will undoubtedly suffer in the long term too.
Unfortunately its not just our smaller species of wildlife that are affected by the impending “mega-drought”. International Animal Rescue Foundation’s marine and fresh water wildlife department has uncovered starling evidence of marine and fresh water mass deaths. 26th May 2015 in Baja, California, thousands of lobsters were washed up on the shoreline dead and alive. Jose Depre, CEO stated “in under two months this is the forth such event occurring on the Baja coast of which the same species of marine life has washed up dead and alive with no apparent reason or cause.
Image: Thousands of lobsters was ashore for the third time this year.
In under two months many more whales have also without reason nor cause washed up along the coast of California. 24th May 2015 a further seven dead whales were sadly seen washed up onto the shoreline. 24th April four dead whales were again washed ashore which has baffled scientists. 7th March 2015 - 1,450 Sea lion pups have washed ashore this year ill and dying - ‘possibly 10,000 have died’ in California, America since the drought began three years ago. Some environmental groups are claiming that ships are the main cause of death however, the sheer fact that California also has seal pups and fish washing up now whales and sharks deepens our concerns regarding such deaths.
Image: Whales and sharks washing ashore along the coast of California.
This year alone California’s Animal Rescue Clinics have been inundated with call after call regarding stranded cold and emaciated sea lion pups. 2015 has been said to be the worst year for sea lions in California of which the drought has been noted as the main blame. Unusually warm ocean water caused fish to move away from the islands where the sea lions give birth.
Due to sea lion prey moving further and deeper away, the moms are actually gone away longer from the pups. Because they’re gone longer, the pups aren’t getting enough (food) over time. They’re leaving the islands early, and they’re showing up on the shores here, starving to death. Environmentalists have stated the warmer ocean water has more to do with local conditions in the eastern Pacific. The current drought event of three years hasn’t more to do with global warming or anything along those lines. It’s more of a local climate event that we’re looking at. Experts hope the warmer-than-normal water is a fluke and not a pattern.
Meanwhile, while the state of California is under an immense drought California’s citizens are trying their hardest to adapt to what appears to be more locally human induced events rather than as explained “global warming or climate change”. However as much as the local non-celebrity citizens are doing their bit for their state, some celebrities have been noted as either doing nothing or simply flouting the laws.
One only has to take a drive around the suburbs of California to view most non-celebrity citizens once lush green lawns now nothing more than a frazzled piece of sod. Look a little further and one will see many celebrity houses with lush green lawns, filled fresh clean swimming pools and, sprinklers to hosepipes at the ready. Its truly crazy and a sharp smack into the face to our local wildlife and communities that would if they dared use a hosepipe fall prey to enforcement.

Picture above is celebrity Khloe Kardashian’s home that is decorated with lush green lawns, trees and crisp blue swimming pool. While on the left hand side of this image you can clearly see the impacts of California’s drought slowly but surely destroying even the hardiest of drought resistant grasses.
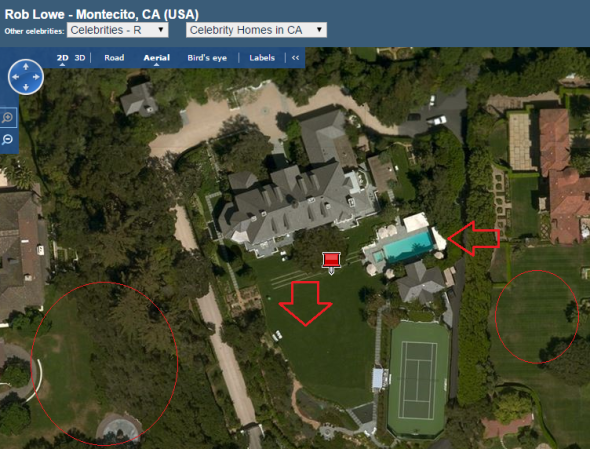
Celebrity Rob Lowe’s immaculate garden can be seen above that is flowing with green lush lawns and shrubs. Meanwhile on either side and circled in red for your attention are the effects of drought. One doesn’t really need to research or understand how much water is required to keep such lawns in this acquired condition. Even within the United Kingdom where rainfall is a weekly occurrence such lawns of this type would not be seen in your everyday garden. Again this really is a slap in the face of those small animals that have no voice to shout for help. Furthermore if such celebrities that are supposed to be setting a good standard continue to flout the laws so will the local citizens.
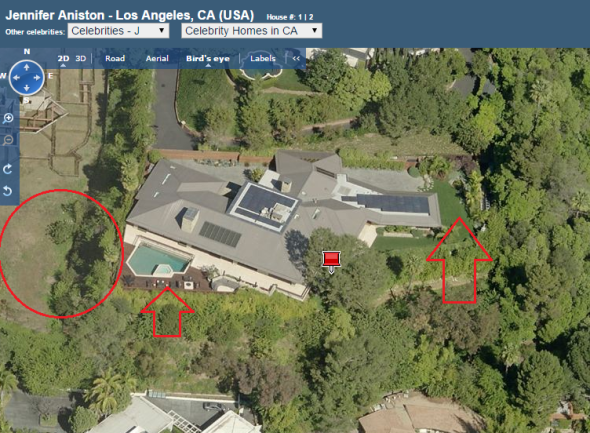
Celebrity Jennifer Aniston does set a small example with the use of solar panels however then, lets herself and community down with lush green lawns and fresh crisp blue swimming pool. While on the left hand-side of this image one again can view the impacts of California’s three year drought slowly browning even the hardiest of drought resistant lawns.
Out of ninety celebrities gardens viewed within California sixty three had lush green lawns and with some thirty eight out of the ninety owning at least five swimming pools. Out of just the ninety observed, forty had hosepipes on show with a sprinkler attachment clearly visible. Only one home that we did view which was that of Kayne Wests that actually showed nothing but bare grey-ish, brown scorched grass.
California’s drought is expected to continue through to next year with little or no hope of the much needed rainfall. Concerning is that should the state of California continue to dry up into a slate of rock any such intense and prolonged rainfall will simply run off placing water reservoirs and concrete canals under immense pressure. Furthermore the longer dry spells persist with misuse of water the chances of heavy rainfall must be taken on board by all Californian residents. Floods may be uncommon but they can occur very quickly without warning and cause untold damage to large swathes of communities and the local wildlife.
There are many community projects that are now taking place all over the state such as Water Free Wednesday, horticultural drought resistant gardening and rebates for those that knowingly help to reduce their water intake. Furthermore tips on how you can save water can be viewed here below.
Thank you for reading.
Dr Jose C. Depre
Environmental and Botanical Conservation.