Embassy Day: For Cats and Dogs in the Horrific Meat Trade.
EMBASSY DAY: 17TH SEPTEMBER 2015 WWW.SAYNOTODOGMEAT.NET
Did you know on the 17th September 2015 from 11:00am the Australian organisation www.saynotodogmeat.net, registration 49 860 343 527 will be hosting peaceful demonstrations around the globe within nine major cities? Embassy Day forms the first (governmental) lobbying in relation to #OperationUnite 2016. Embassy Day will be the organisations second largest demo since April 4th 2015. Back in April Say No To Dog Meat made history by hosting the worlds largest anti pet meat demo in over twenty five countries.
On the 4th April 2015 the Say No To Dog Meat family hit the streets internationally in their thousands marching for dogs and cats in the horrific pet meat trade. The main April protests were non-governmental, however was a reminder that should the (eight governments) the organisation are lobbying not respond to the polite requests from the Aussie organisation. The next step would be Embassy Day, September 2015. Finally after Embassy Day, the organisation will then begin gearing up for phase two of Operation Unite 2016 that will be held October 2nd and 3rd 2016. Followed up with #OperationUnite comes the new #lovefamily campaign too.
Image: (SNTDM) supporter, #lovefamily campaign.
September 17th 2015 will see demonstrators lobbying South Korean embassies within Los Angeles, United States and Ottawa, Canada. Then in New York the Indonesian embassy, followed up with the Cambodian embassy in Seattle, United States will be demonstrated. Meanwhile within the United Kingdom the Vietnamese embassy will be peacefully protested in London, followed up with the Indian consulate in Belfast, Northern Ireland. The Nigerian embassy in Johannesburg, South Africa will follow soon after. The Thailand consulate within Perth and Philippines consulate in Brisbane, Australia will be peacefully lobbied too.
Donna Armes, campaign manager and director confirmed that all embassy consulate generals and ambassadors had been sent communications months before Embassy Day was planned. Furthermore the campaign manager stated a second electronic communication had been sent and received by embassy staff informing them about the peaceful protests, and why the organisation has been forced to lobby all nine embassies. Embassy staff, consulates and ambassadors have failed to acknowledge the Aussie organisations peaceful plans which is a little frustrating but then the organisation didn’t expect a reply anyway.
Say No To Dog Meat volunteers and directors will begin the ‘peaceful demonstrations’ with an up to date speech on current and past issues in relation to both ‘Asian and African’ dog and cat meat trade outside of each embassy. After the main speech the public can stay or depart of which the organisations volunteers and directors will then be handing into the embassies all data and petitions.
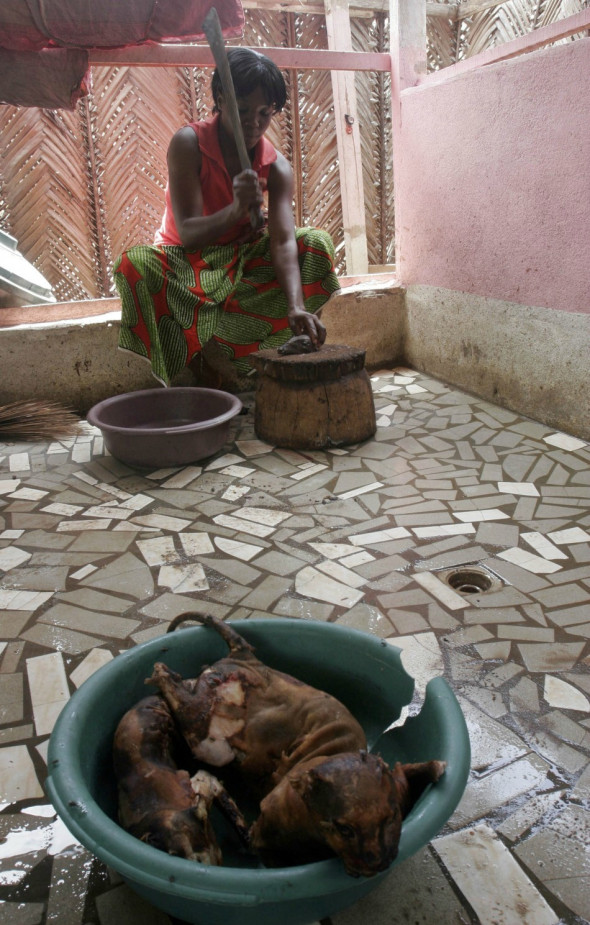
Image: Nigeria, woman prepares dog carcass for [404 joint delicacy, peppered dog soup].
Each petition contains from 10,000 to 200,000 signatures. Statistics on pet meat consumption death rates, virus and disease, regulations and violations of current standing law, predictive model data research, food hygiene violations will be handed into the consulate generals and ambassadors too. Presidential letters will also feature within the pack of which each government has a set six to eight months to respond. The organisation is not expecting an immediate or even positive response, of which OPERATION UNITE will continue to go ahead come October 2016.
For the very first time in history the Indian and Nigerian embassies will be lobbied by the organisation in relation to the Indian, Nagaland and Nigerian pet meat trades. Nigeria is the largest dog meat consuming country on the continent of Africa and third largest on the planet. Furthermore deaths from consumption of diseased or rabies infested pet meat has skyrocketed this year alone with some eighty people dead already. Meanwhile the Indian Nagaland state loses on average an estimated forty people a year via the direct consumption of rabies infested dog meat. Rabies is also on the rise in both pet meat consuming zones. India is where 85% of all human rabies deaths occurred between 1995 and 2004. Over this period there were 21404 rabies deaths a year there. Death rates for 2014 are yet to be seen.
“About 3.5 million dog bites are registered every year in India. The Government cannot give vaccine free of cost to all people. From 2006, the price of vaccine has increased…”
Despite many protests against the South Korean Bok Nal pet meat trade that began in June and ended in the first week of August. The South Korean government took no notice of expert knowledge, scientific data or petitions handed to them. Instead they allowed traders to continue the horrific disease riddled trade, and took little notice of their own laws and guidelines implemented to protect dogs and cats in meat trade. Dare we ask what the point is in introducing animal protection laws, just to allow native citizens to continue violating them?
From 2013-2015 Say No To Dog Meat has vainly lobbied the Viet Nam health minister and president Trương Tấn Sang to bring an end to the pet meat trade. On the 19th August 2014 reports issued by the (World Health Organisation) confirmed that deaths rates had increased slightly to forty (per year), however its estimated that some one hundred people die annually from rabies infection.
Despite the Aussie organisation sending more than enough scientific evidence to the Vietnamese health minister and president the trade continues. From 1995-2004 the then death rate from rabies in Viet Nam stood at some 1,550. Since 2004 the Vietnamese pet meat trade has increased. Death rates continue to increase within the country from the direct consumption of diseased pet meat, statistics from 2014 showed many of these deaths were infant related either bitten by dogs on private land or from consuming rabied infected dog and cat meat.
March 16th 2009 the Vietnamese government were handed third party data from; National Institute of Infectious and Tropical Diseases and the National Institute of Hygiene and Epidemiology in Hanoi, Viet Nam that stated; “Most Rabies deaths in Vietnam were from the direct Butchering and eating of either dog or cat meat”.
Vietnamese researchers confirmed;
“In Viet Nam, dogs with rabies have been detected in dog slaughterhouses and workers at dog slaughterhouses are vaccinated against rabies as part of the national programme for rabies control and prevention. However, the private slaughter of dogs is relatively common in the country which increases rabies infection rates”
“Vietnamese doctors already consider dog slaughtering to be a risk factor for rabies transmission, but it is important that other health care workers and policy makers, both in- and outside Vietnam, are aware of this risk factor”
Dog and cat meat trade is now finally illegal within Thailand, unfortunately this doesn’t stop traffickers from snatching dogs and transporting from Thailand into the Viet Nam. Yes the trade may indeed be illegal, but again our own investigative journalists have located street traders openly selling and smuggling unhygienic meat in rural communities.
Back in 2013 [Life With Dogs] stated; “In the past week, Cambodia, Laos, Thailand and Vietnam have signed a deal with the intention of ending the importation and sale of dogs to be used as food. This move was initiated by their governments because of the involvement of animal welfare group Asia Canine Protection Alliance. The ACPA is comprised of four notable animal groups: Animals Asia, Change for Animals Foundation, Humane Society International and Soi Dog Foundation.
We are now in 2015 and as yet [SpeakupFortheVoiceless] and [SayNoToDogMeat] have yet to witness any such decrease of trade within Cambodia, Vietnam and Laos. Trafficking and snatching of pet dogs and cats continues within Thailand feeding the trade within the Viet Nam and China. Why has it taken from 2013 to do nothing? One only has to walk the streets of Hanoi, Saigon, Hoi An and Ben Tre to witness dog meat traders more than active. On June 30 2015, police from Sakol Nakorn intercepted a truck carrying the butchered remains and carcasses of more than 100 dogs. The truck was heading for Tha Rae, [the traditional home of Thailand’s dog meat trade]. Yet trade is illegal!
Within the Philippines the government has introduced tough and stringent laws with regards to pet meat traffickers and peddlers (Please click the links to view current data from government). Say No To Dog Meat recognizes the Philippines as one of few Asiatic countries on the continent that has taken the pet meat trade seriously. Despite a law banning the killing and maltreatment of dogs (Animal Welfare Act of 1998), dog-eating and the industry that supplies it continues particularly in the northern part of the country. Back in June 23 2013, some 12 dogs were rescued in San Pedro Laguna, according to the Department of Agriculture (DA).
The Philippines government aims to eliminate the country’s dog meat trade by 2016, AKF Head and Legal Counsel Heidi Caguioa told Rappler [2014]. Eradication means no more dog meat traders and no more dog meat restaurants. Say No To Dog Meat will be lobbying the Philippines embassy within Brisbane, Australia calling on the government to strengthen the current Animal Welfare Act 1998 and Rabies Act 9482.
Finally Say No To Dog Meat volunteers will be lobbying the Indonesian embassy calling on the government to enact law and close down all known dog meat markets. The Indonesian dog meat trade is allegedly associated with the Minahasa culture of northern Sulawesi, Maluku culture and the Bataks of northern Sumatra, where dog meat is considered a festive dish, usually reserved for occasions such as weddings and Christmas. While Say No To Dog Meat and our comrades Animal Defenders Indonesia, Surabaya Tanpa Dog Meat, Bali Adoption and Rehabilitation Center would like to believe this, the trade on dog and cat meat actually occurs every day of the month.
This September 2015 please unite with Say No To Dog Meat this Embassy Day 2015. For more information please contact the organisation here via email: [email protected]
Image: Say No To Dog Meat, Team Perth.
Chief Executive Officer.
Endangered Species Friday: Ammospermophilus nelsoni
Endangered Species Friday: Ammospermophilus nelsoni
This Friday’s Endangered Species Watch Post (ESP) we focus a little attention on a species of squirrel that’s rarely mentioned within the conservation or animal rights arena. A. nelsoni was identified by Dr Clinton Hart Merriam (December 5, 1855 – March 19, 1942). Dr Merrian was an American zoologist, ornithologist, entomologist, ethnographer, and naturalist. (Image; Archive, A. nelsoni)
Year of identification was back in 1893 of which the species remains endemic and extant to the United States, State of California. Environmentalists undertook two census’s of the species’s current population size, known threats and any new threats to the species back in 1996 and, 2000. Both census’s revealed few changes with regards to current status, of which the species was listed as endangered from 1996 and again in 2000.
Today the San Joaquin Antelope Squirrel as the rodent is commonly know remains at [critically endangered] level. Populations are continuing to decline within a country that one would expect to see good conservation measures increasing population sizes and, eliminating any new and past threats.
To date the current population size remains unknown which “may-well be why the species has qualified for listing on the [critically endangered] list”. Scientists undertook a rather crude population survey on three to ten squirrels per hectare on 41,300 hectares of the best and known remaining habitat. The survey then provided a rough estimate of which stated population sizes could be standing at [124,000 - 413,000]. However as the true population size is currently unknown one must not take this survey into consideration when documenting or teaching students. The following estimates were based on more in-depth multiple crude evaluations back in [1980].
Current “trend” evaluations from 1979 have confirmed that many San Joaquin Antelope Squirrel populations have unfortunately decreased throughout their known range although, even these surveys are still pretty much sketchy. A further trend evaluation survey back in 1980 revealed more-or-less the same findings from (1979) of which the species has decreased through much of its small (clustered range) manly within, San Joaquin Valley, California.
Recent protection efforts in the southwestern San Joaquin Valley likely have to some degree slowed the rate of decline and, the species remains common in [some protected areas]. Probably the rate of decline is less than 30% over the past 10 years. Nevertheless the species is still in decline over much of its range and, despite conservation efforts the San Joaquin Antelope Squirrel is sadly nearing extinction (within the wild).
Data proves for now the species has declined throughout much of its former range by some twenty percent. Back in 1979, extant, uncultivated habitat (but including land occupied by towns, roads, canals, pipelines, strip mines, airports, oil wells, and other developments) for the species was estimated at 275,200 hectares (680,000 acres, 2,752. None of the best historical habitat remained.
One study indicated that densities in open Ephedra plots and shrubless plots ranged from 0.8 to 8.0 squirrels per hectare, but all but two sites had densities of four or less per hectare. Densities on shrubless, grassy dominated sites were equal to or higher than those on shrubby sites.
The San Joaquin antelope squirrel is dull yellowish-brown or buffy-clay in color on upper body and outer surfaces of the legs with a white belly and a white streak down each side of its body in the fashion of other antelope squirrels. The underside of the tail is a buffy white with black edges. Males are approximately 9.8 inches and females are approximately 9.4 inches in length
Breeding normally takes place during late winter to early spring of which young will normally be born from the beginning of March. Female gestation normally lasts no longer than one single month. Young do not normally emerge from the den until around the first or second weeks of April. The San Joaquin antelope squirrel has only one breeding cycle during the entire year of which this is timed just right so that when young are born there is much vegetation and food for young to feed and hide within after weening. Weening of young is believed to start before the young even emerge from the den.
A. nelsoni is omnivorous, feeding mostly on green plants during the winter and insects and carrion when these are available. It occasionally caches food. The squirrels live in small underground familial colonies on sandy, easily excavated grasslands in isolated locations in San Luis Obispo and Kern Counties.
Image: A. nelsoni. Credit (Mark Chappell).
Half of the remaining habitat supports fewer than one animal per hectare, 15% of the remaining habitat supports 3-10 animals per hectare (generally four or fewer per hectare, California Department of Fish and Game 1990). The species Spermophilus beecheyi reportedly may restrict the range of A. nelsoni. Among several predators, badger is most important, and lives in small groups.
Threats
The decline is a result of loss of habitat due to agricultural and urban development as well as oil and gas exploration practices. Primary existing threats include loss of habitat due to agricultural development, urbanization, and petroleum extraction, and the use of rodenticides for ground squirrel control. Overgrazing and associated loss of shrub cover is a concern in some areas. These threats will be alleviated by the implementation of the San Joaquin Endangered Species Recovery Plan. There are some discussions that the current drought within the region “may” have a profound effect onto the species however, this concern remains just that and, no proven data surveys have shown drought to be of a threat as yet.
Thank you for reading and, have a nice weekend from all the team at International Animal Rescue Foundation.
Dr. Jose C. Depre
Environmental and Botanical Scientist.
Revelation 16:16 Har-Ma ged’on or Human Fault?
Revelation 16:16 Har-Ma ged’on or Human Fault?
Since 2000 International Animal Rescue Foundation has been following, reporting and researching mass animal deaths around the globe and (some) freak unexplained deaths that have left scientists baffled. Furthermore the increasing avian bird flu pandemic that is threatening many birds and dogs looks set to be the largest outbreak in history.
Some of the worst cases we and the I.A.R.F have viewed are unexplained whale, seal and dolphin beaching’s all of which have been occurring along coastlines and within local fresh water rivers. Pollution has been the main number one factor blamed for many land and marine deaths. However other deaths have left ourselves and scientists puzzled as to why many animals have been found dead in large piles, what has led to such large numbers of animals dying off and how can such large die offs be prevented?
The vast majority of animal deaths seem to be occurring within Asia and the United States. Research has shown that there is no real limited location in either the United States or Asia. 8th June 2015 in Florida hundreds of dead fish washed up onto the local shoreline. A few days prior to this a large fish kill in a lake in Mattoon, Illinois was witnessed. Meanwhile in Lake Aldama, Mexico 3rd June 2015 tons of fish were located dead floating on the surface in what has been stated as “unexplained mass deaths”.
Image: 2 waterways that will host 2016 Olympic events in Brazil are filled with dead fish and trash 16 months before the games.
Within the past twenty eight days hundreds of dead fish appeared in the waters of Michoacan, Mexico. Hundreds of dead fish were found washed up along Big Bear Lake in California, America. Meanwhile thousands of dead fish were found washed ashore on a river in Rhode Island. 30th May 2015 tens of thousands of dead fish were found washed up along Flanders bay, New York.
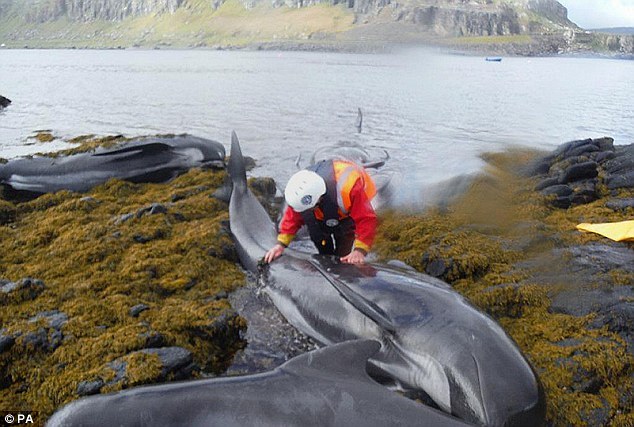
Environmental teams from International Animal Rescue Foundation Scotland, England and France have also reported and viewed with dismay mass die offs and stranding’s off the British, Scottish and French coastlines too. 2nd June 2015 - 21 pilot whales were located stranded, ten of which were reported dead in Skye, Scotland. Within Rennes, France a large die off, of fish was witnessed in the River close to Rennes. 27th may 2015 hundreds of fish were located in the River Darlinton, Great Britain. On the 23rd April “thousands” of dead star fish were located off the coast in Cumbria, Great Britain and, on the 17th April 2015 “scores” of dead “dolphins and whales” were found washed up on the along the coast of France in what scientists state as “strange” and “unexplained”.
Image: Ireland, Lissadell Beach, Co Sligo, strewn with dead starfish.
There are many explanations as to why so many marine and fresh water animals have been found dead most of which are put down to chronic pollution, whales and dolphins colliding with marine vessels, changes in ocean temperatures, earthquakes down to environmental changes and, sonar operations by naval forces. Some marine experts and Animal Activists have blamed military operations within the seas and close to land. Conspiracy theorists are blaming secretive governmental organisations and operations while religious individuals are stating the time is coming 16:16 Har-Ma ged’on. Environmental scientists have found neither evidence of mass animal deaths caused by covert government operations or Har-Ma ged’on nearing.
Conspiracy theorists and religious individuals need to put their suspicions and beliefs to one-side and concentrate on the more realistic issue which is that of human blame. Meanwhile, while there is evidence to prove that human activity and negligence is to blame it must be noted too the “unexplained events” that still cannot be answered are a cause for concern and need more in-depth investigations.
Image: Pilot whales stranded off the coast of Scotland, Skye. Nine died.
Below I have included three major culprits that International Animal Rescue Foundation’s Marine Department have been investigating since 2000. While these three culprits remain major players one must not forget aggressors such as climate change of which reveals little evidence on mass marine deaths and deliberate or accidental damage such as oil spillage or vessel waste dumping out at sea. Below and for your information is collated research in word format and video evidence too. If you’d like to discuss this matter further please do not hesitate in contacting myself or anyone of my team here at: [email protected]
Red Tide: Algae Bloom/ Red Tide.
Image: Red tide (HAB) Harmful Agal Bloom of the coast, Sydney Australia.
An algal bloom is a rapid increase or accumulation in the population of algae (typically microscopic) in a water system. Cyanobacteria blooms are often called blue-green algae. Algal blooms may occur in freshwater as well as marine environments. International Animal Rescue Foundation’s Marine Department has located much evidence of such algal blooms responsible for mass fish and whale deaths.
Of particular note are harmful algal blooms (HABs), which are algal bloom events involving toxic or otherwise harmful phytoplankton such as dinoflagellates of the genus Alexandrium and Karenia, or diatoms of the genus Pseudo-nitzschia. Such blooms often take on a red or brown hue and are known colloquially as red tides.
During the 13th May 2015 reports of many hundreds of Diamondback Terrapins were reported within Flanders Bay. Marine scientists have stated that saxitoxin is to blame for the mass animal deaths however the jury is still out on this issue. I must also note that Flanders Bay has in the past six months been the main focus of attention for marine biologists as hundreds and hundreds of dead marine life has been found washing up within the area with no real explanation.
Saxitoxin (STX) is the best-known paralytic shellfish toxin (PST). Ingestion of saxitoxin (usually through shellfish contaminated by toxic algal blooms) is responsible for the human illness known as paralytic shellfish poisoning (PSP).
The term saxitoxin originates from the species name of the butter clam (Saxidomus giganteus) in which it was first recognized. But, the term saxitoxin can also refer to the entire suite of related neurotoxins (known collectively as “saxitoxins”) produced by these microorganisms, which include pure saxitoxin (STX), neosaxitoxin (NSTX), gonyautoxins (GTX) and decarbamoylsaxitoxin (dcSTX).
Saxitoxin has a large environmental and economic impact, as its detection in shellfish such as mussels, clams and scallops frequently leads to closures of commercial and recreational shellfish harvesting, especially in California, Oregon, Washington, and New England. On researching current marine deaths in the California state of America I must note that Saxitoxin and human induced environmental change has been noted as causing the deaths of many seals and fish. The local seal deaths must not be confused with pollution or Saxitoxin but more increasing water temperature that is forcing fish further away from the shoreline. Due to mother seals having to fish further afield their cubs are being left for longer periods thus starving practically to death.
International Animal Rescue Foundation found quite alarming evidence of Saxitoxin an incredibly potent and toxic chemical known to be used within the armed forces as a “suicide pill” freely on sale via a quick and easy Google search. The Ead department furthermore located members of the public asking where they could obtain such a harmful chemical of which should only be handled by (experienced chemical professionals).
Back in August 2003 Saxitoxin was to blame for the deaths of many humback whales. The deadly alga was the leading suspect in the mass death of humpback whales around 150 miles off Cape Cod, say marine experts.
Carcass sightings suggest that at least 12 whales, mostly humpbacks, have died in the Georges Bank area, making it one of the worst known mass fatalities. “It’s really quite disturbing,” says whale biologist Phillip Clapham of the Northeast Fisheries Science Center in Woods Hole, Massachusetts.
A red tide of the toxic algae Alexandrium fundyense is the most likely culprit. The algae’s poison, saxitoxin, killed 14 whales in the same area in 1987. Saxitoxin can accumulate in mackerel which whales eat. Scientists did also point to a very slim chance of acoustic operations conducted at sea by the Navy.
International Animal Rescue Foundation has found Saxitoxin to be the main culprit thus far related to fish, whale, seal and other marine deaths. Saxitoxin has been blamed for the recent unexplained deaths of thousands of lobsters within California this past month too.
Could it also be a sheer coincidence that all deaths seen within Asia, United States and South America are somehow related to “Saxitoxin” and not religious events, the rebirth of Jesus Christ or covert military operations?
STX is a neurotoxin naturally produced by certain species of marine dinoflagellates (Alexandrium sp., Gymnodinium sp., Pyrodinium sp.) and cyanobacteria (Anabaena sp., some Aphanizomenon spp., Cylindrospermopsis sp., Lyngbya sp., Planktothrix sp.)
STX has been found in at least 12 marine puffer fish species in Asia and one freshwater fish tilapia in Brazil. However, the ultimate source of STX is often still uncertain. In the United States, paralytic shellfish poisoning is limited to New England and the West Coast. The dinoflagellate Pyrodinium bahamense is the source of STX found in Florida.
Recent research shows the detection of STX in the skin, muscle, viscera, and gonads of “Indian River Lagoon” southern puffer fish, with the highest concentration (22,104 μg STX eq/100 g tissue) measured in the ovaries. Even after a year of captivity, the skin mucus remained highly toxic. The various concentrations in puffer fish from the United States are similar to those found in the Philippines, Thailand, Japan, and South American countries. Coincidentally all of these countries have the “largest” amount of fish and whale die offs. However I must note that my mere speculation must not be taken for an answer.
Pollution: Human Negligence.
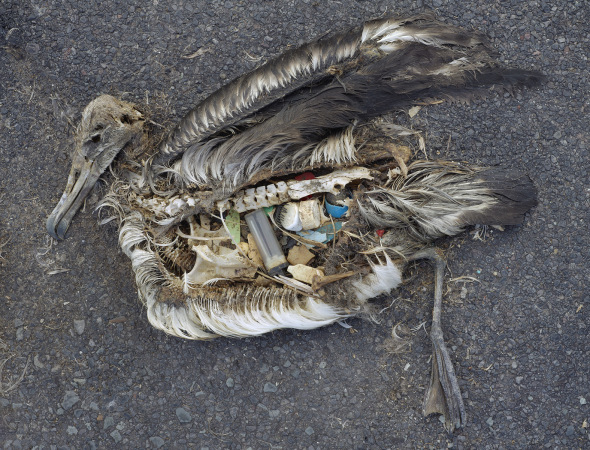

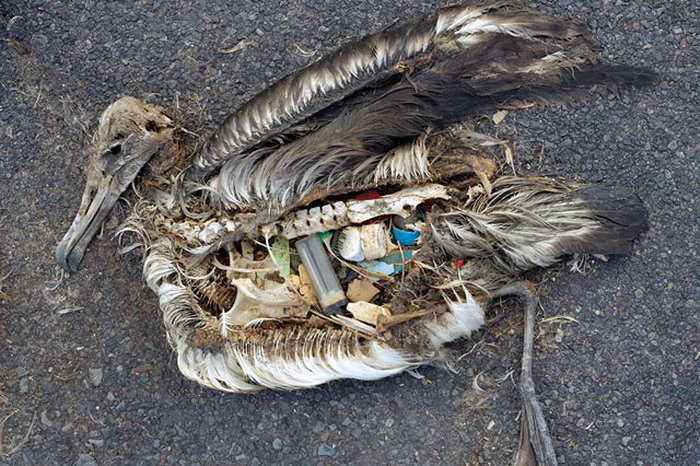
Image: Shocking - stomach contents of a dead Albatross.
I’m a great lover of birds and viewing this image has distressed myself countless times. Daily I ask why do we as humans treat our planet like a dumping ground of which animals suffer dearly.
While Mother Nature is naturally attacking herself we must not forget that human negligence is overall the biggest culprit known to be causing countless marine and fresh water animal deaths. Pollution increases as human population does and a colossal lump of everyday natural and man-made human waste sadly does end up within fresh and marine waters.
10th January 2015 the Environment Agency in Leicestershire, United Kingdom blamed human pollution for causing the deaths of “thousands of fresh water fish”. Farm slurry was the main culprit here of which the Environmental Agency concluded within their report as the main culprit.
Waterway manager for the trust, Neil Owen, said: “It’s really sad that we’ve had so many fish die from the careless actions of an individual which allowed slurry to enter our waterway. The end count was said to be “60,000” fish dead due to one ignorant and unprofessional action of a single farmer.
Meanwhile this past April tons of dead fish have been removed from a Rio de Janeiro lagoon where Olympic events are to be held in 2016, sparking debate among officials and scientists over what caused the mass die-off, as well as fears that the water may be unsafe for athletes.
The die-offs are becoming a common occurrence in Rio, where rivers, lakes and even the ocean are blighted by raw sewage and garbage. Officials have argued over the cause, with Rio’s environmental secretariat insisting last week that the incident is the result of the sudden change in water temperature.
“The intense rains that happened last week and a rise in the sea levels led to a spike in the [sea] water entering the lake, causing a thermal shock,” the secretariat said in a statement, adding that the water temperature had fallen by 7.2 degrees Fahrenheit in a short period of time. Many scientists disagreed with that explanation, pointing to pollution instead.
January 12th 1988 pollution was blamed for the deaths of countless scores of beluga whales. Autopsies of dead belugas washed onto the banks of the river have found very high levels of more than 30 hazardous chemical pollutants, including DDT, polychlorinated biphenyls or PCB’s, the pesticide Mirex, metals such as mercury and cadmium, and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons similar to those found in cigarettes and regarded as cancer-causing agents.
The diseases found in the 72 dead whales examined so far include bronchial pneumonia, hepatitis, perforated gastric ulcers, pulmonary abscesses and even a case of bladder cancer. A majority of the whales appear to have died from septicemia, or blood poisoning, which killed them because their immune systems failed.
While the above report dates back to the last century one would be led to believe that governing bodies would have at least (cleaned their act up). Unfortunately that is not the case. In August of 2014, biologists from the Virginia Aquarium and Marine Science Center Standing Response Team were notified of a particularly unusual sighting regarding a long young female sei whale. She was spotted swimming up the river, which is particularly unusual as these creatures are typically found in the deep waters of the Atlantic.
A necropsy revealed that the whale had swallowed a shard of rigid, black plastic that had lacerated its stomach and prevented it from eating. They found that she had also been struck by a ship. The shard of black plastic was later found to be a discarded DVD case.
To date International Animal Rescue Foundation has uncovered much evidence of marine pollution responsible for the deaths of small and larger fish down to entire shoals of fish and pods of dolphins. Plastic, carrier bags, oil and chemical pollution all reign in at number one and not the Coming of the new Jesus Christ or even a (not so) secret government operation aimed at killing humans and our precious wildlife. Think about it for a brief minute. Why would the United States (E.g) wish to kill hundreds of thousands of fish off when fish is a staple diet and major import and export monetary gain?
Naval Marine Operations: Acoustics.
Image: Whale death caused by naval sonar operations.
Despite natural events and pollution being the major two factors here there still remains yet another problem within our oceans that is angering Animal Activists, Marine Biologists and other experts. Acoustic activities, drilling and military marine operations reign in at number three.
Despite many reports and scholarship articles by leading scientists and marine agencies sounding the alarm acoustic disturbance has been noted and reported to be killing, injuring or seriously impacting on the physical health of whales, fish and crustaceans for some years. Sonars used by international military navy vessels from around the world are giving scientists somewhat of a headache - and - stopping such operations within the deep seas is also another problem especially when sonars are required in all but most of the naval vessels.
Back in 1963 of the Gulf of Genoa, Italy Naval Sonar (NS) operations led to the stranding of 15 Cuvier’s beaked whales (cause - naval maneuvers). Back in 1998 in the Canary islands +12 Cuvier’s beaked whales stranded with a further Gervais’ beaked whale stranding too (cause - FLOTA 88 naval exercise). Back in 2003 the following - Cuvier’s beaked whale (9), Blainville’s beaked whale (3), beaked whale spp (2), Minke whale (2), Atlantic spotted dolphin (1) all stranded, (cause - Naval MFA operation).
One of the very worst cases researched on was seen in Marion Bay, Tasmania where some 145 Long finned Pilot Whales stranded themselves, (cause - “suspected” use of sonar by two naval mine sweepers). Back in 2008 some 26 dolphins stranded themselves off the coast of Cornwall, Great Britain, (cause - Naval exercise but no ship sonar in use except HF hydrographic sonar on HMS Enterprise).
Three of the most commonly seen culprits have been included within this article for your information. Unfortunately while we are aware of these culprits more and more whales, fish and smaller sea creatures are washing up dead around the planet. While some cases cannot be answered due to unknown and non-investigated causes the vast majority of mass animal deaths eventually do indicate - humans as the major player while, natural events such as blooms come second and pollution ranking in at first (Still no evidence of a re-birth of Jesus Christ or the world ending though). Our seas like our lands and airways are becoming more and more congested and with each increase of human activity seen, more and more deaths of both land and marine animals will come.
International Animal Rescue Foundation has located no hard hitting evidence that proves the world is nearing an end, a re-birth of Jesus, Armageddon style apocalypse or (not so) secret military operations responsible for the deaths of many marine, fresh water and land animals.. However while the organisation can rule out a new Jesus re-birth and events written into religious scripture there does remain some suspicion surrounding the High Frequency Active Auroral Research Program or, commonly known as - (HAARP). However any such investigative studies on the (HAARP) program have been quashed as the program will be shutting down after informing Congress last year (2014) that funds needed to be used elsewhere on other weather modification programs. In reality the program is just entering a new phase
Concluding:
We are Mother Natures worst enemy and not any entity within a religious or conspiracy theorists scripture. Humans are polluting the atmosphere, littering the oceans and land, destroying natural habitat, over-populating, displacing animals, killing marine animals through the use of naval exercises and on, and on, and on.
Some people need to look beyond the computer, the conspiracy field of nonsense, religious dates and begin laying the blame at their own two feet. Failing this many more marine creatures and animals will subsequently perish.
Thank you for reading.
Dr Jose C. Depre.
California: Mega-drought looming.
“California mega drought is impending”
DESPITE man-made circulation systems, concrete canals and pipes that bring water from distant mountains to farms and populated areas California is still under an intense three year drought. California’s drought not only affects local citizens but the economy, wildlife and can increase crime and anti-social behavior.
Scientists have already stated a “mega-drought” could be one of the worst in California’s history that’s reduced much Californian landscape to a brown frazzled patch of soil. The people of Los Angeles are not new to drought or lack of rainfall though.
Back in 2011 California recorded a total of 12 inches of rainfall, in 2012 eight inches of rainfall was recorded and, in 2013 a measly (two inches) of rain was recorded for the entire year. Records for the first six months of 2014 recorded a total of one inch of rainfall. 2015 records to date do show a slight improvement although nothing to write home about.
Drought has been recorded within the “California area” since 4000 BC way before the state was founded. Climatologists recently recorded a dry period of some 1,300 years via the use of measuring aged tree stump rings. And, more recently, an extended dry period that began about 1,050 years ago likely helped cause the absolute collapse of intricate Southwest American-Indian societies.
Meanwhile while this three year extended drought is being recorded as “possibly” the worst “mega-drought” in California’s history floods have also took their toll onto the state of America founded in 1850. While the area has been affected by what we consider natural drought since 4000 BC floods have also been noted although these are mostly caused by riverine flooding. Floods of 1825 changed the course of the Los Angeles River from its western outlet into Santa Monica Bay following the course of Ballona Creek to a southern outlet at San Pedro Bay near where it is today. January 1850 floods devastated Sacramento.
Image: 1955-1956 California was hit by some of the worst floods in 90 years.
The Feather River, the Sacramento River’s main tributary in the northern Sierra, rose to 250,000 cubic feet per second and flooded Yuba City and Marysville. The flood destroyed hundreds of buildings (image above) and killed at least 60 people. Such flooding provided support for A. D. Edmonston’s 1951 plan to build the Oroville dam.
December 1861 residents within California witnessed the largest floods since the state was founded in 1850 known as the “Great flood of 1861”. The great flood began December 24th 1861 lasting some forty five days. The “Great flood of 1861” lasted until January 9th to the 12th, 1862. Further flooding events have been noted from 1909, 1933, 1937, 1938, 1939, 1950, 1955, 1964, 1976, 1986, 1995 and 1997.
The most recent recorded flooding event for California was noted December 11th 2014. Documented as “Big Wednesday” Hurricane Marie was blamed for this latest event of flooding. Hurricane Marie‘s center remained well away from land throughout its entire existence, its large size brought increased surf to areas from Southwestern Mexico northward to southern California. Off the coast of Los Cabos, three people drowned after their boat capsized in rough seas.
In Colima and Oaxaca, heavy rains from outer bands caused flooding, resulting in two fatalities. Similar effects were felt across Baja California Sur. Toward the end of August, Marie brought one of the largest hurricane-related surf events to southern California in decades. Swells of 10 to 15 ft (3.0 to 4.6 m) battered coastal areas, with structural damage occurring on Santa Catalina Island and in the Greater Los Angeles Area.
A breakwater near Long Beach sustained $10 million worth of damage, with portions gouged out. One person drowned in the surf near Malibu. Hundreds of ocean rescues, including over 100 in Malibu alone, were attributed to the storm, and overall losses reached $20 million.
While floods have been recorded in California’s history a mega-drought is still threatening many communities, farms and rural populations. International Animal Rescue Foundation’s - Environmental News and Media uncovered startling evidence of “some” farmers now selling their collected water instead of crops as the water is netting more profit at the moment than staple crops are.
“Climate change is not the main aggressive factor here affecting California’s residents and farming communities” Jose Depre stated. “The main problems surrounding California’s drought is the misuse of water and increasing populations”. “People are mostly to blame here and poor water management rather than just “climate change” stated Depre, Chief Environmental Director for International Animal Rescue Foundation, Say No To Dog Meat and Speak up For the Voiceless.Org”.
May 5th 2015 California introduced a newer and tougher water restriction since since the drought of 2012 began. California’s state water board have have approved emergency drought regulations that aim to slash the misuse of water down by some 25%. The measures call for cities and water agencies to reduce water usage by amounts ranging from 8% to 36%. The State Water Resources Control Board drew up the rules to meet Gov. Jerry Brown’s order for a 25% cut in urban water use statewide.
It’s the first time that California has ever put in place mandatory reductions in water use. The plan reflects just how bleak the state’s water picture has become. The snowpack in the Sierra Nevada has shrunk to a record low. Groundwater levels have plummeted across much of California, and in some areas of the Central Valley, the wells of hundreds of families have run dry. Furthermore while families and farming communities are suffering so too are wildlife.
Environmentalists at International Animal Rescue Foundation are now concerned the shortages of water and the impending summer that’s just around the corner will begin to have more than an adverse impact onto local wildlife that are already threatened with drought and wildfires.
While the residents of California can voice their concerns and take the relevant actions to adapt to drought the “silent sufferers” are those non-human species that rely on water to live, feed, bathe and hunt. Many native species of flora and fauna are already being forced to change their routines due to the serious ongoing drought that’s reported to increase this summer 2015. Furthermore the threat of wild fires is only around the corner that will increase pressure on native flora and fauna species furthermore.
75% of Southern California’s water supply derives from the Sierra Nevada Snow Pack. Should this 75% melt Southern California’s wildlife will be placed in extreme danger of death. Human civilization will undoubtedly suffer while the economy, businesses and organisations will feel more than hot pressure. Crime and unemployment will rise too followed by murder and gang related crimes.
From January 1 through to January 25th of this year CalFire responded to 406 wildfires. But in that same time period for the past five years, the average was just 69 wildfires. Meteorologists don’t expect much rain in 2015 during the usually wet spring months, so the heightened fire danger is expected to continue straight into the summer.
One of the very worst recorded wildfires to hit California for “2015” was recorded this February that saw some 50-75 km winds fanning wild fires leading to over five hundred residents being forced to evacuate the two small California towns at the eastern base of the Sierra Nevada. Brown said even rain wasn’t enough to put out the fire because a three-year drought across California created extremely dry timber brush that fueled the flames.
Should the three year drought continue its course of destruction thus seeing wildfires occur the effects onto local wildlife would be catastrophic and something that we do not think the locals are prepared for. Wildfires displace animals, displacement means some if not many of these animals caught up in wildfires can unfortunately end up in human populated areas which can cause some concern especially if larger predatory animals are displaced.
Image: Wild roundfire - 2015 California.
International Animal Rescue Foundation has voiced its concerns regarding drought and black bears that could/will begin to breach California’s human populated areas in search of food. Black bears are very adaptive and very mobile, so they will usually be able to take care of their daily needs in a drought situation. But then they’re coming down to the lake to drink a lot, coming down for food. If the drought persists, it greatly increases the odds of a negative interaction with people. When or if this happens we’ll most likely see hunters brought in to control the species to keep populations intact or even possibly a temporary cull of black bears to reduce human species conflict.
Quote: “It was a surprise to see a bear in this part of the neighborhood”
Farm animals are also affected by California’s “unusual drought” of which residents have reported sightings of cattle and smaller animals within their back gardens. Migrations and hibernation’s are also being thrown of course due to the drought. One commonly known species, the Monarch Butterfly has been seriously affected by the drought of which its populations are decreasing.
Monarch butterfly numbers are falling, in part due to lack of food and the changing weather patterns along their migration route. The butterflies’ winter destination is Mexico; they travel thousands of miles south from Canada and the United States. Some settle along the warmer parts of the California coast, like Pacific Grove, near Monterey.
The larvae (caterpillars) of monarch butterflies eat “only” milkweed. The larvae stage is the only stage of the monarch butterfly that feeds on milkweed; there is something in milkweed that allows the caterpillar to grow and keep all of the vitamins needed to transform into a beautiful butterfly. In turn, the adult butterflies consume all sorts of different foods including nectar, water and even liquids from some of the fruits we consume.
Image: Monarch butterflies decline since records began in 1993
California’s drought has pretty much affected the vast majority of fresh and lush fruit trees that the monarch butterfly requires to thrive on. The World Wildlife Fund for Nature concluded last year in the Sierra Madre of Mexico saw the lowest population count of monarch butterflies since 1993 of which California’s drought was being blamed for.
Newts are staying in hibernation for longer periods too which is not considered normal. Newts would normally be seen out and about now. In Ben Lamond both newts, toads and frogs are literally being overcome by drought that’s seen devastating declines and deaths. While most amphibious creatures dig deep into the soil to take evasive action from such harsh environmental events sadly, the evasive actions taken are not helping to reduce the number of newt, frog and, toad deaths all of which are critically important species of fauna that are required to keep insect populations intact.
When early settlers arrived in California they drained Some 90% of California’s wetlands to create farmland and goldmines of which has had an adverse effect to amphibious species of fauna. Ecologists are trying though to reverse this trend that would help to increase amphibious species. Many amphibians breed and lay their eggs in wetlands. After their aquatic young develop they can survive on land, but they must return to a wetland to create the next generation. With such harsh drought increasing in its third consecutive year many amphibian creatures will be wiped out.
Image: Ben Lamond newt rescued from its natural habitat that has since dried up
Things do work out better for native amphibians though if a wetland dries up for “part of the year”. When it comes to amphibians’ predator control, drought can be a good thing, and timing is everything. While most of the three year drought period has dried up substantial amounts of wetland California’s native frog, toad and newt species will undoubtedly suffer in the long term too.
Unfortunately its not just our smaller species of wildlife that are affected by the impending “mega-drought”. International Animal Rescue Foundation’s marine and fresh water wildlife department has uncovered starling evidence of marine and fresh water mass deaths. 26th May 2015 in Baja, California, thousands of lobsters were washed up on the shoreline dead and alive. Jose Depre, CEO stated “in under two months this is the forth such event occurring on the Baja coast of which the same species of marine life has washed up dead and alive with no apparent reason or cause.
Image: Thousands of lobsters was ashore for the third time this year.
In under two months many more whales have also without reason nor cause washed up along the coast of California. 24th May 2015 a further seven dead whales were sadly seen washed up onto the shoreline. 24th April four dead whales were again washed ashore which has baffled scientists. 7th March 2015 - 1,450 Sea lion pups have washed ashore this year ill and dying - ‘possibly 10,000 have died’ in California, America since the drought began three years ago. Some environmental groups are claiming that ships are the main cause of death however, the sheer fact that California also has seal pups and fish washing up now whales and sharks deepens our concerns regarding such deaths.
Image: Whales and sharks washing ashore along the coast of California.
This year alone California’s Animal Rescue Clinics have been inundated with call after call regarding stranded cold and emaciated sea lion pups. 2015 has been said to be the worst year for sea lions in California of which the drought has been noted as the main blame. Unusually warm ocean water caused fish to move away from the islands where the sea lions give birth.
Due to sea lion prey moving further and deeper away, the moms are actually gone away longer from the pups. Because they’re gone longer, the pups aren’t getting enough (food) over time. They’re leaving the islands early, and they’re showing up on the shores here, starving to death. Environmentalists have stated the warmer ocean water has more to do with local conditions in the eastern Pacific. The current drought event of three years hasn’t more to do with global warming or anything along those lines. It’s more of a local climate event that we’re looking at. Experts hope the warmer-than-normal water is a fluke and not a pattern.
Meanwhile, while the state of California is under an immense drought California’s citizens are trying their hardest to adapt to what appears to be more locally human induced events rather than as explained “global warming or climate change”. However as much as the local non-celebrity citizens are doing their bit for their state, some celebrities have been noted as either doing nothing or simply flouting the laws.
One only has to take a drive around the suburbs of California to view most non-celebrity citizens once lush green lawns now nothing more than a frazzled piece of sod. Look a little further and one will see many celebrity houses with lush green lawns, filled fresh clean swimming pools and, sprinklers to hosepipes at the ready. Its truly crazy and a sharp smack into the face to our local wildlife and communities that would if they dared use a hosepipe fall prey to enforcement.

Picture above is celebrity Khloe Kardashian’s home that is decorated with lush green lawns, trees and crisp blue swimming pool. While on the left hand side of this image you can clearly see the impacts of California’s drought slowly but surely destroying even the hardiest of drought resistant grasses.
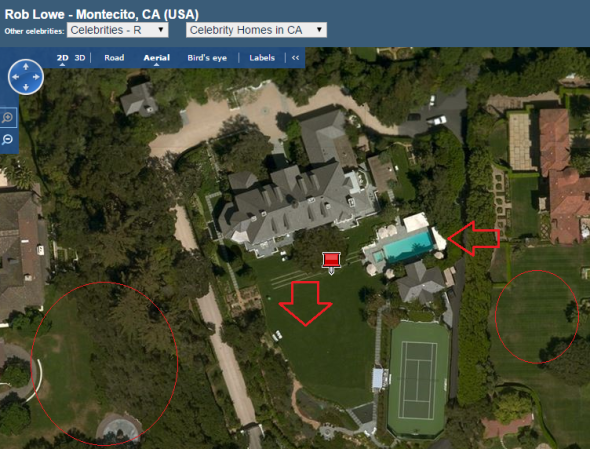
Celebrity Rob Lowe’s immaculate garden can be seen above that is flowing with green lush lawns and shrubs. Meanwhile on either side and circled in red for your attention are the effects of drought. One doesn’t really need to research or understand how much water is required to keep such lawns in this acquired condition. Even within the United Kingdom where rainfall is a weekly occurrence such lawns of this type would not be seen in your everyday garden. Again this really is a slap in the face of those small animals that have no voice to shout for help. Furthermore if such celebrities that are supposed to be setting a good standard continue to flout the laws so will the local citizens.
Celebrity Jennifer Aniston does set a small example with the use of solar panels however then, lets herself and community down with lush green lawns and fresh crisp blue swimming pool. While on the left hand-side of this image one again can view the impacts of California’s three year drought slowly browning even the hardiest of drought resistant lawns.
Out of ninety celebrities gardens viewed within California sixty three had lush green lawns and with some thirty eight out of the ninety owning at least five swimming pools. Out of just the ninety observed, forty had hosepipes on show with a sprinkler attachment clearly visible. Only one home that we did view which was that of Kayne Wests that actually showed nothing but bare grey-ish, brown scorched grass.
California’s drought is expected to continue through to next year with little or no hope of the much needed rainfall. Concerning is that should the state of California continue to dry up into a slate of rock any such intense and prolonged rainfall will simply run off placing water reservoirs and concrete canals under immense pressure. Furthermore the longer dry spells persist with misuse of water the chances of heavy rainfall must be taken on board by all Californian residents. Floods may be uncommon but they can occur very quickly without warning and cause untold damage to large swathes of communities and the local wildlife.
There are many community projects that are now taking place all over the state such as Water Free Wednesday, horticultural drought resistant gardening and rebates for those that knowingly help to reduce their water intake. Furthermore tips on how you can save water can be viewed here below.
Thank you for reading.
Dr Jose C. Depre
Environmental and Botanical Conservation.
Plastic Bag Syndrome.
Shopping bags. Yes I’m going to bore you this Wednesday about your over-usage of shopping bags and how these bags are helping to destroy our environment and are responsible for the deaths of many hundreds if not thousands of animals per year. This article may be boring to some, however I am sick to the core of seeing so many people in hyper-markets purchasing bag after bag just for them bags to later be thrown away. Once you’ve thrown that precious bag away you have then contributed to littering the Earths already fragile ecosystem and trust me the damage doesn’t even stop there….. Its time for a little consumer education…
Brief History;
Believe it or not but plastic bags are becoming a serious environmental problem. So serious that many countries globally have imposed charges for all bags now paper and plastic. You’d probably think that even with a charge of say a few dollars the consumer would keep the bag and then reuse it. However some do many do not. Regardless of the charges imposed production of plastic bags and purchasing still continues. As human population increases so will demand for shopping accessorizes.
Two hundred and sixty seven different species of animals and plants have been known to be affected by plastic bag wastage. Over 100,000 marine animals, including highly intelligent, adorable sea turtles, whales and dolphins, die every year because of plastic bags. The die because of your selfishness. While conservation organisations are helping to clean the seas, beaches and lands of your waste the production of bags continues at a staggering rate. To be precise every five seconds sixty thousand plastic bags are produced every “five seconds” just in the United States alone. That’s one hell of a lot of bags.
The damage plastic bags cause to our wildlife is catastrophic as one can see in the picture below. Even when animals that have died and decomposed digest plastic bag particles or whole plastic bags the bag still remains intact. It takes over one hundred years or more for your average plastic bag to decompose. In that time the digested plastic bag has most likely poisoned another animal or killed a further whale or even a Tiger or Lion.. Even Africa’s pristine parks are not safe from littering so don’t think for one moment that plastic bag refuse is just confined to our oceans.
The picture above depicts a dead decomposing seabird. Look closely though. You can make out many different plastic particles. Lighters, bottle tops and pieces of plastic bag garbage that would most likely have led to this animals painful death. And as explained marine animals are not the only species threatened by plastic bag garbage. The picture below depicts cattle that have also fallen prey to the plastic bag menace. Digesting such toxic plastics can lead to many physical complaints that can lead to eventual death.
Hundreds of cows die annually from choking on plastic bags containing vegetable waste
In November 2008 in Australia, a 10-foot-long crocodile tagged as part of a government wildlife-tracking program turned up dead, having consumed 25 plastic shopping and garbage bags. Whitey, as the crocodile was dubbed, had been relocated to a popular tourist destination called Magnetic Island, and authorities at first feared that he had died as a result of eating garbage left behind by visitors. Said Keith Williams of the group Australian Seabird Rescue, however, “Whitey probably was picking up plastic long before [being moved].”
Plastics take hundreds, perhaps even thousands, of years to break down in most environments, such that it is not a stretch to imagine a single bag killing more than one animal over a very long lifetime on land and sea. And while the statistics are incomplete, some conservationists estimate that at least 100,000 mammals and birds die from them each year, felled by the estimated 500 billion and more plastic bags that are produced and consumed around the world; the numbers of fish killed by them are unknown, but they are sure to number in the millions.
Word of that devastation is spreading, and countries around the world have taken measures to limit or ban the use of throwaway plastic bags. The first to do so was Bangladesh, which banned plastic bags in 2002; following a particularly damaging typhoon, authorities discovered that millions of bags were clogging the country’s system of flood drains, contributing to the destruction.
In the same year, Ireland took another approach and instituted a steep tax on plastics. According to the country’s Ministry of Environment, use fell by 90 percent as a result, and the tax money that was generated funded a greatly expanded recycling program throughout the country. In 2003 the government of Taiwan put in place a system by which bags were no longer made available in markets without charge, and carryout restaurants were even required to charge for plastic utensils.
Larger economies have joined the cause. Australia has called for a voluntary ban, and thus far consumption of the bags has fallen markedly as 90 percent of the country’s retailers have signed on to the program. In 2005, French legislators imposed a ban on all nonbiodegradable plastic bags, to go into effect in 2010. Italy will also ban them that year, and China has already prohibited bags less than 0.025 millimeters thick. “Our country consumes a huge amount of plastic shopping bags each year,” a spokesperson for China’s State Council said on announcing the ban last May. “While plastic shopping bags provide convenience to consumers, this has caused a serious waste of energy and resources and environmental pollution because of excessive usage, inadequate recycling and other reasons.”
In the United States, however, measures to ban or curtail the use of plastic bags have met with official resistance. With its powerful lobby, the plastics industry argues that jobs will disappear—and the industry employs some two million workers, at least in good times—if the trade in plastic bags is reduced. But these are not good times, bans or no, and critics point out that Americans alone throw out at least 100 billion bags a year, the equivalent of throwing away 12 million gallons of oil, which seems an intolerable waste.
Thus, even in the United States, the no-bags campaign is gaining ground. During its 2008 session, the New York State Legislature passed legislation requiring the “reduction, reuse, and recycling” of checkout bags. The previous year, the city of San Francisco banned plastic bags altogether, at least the flimsy ones of yore. National Public Radio reported a few months later that the ban had been a boon for local plastics manufacturers, who have been introducing heavy-duty, recyclable, and even compostable bags into the marketplace.
And then New York City Mayor Michael Bloomberg had been talking of imposing a citywide tax of six cents for every plastic bag dispensed—one source of quick revenue in tight times, at least until consumers catch on and stop paying the surcharge by carrying their own shopping bags. Just so, speaking directly to our wallets, more and more grocery stores in the United States are offering small incentives to customers who do so. Trader Joe’s, a popular California-based chain, offers such customers raffle tickets for free groceries, while Albertson’s, another chain, gives a small cash credit.
Plastic Bag Poisoning;
Plastic bags are made of polyethylene and polyethylene is a petroleum product. When animals consume such plastic bags they are then poisoned by the chemicals within that bag as it passes through the animals digestive system or they simply choke to death. In many case animals stomachs and intestines become so clogged with plastic bag waste that many die just from this complaint. Plastic bags are often mistaken as food by marine mammals such as turtles that believe a floating bag is prey such as jelly fish. 100,000 marine mammals die yearly by eating plastic bags.
When plastic is cast out to see photo-degradation breaks the plastics down into what we call mermaid tears or nurdles. Mermaid tears or nurdles are basically very small plastic particles that have been broken down by the suns exposure. Smaller sea-life species of animals such as turtles, fish even shell fish are then exposed to an almost invisible man made silent killer.
These tiny plastic particles can get sucked up by filter feeders and damage their bodies. Other marine animals eat the plastic, which can poison them or lead to deadly blockages. Nurdles also have the insidious property of soaking up toxic chemicals. Over time, even chemicals or poisons that are widely diffused in water can become highly concentrated as they’re mopped up by nurdles.
These poison-filled masses threaten the entire food chain, especially when eaten by filter feeders that are then consumed by large creatures.
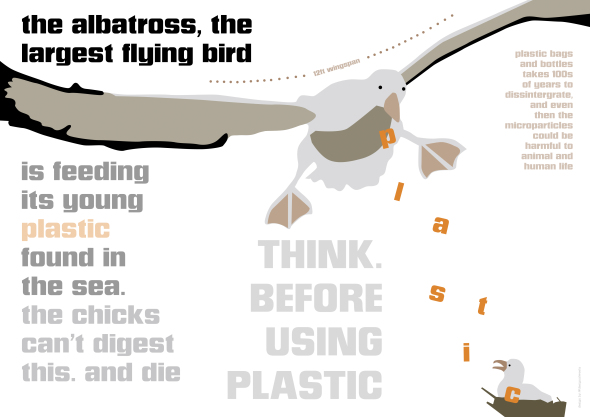
Plastic has acutely affected albatrosses, which roam a wide swath of the northern Pacific Ocean. Albatrosses frequently grab food wherever they can find it, which leads to many of the birds ingesting — and dying from — plastic and other trash. On Midway Island, which comes into contact with parts of the Eastern Garbage Patch, albatrosses give birth to 500,000 chicks every year. Two hundred thousand of them die, many of them by consuming plastic fed to them by their parents, who confuse it for food
. In total, more than a million birds and marine animals die each year from consuming or becoming caught in plastic and other debris.
“More than a million birds and marine animals die each year from consuming or becoming caught in plastic and other debris”…
Plastic bag menace facts and figures;
- Each year, an estimated 500 billion to 1 trillion plastic bags are consumed worldwide. That’s over one million plastic bags used per minute.
- According to the Worldwatch Institute’s State of the World report. Some 4 to 5 trillion plastic bags—including large trash bags, thick shopping bags, and thin grocery bags—were produced globally in 2002. Roughly 80 percent of those bags were used in North America and Western Europe.
- Every year, Americans reportedly throw away 100 billion plastic grocery bags.
- The average American family takes home almost 1,500 plastic shopping bags a year…
- Americans use and dispose of 100 billion plastic shopping bags each year and at least 12 million barrels of oil are used per year in the manufacture of those plastic grocery bags.
- Less than 5 percent of plastic grocery bags are recycled in the U.S.
- Plastic bags were introduced into supermarkets in 1977.
- Scientists estimate that every square mile of ocean contains about 46,000 pieces of floating plastic.
- Researchers have found that plastic debris acts like a sponge for toxic chemicals, soaking up a million fold greater concentration (than surrounding water) of such deadly compounds as PCBs and DDE. Becoming highly toxic poison to marine animals which frequently consume these particles.
- Plastic bags can take up to 1,000 years to break down, so even when an animal dies and decays after ingesting a bag, the plastic re-enters the environment, posing a continuing threat to wildlife.
- There is now six times more plastic debris in parts of the North Pacific Ocean than zooplankton.
- At least 267 different species are known to have suffered from entanglement or ingestion of plastic marine debris.
- The amount of petroleum used to make a plastic bag would drive a car about 115 metres. It would take only 14 plastic bags to drive one mile!
- The production of plastic bags requires petroleum and often natural gas and chemicals. Its production is toxic to the air.
- Packaging now accounts for 1/3 of all household waste.
- Every year we make enough plastic film to shrink-wrap Texas.
- In 2007 in the U.S, about 31 million tons, or 12.1 percent of total municipal waste, was plastic. Over 380 billion plastic bags, sacks and wraps are consumed in the U.S. each year, costing retailers an estimated $4 billion.
- Over 100,000 marine animals, including highly intelligent, adorable sea turtles, whales and dolphins, die every year because of plastic bags.
Plastic bags killing off many threatened and endangered species of marine life;
While poaching and over-fishing is affecting many species of animals within the deep blue seas and shorelines so too are you the consumer that unknowingly when throwing that plastic bag away or using it as a smaller sized refuse bag are actually contributing to the extinction of our threatened species of marine life.
Since 1950, plastics have played an omnipresent part of our daily lives. Most of the marine debris in the world is comprised of plastic materials (between 60 to 80% of total marine debris). Field studies have shown that mega- and macro-plastics have concentrated in the highest densities in the Northern Hemisphere, adjacent to urban areas, in enclosed seas and at water convergences. The longevity of some plastics is estimated to be hundreds to thousands of years!
The environmental impacts resulting from the accumulation of plastic waste are huge and increasing. Plastic debris affects wildlife, human health, and the environment too. The millions of tons of plastic bottles, bags, and garbage in the world’s oceans are breaking down and leaching toxins posing a threat to marine life and human. Plastic materials in landfills sink in harmful chemicals into groundwater. Chemicals added to plastics are dangerously absorbed by humans like altering hormones. Research on plastics includes a large and robust literature reporting adverse health effects in laboratory animals and wildlife at even low doses. Plastic debris is ingested by hundreds of species choking and starving them. Floating plastic debris can spread invasive species.
36 per cent of Australian sea turtles are affected by marine litter, with some 18,000 pieces of plastic litter floating on every square kilometer of the world’s oceans. Green turtles are the most common species seen in WA with up to 30,000 females nesting along the coast and along fringing reefs at Shark Bay to Murchison River between October and February each year.
According to the WA Department of Environment, divers may see large juveniles around Rottnest Island reefs. University of Queensland marine biologist Dr Kathy Townsend said the problem of marine waste had to be tackled before the already low population numbers of sea turtles became even more depleted.
“This thing is everyone’s fault, and because it’s everyone’s fault no one takes responsibility,” Dr Townsend said. “We need to stop generating so much waste. We are doing the inconceivable, we are starting to fill up the oceans of the world.”
The Turtles in Trouble program found turtles had swallowed balloons, plastic bags, nylon rope, styrofoam and thongs, among other things, possibly mistaking them for jellyfish. Once ingested, the plastic causes a gut impaction which leads to the contents of the animal’s gut decomposing.
“The animal becomes positively buoyant and it can’t dive down to eat, it can’t get out of the way of predators, it can’t get out of the way of boats, so it really is quite a tragic thing,” Dr Townsend said. It can result in so-called “floating syndrome”, where the turtle may take months to gradually starve to death. “It’s a really long, drawn-out, painful death,” Dr Townsend said.
Earthwatch Australia executive director Richard Gilmore said a number of measures can be taken to reduce marine rubbish.
“Australia’s marine environment is absolutely fundamental to our economy, our environment and to our way of life,” Mr Gilmore said.
Dr Townsend said that everyone can do their share. “Start refusing those items that have a useful lifetime of only minutes and yet take years if not decades to degrade,” she said. “Do you really need to have a plastic top on your paper coffee cup? Refuse that, you don’t need that”.
Marine rubbish also affects Victoria’s famous fairy penguins, which frequently get entangled in debris. Dr Townsend said if the problem is not addressed it will only get worse, but with awareness, she hopes the correct choices will be made to reduce the amount of rubbish reaching the marine environment.
Picture below depicts what a turtle believes is food. A plastic bag that to the turtle appears much like its prey - jellyfish..
Even dolphins are not safe from the plastic bag menace. The video below depicts unselfish kind and considerate boatmen that located a baby dolphin in distress. The plastic shopping bag appeared to have been half ingested and smothering the baby dolphin. Had these kind men not taken evasive action the baby dolphin would most certainly have perished from suffocation.
While sea turtles are under threat from plastic bags too being one of the oceans most endangered species the Maui’s dolphins are also under attack from this dreaded plastic bag syndrome as we call it. A slow breeding rate and small population size have made of Maui’s dolphin a very endangered subspecies. In fact, just more than one human-induced death every seven years seriously threatens the chances of population recovery.
However, over since March 2001, seven dead Maui’s dolphins have been found. Five of these deaths were due to fishing, one was impossible to determine and one was because of natural causes. This dolphin is vulnerable to set net (gill net) and trawl fishing, marine pollution and debris, boat strikes and genetic bottleneck.
Dolphins like Maui’s which inhabit shallow coastal waters are vulnerable to the pollutants which humans allow into the sea. Chemicals from industrial waste, stormwater and agricultural runoff like PCBs, DDT, dioxins and metals have been found in Hector’s dolphin’s blubber (including Maui’s dolphins).
These pollutants bio-accumulate, which means they increase in potency as they move up the food chain. Maui’s dolphins are near the top of their food chain and these pollutants can be passed on to young dolphins through their mother’s milk. High levels of exposure can cause loss of fertility and compromise immune systems in marine mammals. Another form of pollution which threatens Maui’s dolphins is solid rubbish such as plastic shopping bags which can be mistaken for squid and ingested, killing the dolphin.
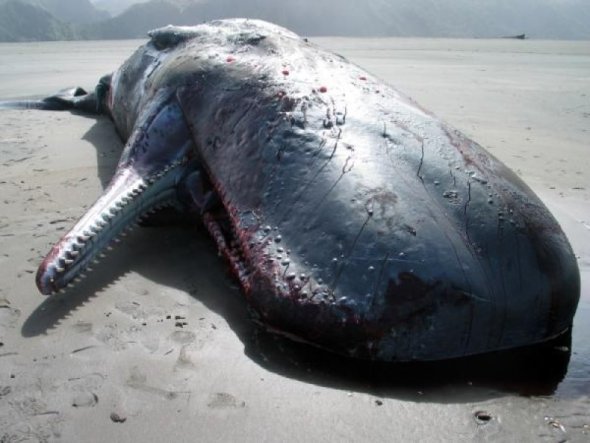
And if you believe that plastic bags only harm little animals then think again. Tesco and Waitrose were shocked to find that a dead sperm whale washed up on the Granada coast had sadly perished due to plastic bag digestion. When marine scientists opened the dead sperm whale up to one hundred plastic carrier bags were found in the stomach of the whale. Read more below;
A dead sperm whale that washed up on Spain’s south coast had swallowed 17kg of plastic waste dumped into the sea by farmers tending greenhouses that produce tomatoes and other vegetables for British supermarkets.
Scientists were amazed to find the 4.5 tonne whale had swallowed 59 different bits of plastic – most of it thick transparent sheeting used to build greenhouses in southern Almeria and Granada. A clothes hanger, an ice-cream tub and bits of mattress were also found.
The plastic had eventually blocked the animal’s stomach and killed it, according to researchers from the Doñana national park research centre in Andalusia.
Researchers at first found it hard to believe that the 10-metre animal had swallowed the vast amount of plastic they found protruding through a tear in its stomach.
In all the whale’s stomach contained two dozen pieces of transparent plastic, some plastic bags, nine metres of rope, two stretches of hosepipe, two small flower pots and a plastic spray canister.
All were typical of the closely packed Almeria greenhouses that cover about 40,000 hectares – and are clearly visible in satellite photographs taken from space.
Desert-like Almeria has transformed itself into Europe’s winter market garden thanks to the plastic greenhouses where plants are grown in beds of perlite stones and drip-fed chemical fertilisers. Local farmers report that Tesco, Waitrose and Sainsbury’s are all valued customers.
Estimates of how much plastic waste is generated vary from 45,000 tonnes to more than 88,000 tonnes.
Much is treated in special waste centres, but environmentalists complain that local riverbeds are often awash with plastic detritus and, with greenhouses built right up to the high-tide line, some also ends up in the sea.
“The problem of degraded plastics that are no longer recyclable still remains,” Renaud de Stephanis, lead researcher at Doñana, and his team reported in the Marine Pollution Bulletin.
Only about 1,000 sperm whales – the world’s biggest toothed whales – are thought to live in the Mediterranean. They live for up to 60 years and are often killed after getting caught in nets or being hit by ships.
Now another man-made danger has been detected. “These animals feed in waters near an area completely flooded by the greenhouse industry, making them vulnerable to its waste products if adequate treatment of this industry’s debris is not in place,” warned de Stephanis.
• This article was amended on 10 July 2014 to clarify a statement about the amount of plastic waste generated by the Almeria greenhouses.
Countries taking a prime stance against Shopping Bag Syndrome;
Since the early 1990’s and beginning of the Millennium governments around the world have taken quite a significant stance against the production and selling of shopping bags. Some countries have banned plastic shopping bags whereas others have implemented a charge. These charges have been welcomed by many people although not everyone is pleased.. International Animal Rescue Foundation’s Marine Conservation Team surveyed 100 shoppers at Tesco, J.S Sainsburys, Morrison’s, ASDA and the Cooperative Group when we released our last marine article in 2013 relating to marine pollution.
Out of the 100 shoppers questioned that had mostly a shopping cart filled with bags the majority were not pleased that they had to purchase from five to ten or more shopping bags valued at around 0.02p and 0.04p. International Animal Rescue Foundations Marine Conservation Unit questioned the Store Managers of which neither they nor their staff that worked on the checkouts were actually made aware as to why customers were being charged for plastic bags. On surveying the stores main communications boards there was no customer feedback stating why charges were introduced and the dangers plastic bags cause to the environment. However two stores I.e Tesco and the Morrison’s it was observed small caged bins that had free second hand used bags were in place for the public to use or place their old unwanted bags into to be reused by the public. International Animal Rescue Foundation welcomes this initiative although its very limited and many stores across the United Kingdom and Germany did not have such bins in place for second hand bags to be used.
Since this small survey International Animal Rescue Foundation has been working on trial posters of which they hope to educate not only the staff within these large hypermarkets but also the public. Education and awareness is key to International Animal Rescue Foundations mission statement. If customers can be made “visually” aware of the impacts throw away plastic bags have to the environment then its hoped a change in the way public use bags is seen. We can all only but try. Or lobby for a complete ban on plastic bags.
Rwanda takes the lead;
A Danish company has built a plant for biodegradable packaging in the Rwandan capital Kigali. The hilly, green country is a shining example for other African countries because of its total plastic bag ban. Rwandan entrepreneurs, however, don’t believe it’s the optimal solution. “Africa needs a recycle system.”
Not only do countless bags make streets, roadsides and parks of many African countries look awful, they also pollute the environment. They clog the drains and choke the soil. Many sea turtles die after eating bags that probably look like jellyfish to them. And until recently eating dumped plastic bags was the cause of death for 70 per cent of all cattle in the Mauritanian capital of Nouakchott. Finally the most shocking fact is that – depending on thickness - plastic bags dumped in the environment may take between 20 and 1000 years before breaking down.
Many African governments are now looking at the clean streets of Rwanda with admiration as all plastic bags have been banned since 2008. Mauritania and Mali followed with a ban in 2012. Many other African countries are trying to ban the import and production of bags made of very thin plastic and some are considering a wider ban.
‘Products in paper bags are less attractive’
Rwandese entrepreneurs doubt whether a total bag ban is the best solution. “Although I’m proud of our clean streets, for an entrepreneur like me the bag ban is a nightmare”, Rwandese supermarket owner Emmile Mulega (44) says. The brown paper bags he needs to use are more expensive and less attractive. “Customers want to see what they buy. Therefore products in paper bags are less attractive.”
According to the Rwandan businessman the paper bags are particularly not suitable for wrapping meat. “Before you get home, the bag is completely wilted. But currently we don’t have any choice.” Mulega believes that some products just need plastic packaging. A recent report on France24 showed Rwandan bakers complaining about paper bags tearing up too easily causing the bread it’s supposed to protect to spoil too soon.
A fully biodegradable packaging plant in Kigali
It’s for these reasons that the Danish company Field Advice has started the construction of a plant for fully biodegradable packaging in Kigali this year. “The ratio of ingredients can determine in advance when the plastic will decompose,” Field Advice-director Mark Remmy explains, while he shows how he pulverizes a so-called oxo-biodegradable plastic fork between his fingers. “Rwanda is an extremely interesting market for our company because it ensures a great demand. “Rwandans face great difficulty to transport groceries in a paper bag during the rainy season for example.” Also, the production of a paper bag consumes more water and energy than an oxo-biodegradable bag.
Supermarket owner Mulega supports the idea of biodegradable packaging, but adds that Africa needs a waste recycling system as well. “Lots of plastic packaging still enters our country because of the large amount of imported goods. We should collect and reuse this trash. This would not only benefit the environment but also create employment opportunities.”
Countries that are taking the lead in banning Plastic Bag Syndrome;
England
In 2007, Modbury became the first town to ban the plastic bag in Britain, where 13 billion plastic bags are given away every year. If customers forget to bring their own, reports the Times Online, “a range of bags made of recycled cotton with organic and fairtrade certification will be available from other outlets”.. Other cities have followed suit, some just a few months ago, and there are efforts to make London plastic bag-free by the time the Olympics come around in 2010. According to the Daily Mail, “Londoners use 1.6billion plastic bags a year - for an average of just 20 minutes per bag.”
Mexico
Mexico City adopted a ban last summer—the second major city in the western hemisphere to do so.
India
India seems to be taking the lead in bans on plastic bags, although enforcement is sometimes questionable. Cities including Delhi, Mumbai, Karwar, Tirumala, Vasco, Rajasthan all have a ban on the bag.
Burma
A ban went into effect (with little notice) in Rangoon late last year. In neighboring China, the use of plastic bags is restricted.
Bangladesh
Plastic bags have been banned in Bangladesh since 2002, after being found to be responsible for the 1988 and 1998 floods that submerged most of the country.
Rwanda
The country, which has had a ban on plastic bags for years, has a reputation for being one of the cleanest nations not only on the continent, but in the world. Now that’s pretty classy!
Australia
Sydney’s Oyster Bay was the first Australian suburb to ban plastic bags. Twelve towns in Australia are now said to be plastic bag-free—an effort to cut down on the estimated 6.7 billion plastic bags used in Australia every year.
Taxed, not banned
Plenty of other places have chosen not to ban plastic bags, but to discourage them through financial means. There have been taxes on plastic bags since before 2008 in Italy, Belgium, and Ireland, where plastic bag use dropped by 94 percent within weeks of the 2002 ban. In Switzerland, Germany, and Holland, the bags come with a fee. And, in one lonely case (that I could find) of a reversal on a ban after it was implemented, Taiwan had a ban on plastic bags for three years before it lifted it in 2006.
And if this is not a fare shed load of information about plastic bags and the damage they cause to the environment, fauna and flora please do remember before you even purchase a plastic bag rather than “reusing” the bag you only purchased yesterday or just threw away then take this information below on board.
- According to MSN, the production of plastic bags creates enough solid waste per year to fill the Empire State Building two and a half times.
- The Worldwatch Institute estimates that in the U.S. alone, an estimated 12,000,000 barrels of non-renewable petroleum oil are required to produce the 100 billion bags consumed annually. That’s over $500,000,000 the country could be saving to put towards clean, green energy.
- They can take from 400 to 1,000 years to decompose but their chemicals residues remain for years after that.
- Over 100,000 marine animals, including highly intelligent, adorable sea turtles, whales and dolphins, die every year because of plastic bags.
Conclusion
Plastic bag syndrome as we call it must be addressed by every government globally. On a personal note we as conservationists do not believe the plastic bag tax is helping at all. Yes the price of paying for bags has put some people off. However eight out ten consumers still do not reuse their plastic bags. They later end up on the garbage tip, floating in some stream or within our already threatened marine ecosystems polluting the seas more and killing off vulnerable species of aquatic wildlife large and small. As the planets populations grow so will the need for more bags. Every five seconds a alone some 100,000 plastic bags are churned out globally without a care in the world of what damage they are inflicting to the environment from careless consumers. International Animal Rescue Foundation calls for a stricter response to this issue of which we believe a mandatory fine should be brought into punish consumers that carelessly do not reuse their bags or just throw them into the garbage. More stricter fines and/or imprisonment must be looked into as well with regards to “all waste that is recyclable not being recycled”.. If you think about it plastic bag syndrome is no different to that of fly tipping.
International Animal Rescue Foundation will be monitoring hypermarkets all over Europe this coming 2015. The conservation company will also be asking Managers and CEO’s of large supermarket chains to include our posters within their stores where there is high yet slow customer traffic such as tills and customer service points. Lastly as of next year we will be showcasing a video on our road shows around Europe aimed at Store managers and Chief Executive Officers in the hope they will do more “in store” to help the public help sustain our wildlife.
Thank you for reading.
Dr Josa C. Depre.
Chief Environmental Officer