ENDANGERED SPECIES MONDAY | PHOCARCTOS HOOKERI EXTINCTION LOOMING - NATIONAL EMERGENCY.

ENDANGERED SPECIES MONDAY | PHOCARCTOS HOOKERI
This Monday’s endangered species (E.S.P.) article I’ve chosen to document on the New Zealand sea lion. Image: New Zealand Sea Lion. Credits: Tui De Roy.
Listed as (endangered) the species was identified by Dr Gray back in 1866. Dr Gray John Edward Gray, FRS (12 February 1800 – 7 March 1875) was a British zoologist. He was the elder brother of zoologist Dr George Robert Gray and son of the pharmacologist and botanist Dr Samuel Frederick Gray (1766–1828).
Dr Gray was Keeper of Zoology at the British Museum in London from 1840 until Christmas 1874, before the Natural History holdings were split off to the Natural History Museum published several catalogues of the museum collections that included comprehensive discussions of animal groups as well as descriptions of new species. He improved the zoological collections to make them amongst the best in the world.
Scientifically identified as the Phocarctos hookeri the species was listed as vulnerable from 1994-2008. Unfortunately due to continued population declines the New Zealand seal is now bordering complete extinction within the wild (and things really aren’t looking good neither) Endemic to Australia (Macquarie Is.); and New Zealand (South Is.), the species is also native to the Pacific North West.
To date there is estimated to be no fewer than 3,031 mature individuals remaining within the wild. New Zealand sea lions are one of the largest New Zealand animals. Like all otariids, they have marked sexual dimorphism; adult males are 240–350 cm long and weigh 320–450 kg and adult females are 180–200 cm long aMnd weigh 90–165 kg. At birth, pups are 70–100 cm long and weigh 7–8 kg; the natal pelage is a thick coat of dark brown hair that becomes dark gray with cream markings on the top of the head, nose, tail and at the base of the flippers.
Adult females’ coats vary from buff to creamy grey with darker pigmentation around the muzzle and the flippers. Adult males are blackish-brown with a well-developed black mane of coarse hair reaching the shoulders. New Zealand sea lions are strongly philopatric.

Image: New Zealand Sea Lion Pup. Credits: NZ Fur Seals.
Back in 2012 populations of New Zealand sea lions “were estimated to be standing at a population count of 12,000 mature individuals”. However since that count took place, from (2014) populations have ‘allegedly plummeted’ to all new levels although there doesn’t appear to be any evidence as to why the species suddenly declined - fish trawling and disease have been noted though!.
Like the Maui’s dolphin, the sea lion has come under intense scrutiny this year after research showed its numbers had halved since 1998. It has been classed as nationally critical and if its decline is not stemmed will be extinct within 23 years. A bacterial infection severely reduced breeding in 1997-98, and the species has failed to recover.
Its decline has been compounded by deaths due to squid fisheries, which trawl at a similar depth to the sea lions’ hunting grounds. Conservation groups call the population decline “a national emergency and are calling on stricter by-catch limits and a change in fishing methods”.
BACK IN 2012 THE NEW ZEALAND HERALD REPORTED THE FOLLOWING
In a country with 2800 threatened species, conservation in New Zealand is often about picking winners. The Department of Conservation’s budget and energy can extend only to active interventions for 200 of these endangered species.
Whether a species is protected depends on funding, community input, national identity and research. DoC spokesman Rory Newsam says interventions are often made because the department believes it can “get the most bang for its buck”. But animals and plants are not always invested in because they have a greater chance of survival.
The kakapo receives a relatively large chunk of funding despite being functionally extinct on the mainland. Some ecologists argue too much is spent rescuing the rare parrot, while more crucial parts of our ecosystem are left behind. But the kakapo is protected because it is a charismatic species and the public considers it integral to New Zealand’s ecological identity.
Conservationists say kakapo are a window to New Zealand’s history. They are believed to have inhabited the Earth for millions of years. To kill them off in a fraction of that time is an indictment on the way we live.

Image: New Zealand Sea Lion. Image Credits One Newz.
New Zealand sea lions are known to predate on a wide range of prey species including fish (e.g. hoki and red cod), cephalopods (e.g. New Zealand arrow squid and yellow octopus), crustaceans, seabirds and other marine mammals. Studies indicate a strong location effect on diet, with almost no overlap in prey species comparing sea lions at Otago Peninsula and Campbell Island, at the north and south extents of the species’ breeding range. New Zealand sea lions are in turn predated on by great white sharks, with 27% showing evidence of scarring from near-miss shark attacks in an opportunistic study of adult NZ sea lions at Sandy Bay, Enderby Island.
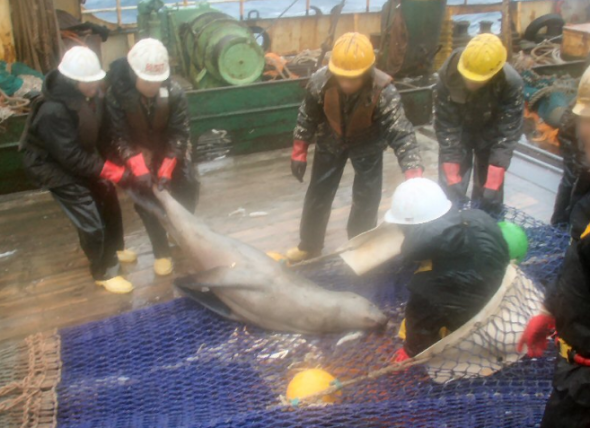

Image: Dead New Zealand Sea Lion in Fishing Net.
Since 2012 New Zealand conservationists, and the public community have been calling on the New Zealand government to do everything they possibly can to preserve this species. Unfortunately as you can see above fishermen are still accidentally killing the species off. As the species is protected under law and listed as endangered, the New Zealand government must take action against these perpetrators, otherwise extinction will most certainly occur.
The Maori people of New Zealand have traditionally hunted Sea Lions, presumably since first contact, as did Europeans upon their arrival much later. Commercial sealing in the early 19th century decimated the population in the Auckland Islands, but despite the depletion sealing continued until the mid-20th century when it was halted.
Commercial sealing in the early 19th century decimated the New Zealand Sea Lion population in the Auckland Islands, but despite the depletion sealing continued until the mid-20th century. The population has yet to fully recover from the period of over exploitation. At the present time, New Zealand Sea Lions have a highly restricted distribution, a small population, and nearly all of the breeding activity is concentrated in two subantarctic island groups. This restricted and small breeding population in combination makes them vulnerable to disease outbreaks, environmental change, and human activities.
The commercial Arrow Squid trawl fishery near the Auckland Islands reported their first New Zealand Sea Lion bycatch mortalities in 1978. Reported or estimated mortality between 1995 and 2007 averaged 92 animals annually (range 17-143) which was 3.7% of the estimated number of mature individuals in the Auckland Island area. Of particular concern is that most bycatch animals are females (up to 91%). New Zealand Sea Lions are also incidentally caught in other trawl fisheries around the Auckland and Campbell Islands.
Apart from direct mortality, competition and habitat modification caused by fishing activity may also be impacting New Zealand Sea Lion foraging areas. Epizootic outbreaks at the Auckland Islands in 1998, 2002, and 2003 led to more than 50%, 33%, and 21% early pup mortality respectively, and were also responsible for the deaths of some animals from other age classes during 1998.
The source of the suspected bacterial agent and cause of the outbreak and subsequent mortality for the 1998 outbreak are unknown, however the 2002 and 2003 outbreaks have been identified as being caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae.
The future of the New Zealand sea lion doesn’t look good at all. I highly suspect that we’re going to lose the species within 10-20 years (if that). More needs to be done to preserve the species habitat and its current fishing grounds as well as protecting from bacterial outbreaks. Failing this the species will be extinct within 10-20 years max. I am highly doubtful here, which is very rare for me to speak about.
Thank you for reading.
Dr Jose C. Depre. PhD. MEnvSc. BSc(Hons) Botany, PhD(NeuroSci) D.V.M.
Environmental, Botanical & Human Scientist.
ENDANGERED SPECIES MONDAY | SUNDASCIURUS HIPPURUS

ENDANGERED SPECIES MONDAY | SUNDASCIURUS HIPPURUS
This Mondays (E.S.P) post - [Endangered Species watch Post] I am documenting on the horse tailed squirrel, scientifically identified as Sundasciurus hippurus. (Image: Horse tailed squirrel. Credits: Con Foley)
Listed as [near threatened] the species was first discovered back in 1831 by French Dr Étienne Geoffroy Saint-Hilaire (15 April 1772 – 19 June 1844) who was a French naturalist who established the principle of “unity of composition”. He was a colleague of Jean-Baptiste Lamarck and expanded and defended Lamarck’s evolutionary theories.
Geoffroy’s scientific views had a transcendental flavor (unlike Lamarck’s materialistic views) and were similar to those of German morphologists like Lorenz Oken. He believed in the underlying unity of organismal design, and the possibility of the transmutation of species in time, amassing evidence for his claims through research in comparative anatomy, paleontology, and embryology.
Dr Geoffroy ‘allegedly’ named the squirrel ‘the horse tailed squirrel’ because the squirrels tail resembled that of a horse tail, although even I myself find that somewhat difficult to digest, as in all due honesty the tail looks more like a bushy tail, which horses don’t really host. Horses tend to have long, slender and non-bushy tails, while others do host a type of busy but lose tail. I could be wrong?!
While as yet I cannot prove this, I do believe that Dr Geoffroy may have named the squirrel after a wild dwarf Asiatic horse endemic to South East Asia - that as yet we environmentalists have as yet to discover more about, furthermore that species of horse is likely to be extinct.
Moving on and (as explained) the horse tailed squirrel has been listed as [near threatened]. From 1996-2012 the species was placed into the category of [lower risk/least concern]. Lower risk/least concern is defined as: A taxon is Least Concern when it has been evaluated against the criteria and does not qualify for Critically Endangered, Endangered, Vulnerable or Near Threatened. Widespread and abundant taxa are included in this category.
International Animal Rescue Foundation Asian Environmental Scientists have been studying this species (among others) and can confirm from camera traps that the mammal’s populations are still declining significantly. However to what extent we’re still unsure.
As yet there have been ‘no reported extinctions’ within anyone of the species endemic countries being: Brunei Darussalam; Indonesia (Kalimantan, Sumatera); Malaysia (Peninsular Malaysia, Sabah, Sarawak) and Thailand. Since 2012 environmental fauna scientists have tried in vain to establish a mean population count, unfortunately as yet we (the organisation) and non-related organisations cannot determine a true population count.
Back in 2004 Dr’s Han and Giman pers. comm stated that the species was common, furthermore there was no evidence to prove the species was severely fragmented, or nearing endangered. The species prefers to inhabits lowland forests, however is also located in secondary forests too. Scientists reported that within these secondary forests species populations were on the decline.
Unlike your normal European squirrel the species can commonly be located at ground level foraging for food ranging from nuts, fruits, seeds and insects. Interestingly the species is diurnal (again unlike the European squirrel). Diurnal means the species will be active either during the day or night. Whereas the European squirrel is normally pretty active during the daytime, then rests during the night.
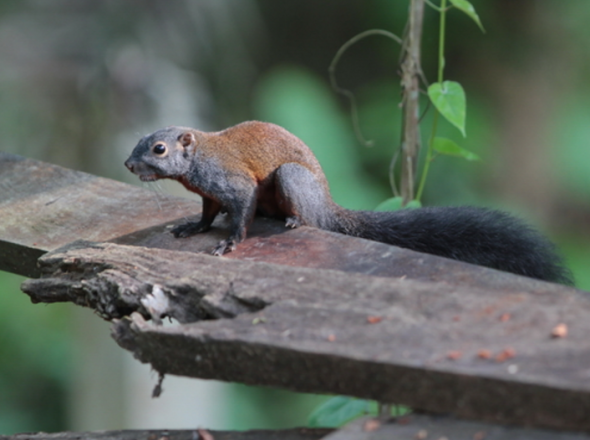

Image: Horse tailed squirrel: Photographer unknown
While the species ‘often lives within the trees’, horse tailed squirrels will spend a majority of their time at ground level. It has been suggested that one of the reasons for low densities of this species in Malaysian tropical rain forest is competition from the great variety of other arboreal vertebrates (such as birds, and especially primates) for food, especially fruits and leaves, which are among the food items preferred by squirrels.
There are by few very few threats actually known, however don’t take that as positive news. The species is threatened by habitat loss due to logging and agricultural conversion. I expect the first extinctions are likely to be witnessed within Malaysia (based on past and current research). Malaysian deforestation and palm oil plantations all pose a very high threat to the horse tailed squirrel as well as many other species of flora and fauna.
Nearly 60% of Malaysia is still covered with natural rain forest, unfortunately much of Malaysia forests are devoted to cash crop plantations, particularly oil palm and rubber, with tree crops occupying 17% of Malaysia’s land area. These are ideally suited to Malaysia’s hot, wet, and humid climate.
While many of us are aware of ‘palm oil devastation’ which is probably by far the biggest threat to a wide number of animals and plants - including the horse tailed squirrel. I would also like to point out to many non-meat and dairy consumers (I.e: Vegans), that while coconut plantations are for now considerably small. These plantations are still being developed and farmed within areas that once saw pristine green forests - now nothing more than a brown churned up heap of land growing and harvesting coconuts too.
In Malaysia, coconut is the fourth important industrial crop after oil palm, rubber and paddy in terms of total planted area. It is also one of the oldest agro-based industries. As an industry, coconut contributes very little to the overall economy of Malaysia (contribution to export earnings of about 0.08% in 2006).
Recent competition with oil palm for land has also resulted in the decline of the total area under coconut cultivation: in 2001, the area was about 151,000 ha and this has gradually decreased to the acreage of 109,185 ha in 2007. Based on the estimates given under the 9th Malaysia Plan, it is anticipated that the acreage will consolidate to around 80,000 ha by 2010. However regardless of this ‘alleged decline’ most if not all coconut plantations are farmed within forests where species such as the horse tailed squirrel is inhabiting.
The species is found in several protected areas, including Pasoh Forest Reserve. Environmentalists state the need for further comparative study on this species’ abundance, density and distribution and its relationship to forest structure or habitat quality, spatially and temporally, in hill dipterocarp forest of Malaysia is greatly needed.
For now the future of the horse tailed squirrel is uncertain. I’m doubtful the species will remain extant within Malaysia for much longer - with possible localized extinctions witnessed here soon. More research needs to be undertaken on the species, furthermore we also need to research just how much ‘pristine green forest is being converted for fruit, cereal crops, oils and plant milk crops’ rather than just palm oil. While I find palm oil agriculture incredibly concerning. Knowing that anyone of our vegan, vegetable and fruit crops is originating from areas where animals are being killed - is just as concerning too.
Thank you for reading.
Dr Jose C. Depre PhD. MEnvSc. BSc(Hons) Botany, PhD(NeuroSci) D.V.M.
Master of Environmental Botanical & Human Science.
(Environmental, Botanical & Human Scientist).
Endangered Species Monday | Potorous gilbertii - Back From The Brink Of Extinction.
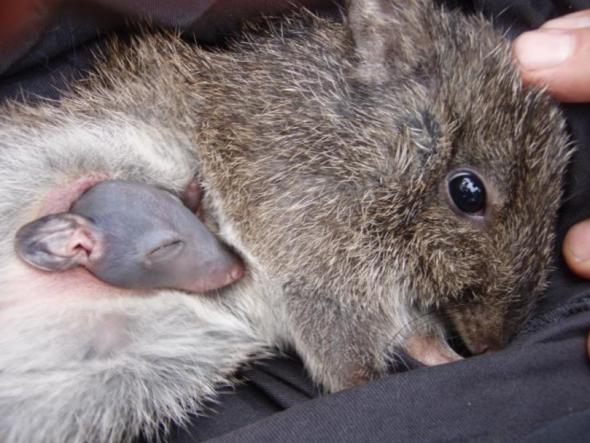

Endangered Species Monday | Potorous gilbertii
This Monday’s (ESP) post, I’ve decided to document a little more on Australia’s wildlife. This Monday I have dedicated this post to one of Australia’s most endangered marsupials. Commonly known as the Gilbert’s Potoroo. (Image Credit Parks and Wildlife Australia).
Identified as the worlds ‘rarest marsupial’, the species is scientifically known as the Potorous gilbertii. Listed as (critically endangered) the species was primarily identified back in 1841 by Dr John Gould FRS - 14 September 1804 – 3 February 1881) who was a British ornithologist and bird artist. He published a number of monographs on birds, illustrated by plates that he produced with the assistance of his wife, Elizabeth Gould, and several other artists including Edward Lear, Henry Constantine Richter, Joseph Wolf and William Matthew Hart.
Dr Gould has been considered the father of bird study in Australia and the Gould League in Australia is named after him. His identification of the birds now nicknamed “Darwin’s finches” played a role in the inception of Darwin’s theory of evolution by natural selection. Gould’s work is referenced in Charles Darwin’s book, On the Origin of Species.
Life hasn’t been at all easy for the P. gilbertii. It was only back in 2012 that conservation and environmental scientists (rediscovered) the species of which it was believed the marsupial had gone completely extinct within the wild. Endemic to Australia there is very little known in relation to when threats came about, increased and decreased. However I can state now; as small as populations are known - P. gilbertii’s populations are ‘currently stable within the wild’.
While though populations are stable, there are only thirty to forty actually known to be living within their endemic wild, so there is still a large amount of concern for the worlds most endangered marsupial. Back in early 1980’s the species had been listed as (completely extinct within the wild after studies from the 1800’s turned up nothing). Fortunately though environmental scientists went on the prowl and were not under any circumstances ready to write this species off whatsoever. They were technically looking for an animal that hadn’t been seen since the 1880’s-1990’s. Their work though eventually paid off.
“THEN CAME A BREAK THROUGH IN 1994”
Environmental scientists come 1992-1993 were ready to write the species off, call off all explorations and projects that were aimed at hopefully rediscovering the species. Fortunately though the Australian Parks and Wildlife Service persisted - and come 1994 a spotting was recorded. After so many years believing the Gilbert’s Potoroo had gone extinct, scientists discovered an extremely small population - to the joy of many. Finally there was hope, and today the species remains under full governmental protection.
Native to South-western and Western Australia the remaining populations was taken by three collectors between 1840 and 1879 in the vicinity of King George’s Sound (Albany), but exact locations are unknown. Skeletal material is common in cave deposits between Cape Leeuwin and Cape Naturaliste. Sub-fossil skeletal specimens have been located in coastal sand dunes between these localities. It is currently restricted to Mt. Gardner promontory in Two Peoples Bay Nature Reserve.
The entire population (consisting of 30-40 mature individuals) as explained above remains inhabits the Two Peoples Bay Nature Reserve of which they enjoy protection from the local parks wildlife board. While populations are identified as extremely small, mother will give birth to either 1-2 babies every year, normally its 2 babies. Like kangaroos the species has the ability to keep a second embryo in a state of diapause while the first embryo is growing. If the first baby does not go to term, a second baby starts growing right away.
Check out the Gilbert’s Potoroo Action Group by clicking this link
Diapause is considered a rare phenomena - especially in kangaroos, although its been witnessed quite a lot over the past few years by European, British and Australian Zoologists. The last diapause event (that I’m aware of) was witnessed at the Taronga Zoological Gardens in Australia. You can read the story >here.< The gestation period for Gilbert’s potoroo is unknown, but is estimated to be similar to the long-nosed potoroo at 38 days.
Since so few are alive today, much of the reproductive cycle for Gilbert’s potoroo remains unknown. However, the main breeding period is thought to be November–December with similar breeding patterns to those of the long-nosed potoroo. Scientists have tried to breed them in captivity, but recent attempts have been unsuccessful, citing diet, incompatibility, and age as possible factors that influenced the lack of reproduction. Reproduction in the wild is thought to be progressing successfully as many females found in the wild are with young.
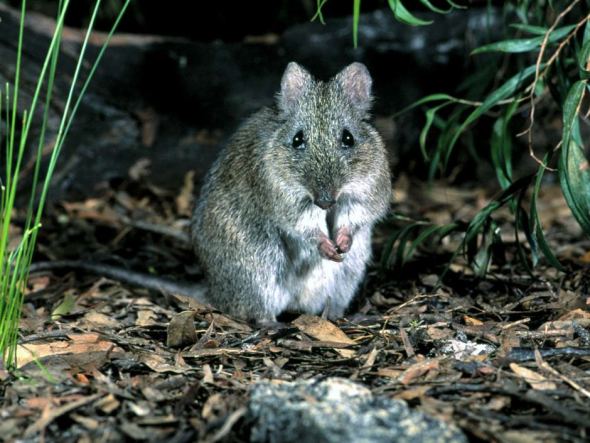

Image: Gilbert’s Potoroo. Photographer Mr Dick Walker.
In 2001, the Gilbert’s Potoroo Action Group was formed to help in the education and public awareness of the potoroo. The group also helps with raising funds for the research and captive-breeding programs for Gilbert’s potoroo. In efforts to protect the remaining population, three Gilbert’s potoroos (one male and two females) were moved to Bald Island in August 2005, where they are free from predation. Since that time, an additional four potoroos have been sent to establish a breeding colony.
THREATS
Fire is the critical threat (present and future) to this species as the Mt. Gardner population is in an area of long unburnt and extremely fire prone vegetation, and a single fire event could potentially wipe out the species (except for the few individuals in captivity and on Bald Island). This species is in the prey size range of both feral cats and foxes, and both are known to exist in the Two Peoples Bay area, thus this species is likely threatened by these predators.
Maxwell et al. (1996) states that the reasons for the decline of the species are unknown. Predation by foxes has probably been significant. Changed fire regimes may have altered habitat and/or exacerbated fox and cat predation by destroying dense cover. Gilbert’s notes record it as “the constant companion” of Quokkas, Setonix brachyurus
Unlike Gilbert’s Potoroo, the Quokka, although declining, persists over much of its pre-settlement range. The difference has not been explained. Maxwell et al. (1996) and Courtenay and Friend (2004), suggest that dieback disease caused by Phytophthora cinnamomi threatens persisting populations by eliminating plant symbionts of hypogeal, mycorrhizal fungi which are the principal food of Gilbert’s Potoroos. Altering vegetation structure and eliminating plants that provide food are direct threats to this species.
For now and based on various accounts, research and up to data documentaries. The species is still in danger. As explained above a single large and sporadic fire within the species habitat - could kill off the entire identified populations, which would be a catastrophe. While there is minimal threat from predators such as foxes and feral cats - this could change. So the need for persistent monitoring is a must. Finally we have disease, with populations being so small at around 30-40, any single disease could like fires wipe the entire species out within a single week.
Within the article above I’ve included various links for your immediate attention and information, as well as a link to the main working group that is helping (and doing all they can) to preserve the species. Furthermore I’ve included a donation link for you to donate to the Gilbert’s Potoroo Action Group. While I’m not entirely sure whether you can volunteer, there is a link on the main website below (highlighted: Volunteer Today). Just click the link, follow the instructions and, I’m confident someone will get back to you as soon as possible.
Volunteer Today
Thank you for reading, please don’t forget after reading to share this article, and hit the like button too.
Dr Jose Carlos Depre Depre PhD. MEnvSc. BSc(Hons) Botany, PhD(NeuroSci) D.V.M.
Environmental & Human Science
Endangered Species Friday | Bubalus mindorensis | Asia’s Next Extinction!

Endangered Species Friday | Bubalus mindorensis
This Friday’s (ESP) Endangered Species Post, I’m touching on a very undocumented species of buffalo that is so endangered - its extremely likely the species will go extinct within the next ten years maximum. (Photographer unidentified).
Listed as (critically endangered) the species was primarily identified back in 1888 by French born Dr Pierre Marie Heude (25 June 1836 – 3 January 1902) whom was a French Jesuit missionary and zoologist. Born at Fougères in the Department of Ille-et-Vilaine, Heude became a Jesuit in 1856 and was ordained to the priesthood in 1867. He went to China in 1868. During the following years, he devoted all his time and energy to the studies of the natural history of Eastern Asia, traveling widely in China and other parts of Eastern Asia.
Endemic to the Philippines B. mindorensis first came to the attention of environmentalists when conservationists began studying the Mindoro Water Buffalo in the early 1940’s of which they found insufficient data relating to the species. Unfortunately from 1986-1996 the species was then suddenly re-listed as (endangered).
Yet the Tamaraw had been known to overseas and native conservation scientists for over THIRTY YEARS of which today we’re now seeing a possible new extinction occurring within the Philippines. How is this possible, when scientists knew about the status of the species, why hasn’t a single zoo removed small populations to house in protective breeding captivity for later reintroduction into the same habitat, or new pastures?
Meanwhile from the year 2000 to 2008 the species was again (re-listed from endangered to critically endangered). Today the Tamaraw is now bordering complete extinction within the wild, and from what we know there is ‘possibly’ no protective captivity projects anywhere around the globe to preserve the species for future reintroduction in the wild. We do hope that we’re wrong?
From what we know based on the last census from 2013 (three years ago) there was noted within the wild only 105 mature individuals remaining. This equates to exactly 105-210 mature individuals (estimate). Within the past three years its very likely we have probably lost half of the remaining populations known, which could mean there is only 52-205 mature individuals remaining within the wild to date.
The species is not known to be fragmented, however populations are still declining. The major threat was once identified as hunting, although ‘allegedly’ isn’t known to be a threat now?. As a scientist and environmental crime CEO I find this very difficult to comprehend, due to the amount of horned ungulates which are being located throughout South East Asia. I must state though: my environmental crimes officers as yet haven’t located any Tamaraw horns or trophy heads.

Image: Tamaraw. Credits: Ruisu Fang.
Formerly, Tamaraw were found across the whole of Mindoro from sea level to the high peaks (to over 1,800 m), inhabiting open grassland or forest glades, thick bamboo-jungle, marshy river valleys, and low to mid-elevation forests. The species is currently confined to a few remote areas over 200 m, and is most often recorded in secondary forest and mixed forest/grassland.
Tamaraw are largely solitary, although females occur with offspring. Males and females occasionally associate temporarily throughout the year, which is similar to other bovines species, such as African buffalo, banteng and gaur. The solitary nature of the species is probably an adaptation to forest habitats, where large groups would prove to be a hindrance. Tamaraw feed primarily on grasses, as well as young bamboo shoots, in open grasslands, resting within tall grasses or dense forest. Although formerly diurnal, Tamaraw have become largely nocturnal due to human encroachment and disturbance.
“WE’RE LOSING THEM, AND FAST”
I do find it quite disheartening to know that the Philippines “national animal symbol” isn’t really being preserved or even protected from nearing complete extinction, although there are some projects out there that are helping to save the species from extinction, the problem is of course, as usual, funding!. One would think that a country that’s so wealthy, and a country that has introduced so many animal, wildlife and environmental laws would at least be fighting to protect the tamaraw. From what I have read and heard from the locals - they are trying their utmost hardest, unfortunately not everyone thinks the same as many kind Filipinos.
THREATS
The main current threat to the Tamaraw is habitat loss due to farming by resettled and local people, with a high human population growth rates in and around its remaining habitat. In some areas, fires set for agriculture are a threat to the species’ habitat. Cattle ranching and farming activities pose a number of threats, including the risk of diseases spreading to the Tamaraw from livestock and burning of pastures leading to a reduced number of palatable grass species.
Historically, Tamaraw were hunted for both subsistence and sport, which led to a period of drastic decline in numbers of individuals and populations. Hunting was carefully regulated prior to World War II, but since then a growing human population, logging operations, ranching, and widespread availability of firearms on Mindoro have caused a dramatic decline in numbers.
Since the 1980s, sport hunting has reduced due to a decline in the Tamaraw population, closure of nearby ranches, and more intensive patrolling and awareness activities since the establishment of the protected area. International trade in this species or its derivatives has not been reported. Although protected by law, the illegal capture and killing of this species continues.
While its currently “illegal to poach or hunt” the species “we believe some are still being poached within the Philippines to provide horns to both China and Viet Nam”. As yet there is NO EVIDENCE to back these claims up, however I.A.R.F.A environmental crimes officers have located in Viet Nam a lot of ‘counterfeit Rhinoceros horn’, which when analysed, has proven to us the horn[s] most certainly aren’t from rhinos, but from a buffalo species. So this area of the counterfeit rhino horn trade still needs intensive investigation.
The current plight of the tamaraw is not looking good, and from our own investigations and third party environmental investigations relating to the species - extinction is very likely to occur in around five to ten years (if that).
“THE TAMARAW IS ASIA’S NEXT EXTINCTION”
Thank you for reading.
Dr Jose Carlos Depre. PhD. MEnvSc. BSc(Hons) Botany, PhD(NeuroSci) D.V.M.
Environmental, Botanical & Human Scientist.
Endangered Species Monday | Heteroglaux blewitti - Extinction is now Imminent.

Endangered Species Monday | Heteroglaux blewitti - Extinction is now Imminent
This Mondays (ESP) article (Endangered Species Article), I am am documenting yet again on a species of forest owl (being the third time). This time I know for sure the species is going to go extinct - and sadly there is little that can be done to preserve the bird, although environmentalists are still battling, unfortunately it’s not looking good at all. (Image Credit: Birds of the Bible for Kids).
Listed as (critically endangered), the species was identified back in 1873 by Dr Allan Octavian Hume CB (6 June 1829 – 31 July 1912) was a civil servant, political reformer, ornithologist and botanist who worked in British India. He was one of the founders of the Indian National Congress, a political party that was later to lead in the Indian independence movement. A notable ornithologist, Dr Hume has been called “the Father of Indian Ornithology” and, by those who found him dogmatic, “the Pope of Indian ornithology.”
As an administrator of Etawah, he saw the Indian Rebellion of 1857 as a result of misgovernance and made great efforts to improve the lives of the common people. The district of Etawah was among the first to be returned to normalcy and over the next few years Dr Hume’s reforms led to the district being considered a model of development. Dr Hume rose in the ranks of the Indian Civil Service but like his father Joseph Hume, the radical MP, he was bold and outspoken in questioning British policies in India.
He rose in 1871 to the position of secretary to the Department of Revenue, Agriculture, and Commerce under Lord Mayo. His criticism of Lord Lytton however led to his removal from the Secretariat in 1879. Back in 1988 the Forest Spotted Owlet was listed by environmentalists as threatened. Unfortunately since the 1980’s habitat destruction, poaching, deforestation and gradual human population increases have skyrocketed.
“CONTRADICTIONS”
Conservationists allegedly from 1994-2012 battled hard to preserve the species of Spotted Owlet, regrettably their battles have been lost. Back in 2013 a further census was undertaken of which proved the species was nearing complete extinction within the wild. Today (2016) its incredibly likely we’ll lose the Spotted Owlet from all of its range.
Endemic only to India there is estimated to be (from the last census of 2013) a depressing total of 50-260 mature individuals remaining. The total number of “sub-populations has been identified as 2-100. Furthermore within the past ten years from 2006-2016 there has a been “ALLEGEDLY” a continuous population decrease of exactly 10%-19%. International Animal Rescue Foundation India has also reported within the past four years that “very small populations known are still decreasing”, and from records kept the species is highly likely to be extinct within the next 730 days, which is exactly two years.
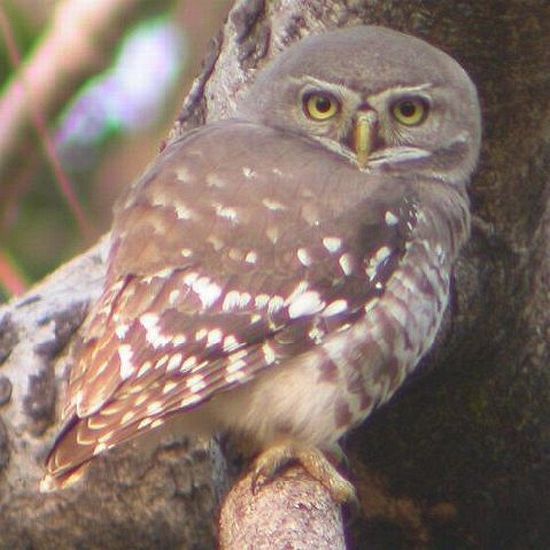

Image credit: Ashley Banwell / World Birders
The International Union for the Conservation of Nature RED LIST have ‘deliberately lied’ and ‘misinformed the general public’ stating the the bird listed hereto was extant from the years of 1988-1996. Conservationists from International Animal Rescue Foundation India in New Delhi hasn’t no reports from 1988-1996 because the bird was only re-discovered in 1997 after it was described in 1873, and it was not seen after 1884 and considered extinct until it was rediscovered 113 years later in 1997 by Pamela Rasmussen. Source: Ripley, S. D. (1976). “Reconsideration of Athene blewitti (Hume).”. J. Bombay Nat. Hist. Soc. 73: 1–4.
So whatever the IUCN are talking about is either codswallop or deliberate misinformation to garner further donations from the public?. I mean how on earth can one make this absurd lie up? Maybe the IUCN can produce documented evidence that proves the species has been active from the 1980’s to 1997? I highly doubt that they can, furthermore this lie (among many more) also brings into question any other lies the organisation “may have been publishing within the public domain” to misinform the general public?
Moving on - the population is estimated (as explained) to number 50-249 mature individuals based on the number of records from known sites, with c. 100 individuals now recorded from Melghat Tiger Reserve. This estimate is equivalent to 75-374 individuals in total, rounded here to 70-400 individuals. Given the increasing number of records and sites known within its range it may prove to be more common than previous evidence has suggested.
Trend Justification: The species faces a number of threats which in combination are suspected to be causing a decline at a rate of 10-19% over ten years.
THREATS
Listed on CITES APPENDIX I (The highest listing) meaning all hunting, poaching and any trade of this species is strictly forbidden (unless otherwise stated). Given its rarity, identification of threats is difficult. Forest in its range is being lost and degraded by illegal tree cutting for firewood and timber, and encroachment for cultivation, grazing and settlements, as well as forest fires and minor irrigation dams.
The site of its initial discovery in 1872 (Chhattisgarh) has completely been encroached by agriculture. Large areas of forest in the Yawal Wildlife Sanctuary and Yawal Forest Division as well as the Aner Wildlife Sanctuary and the Satpuda mountain ranges in Maharashtra have recently been subject to encroachment leading to habitat loss for this species.
It is likely that other forest areas where it occurs are under similarly intense pressure. Overgrazing by cattle may reduce habitat suitability. The proposed Upper Tapi Irrigation Project threatens 244 ha of prime habitat used by the species. It suffers predation from a number of native raptors, limiting productivity, and it faces competition for a limited number of nesting cavities.
The species is hunted by local people and body parts and eggs are used for local customs, such as the making of drums. Pesticides and rodenticides are used to an unknown degree within its range and may pose an additional threat.
These owls typically hunt from perches where they sit still and wait for prey. When perched they flick their tails from side to side rapidly and more excitedly when prey is being chased. It was observed in one study that nearly 60% of prey were lizards (including skinks), 15% rodents, 2% birds and the remaining invertebrates and frogs. When nesting the male hunted and fed the female at nest and the young were fed by the female.
The young fledge after 30–32 days. The peak courtship season is in January to February during which time they are very responsive to call playback with a mixture of song and territorial calls. They appear to be strongly diurnal although not very active after 10 AM, often hunting during daytime. On cold winter mornings they bask on the tops of tall trees. Filial cannibalism by males has been observed.
Thank you for reading.
Dr Jose Carlos Depre - PhD. MEnvSc. BSc(Hons) Botany, PhD(NeuroSci) D.V.M.
Environmental, Botanical & Human Scientist.
www.speakupforthevoiceless.org
Endangered Species Monday: Papilio homerus |Extinction Imminent.
Endangered Species Monday: Papilio homerus
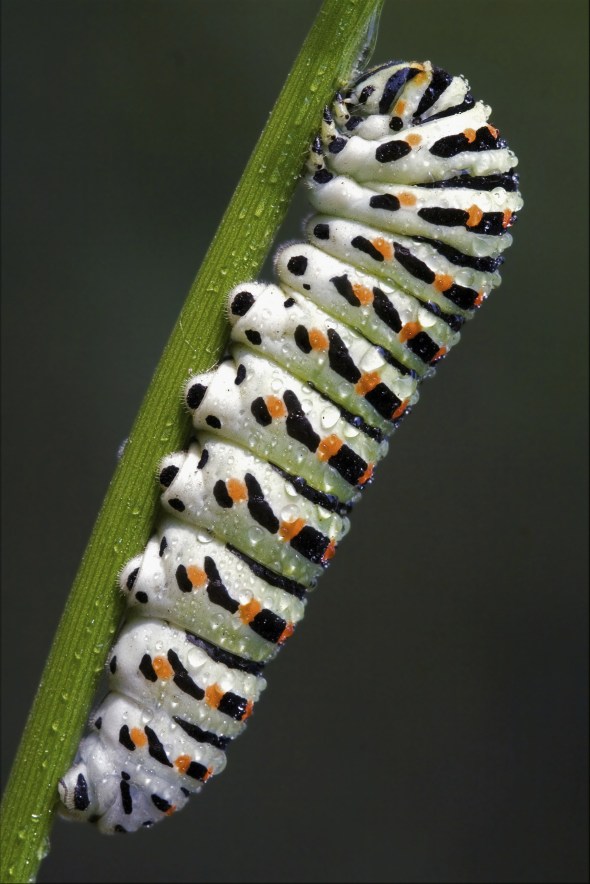
This Mondays (Endangered Species Post) E.S.P, I document again on this stunning species of swallowtail butterfly. I last documented on this amazing species of butterfly two years back, unfortunately conservation actions that were ongoing back then still don’t seem to really be improving the current status of the largest swallow tail butterfly in the Western Hemisphere. Image credited to Dr Matthew S. Lehnert.
Despite the species nearing (complete extinction) within the wild, with a possible extinction likely to occur soon, biologists and conservationists are doing all they can to improve the current status of this beautiful insect, we can only hope for the best, or that the Jamaican Government increases further protection for the species, thus earmarking funding for conservation teams on the ground to preserve our largest Western Hemisphere species of swallowtail.
Endemic to Jamaica, the species was first discovered by Professor Johan Christian Fabricius (7 January 1745 – 3 March 1808) who was a Danish zoologist, specializing in “Insecta”, which at that time included all arthropods: insects, arachnids, crustaceans and others. He was a student of Professor Carl von Linnaeus, and is considered one of the most important entomologists of the 18th century, having named nearly 10,000 species of animals, and established the basis for the modern insect classification.
Professor Johan Christian Fabricius first identified and documented on P. homerus back in 1793. The common name for this swallowtail butterfly is known as the Homerus Swallowtail, which is listed as [endangered]. Back in 1983 the species was first listed as [vulnerable]. Then from 1985-1994 the species was re-listed as [endangered]. Evidence shows from 2007 we almost lost the species, of which conservation press and media pleaded with the public for help, which did in a way increase awareness. Sadly we need more awareness on and about this butterfly.
The specie hosts a wingspan of some fifteen centimeters, the Jamaican swallowtail is said to be the second largest swallowtail of its kind on the planet, with the African swallowtail alleged to be the largest. The species can only be located within the forests of Jamaica, of which habitat loss remains the largest yet significant threat associated with this species of swallowtail butterfly, butterfly collecting is alleged to be the second largest threat. Parasitic wasps also pose a large threat to the P. homerus too.
Back in the 1930’s P. homerus was considered to be somewhat common throughout Jamaica, however, regrettably the species can now only be located within the Blue and John Crow Mountains in eastern Jamaica. Population count is [estimated to be no fewer than fifty individuals], which theoretically makes this super stunning butterfly one of the planets most threatened species of insects.
P. homerus is included on the Convention of International Trade in Endangered Species wild flora and fauna (Cites), of which (all domestic and international trade of this species is strictly illegal). Collection for display and trade is illegal, and finally destruction of the swallowtail butterflies habitat is furthermore strictly ‘forbidden’.
It has been suggested that the species could/may ‘benefit from captive breeding’, more data on this subject can be located hereto http://www.troplep.org/TLR/1-2/pdf005.pdf The caterpillars feed exclusively on Hernandia jamaicensis and H. catalpifolia; both of which also are endemic to Jamaica.
The Giant is a peaceful lover of a quiet habitat and is normally found in areas that remain undisturbed and unsettled for the most part, although due to destruction of its habitat can rarely be found at some cultivated edges of the forests on the island. P. homerus primary and favorite residence is usually the wet limestone and lower montane rain forests, however, it is now isolated to only 2 known locations on the island of Jamaica. The reproduction habits are not well known but like most of its fluttering cousins, it feeds on leaves and flowers where it also breeds and lays eggs that develop on the host plants.
P. homerus future remains critical, and its quite likely that we’re going to see yet another extinction occur sometime very soon. As much as I hate to say this, I do honesty believe that a complete wild extinction may occur in no fewer than 1-2 years (if that). However I believe based on the current populations, data, and habitat destruction, that extinction will occur sooner than that. I am not aware (as explained) of any captive breeding programmes, which if such projects are not undertaken now, we’ll see the species gone for good in under a year.
Image: P. homerus caterpillar.
Thank you for reading, and please share this article to create more awareness relating to the Jamaican swallowtail, and lets hold our breath and pray to almighty God that somewhere out there, wherever God may be, a miracle may occur.
Dr Jose C. Depre
Follow me on Twitter here: https://twitter.com/josedepre11
Follow our main Facebook page here: https://www.facebook.com/InternationalAnimalRescueFoundationAfrica/
International Animal Rescue Foundation and Environmental News & Media are looking for keen, enthusiastic, environmental and animal lovers to write alongside us. We do not pick sides, and show both sides to every-story. We like to take a more middle stance, rather than a one-sided stance. If you would like to spare an hour of your time, per week, voluntarily writing for us, or your own environmental/animal welfare related issue please contact us via the contact box below.
Please note that we have since moved our main communications website to a new and more professional server that will be hosting everything from real life news, real time projects, world stories, environmental and animal rescues and much more. International Animal Rescue Foundation is a 100% self funded environmental company. While we don’t rely on donations, you can make a donation to us via our main Anti Pet & Bush Meat Coalition organisation page.
Have a nice day.
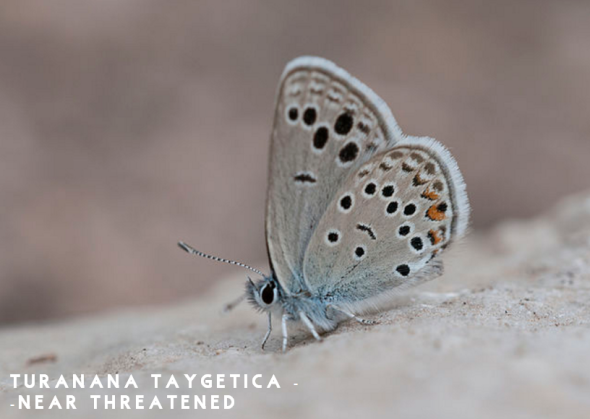
Endangered Species Monday: Turanana taygetica | Dedicated to Mme Taylor Nicole.
Endangered Species Monday: Turanana taygetica
This Mondays (ESP) Endangered Species watch Post I touch up on the T. taygetica identified by Dr Rebel back in 1902. Image credited: Zeynel Cebeci I am also dedicating this article to the early Mme Taylor Nicole who sadly passed away last week to Mother Christina Ann. Mme Ann is an unselfish animal rights activist dedicating her time, love and care to African, American and international wildlife. Mme Ann regularly undertakes animal rights projects for the Start for Animals Project, Missouri, United States.
The ‘odd spot blue butterfly’ as the species is commonly known was primarily identified by Dr Hans Rebel whom was an Austrian entomologist who specialized in Lepidoptera. Rebel, who had an early interest in natural history and butterflies, first became a lawyer. He devoted his spare time to studying Lepidoptera and established the entomological section of the Botanical and Zoological Society of Vienna.
He succeeded Alois Friedrich Rogenhofer (1831–1897) as keeper of the Lepidoptera collection of the Naturhistorisches Museum in Vienna, a post he held from 1897 to 1932. Dr Rebel enriched the collections and as a grand voyageur, made many collecting trips in Austro-Hungary and five trips in the Balkans. He directed the Department of Zoology in 1923 and was the museum’s director general in 1925.
T. taygetica is listed as [near threatened], although new data from Cites has suggested that the species may soon be re-listed as [vulnerable]. To date there is very little knowledge known about this specific species of butterfly, and the split related species identified as T. endymion.
Endemic to Greece and Turkey (Europe), populations of this stunningly beautiful insect are known to be decreasing quite rapidly. The odd-spot blue butterfly occurs in dry, calcareous places covered with low-growing shrubs, and are commonly witnessed drinking the nectar from the herb plant identified as Thyme, scientifically known as Thymus vulgaris. Males are known to leave their normal habitat for more ‘damper patches of ground’, while females commonly lay their eggs within the species of flora identified as Acantholimon karamanicum.
Image: Odd spot blue Butterfly shares its habitat with the L. thetis.
The odd spot blue butterfly shares its habitat with this utterly stunning copper-tinged Lycaena thetis (pictured above), both of which contrast one-another beautifully. Both butterflies caterpillars also share the same species of food-plant which is quite a rare behavior within the world of butterflies.
The Turanana taygetica (scientific identification) is not known to be listed on anyone of the Cites Appendices either, despite the fact the species is near threatened/vulnerable, with populations declining quite rapidly within Greece and Turkey. Furthermore populations have plummeted to a staggering 30-50% over the past two decades. To date there is no-known true or mean population count. International Animal Rescue Foundation England are though looking into this, and hope to release a more accurate report addressed too the Convention on International Trade of Endangered Species wild flora and fauna (Cites).
Major Threats
This species has a restricted distribution. It is threatened by changes in the agricultural practices (mainly abandonment), quarrying and tourist activities. In Greece it is a popular butterfly for collectors. One population in Greece was recently destroyed by the building of a road. Regarding its limited distribution it might get threatened on the longer run by climate change. As the species is not treated in the Climatic Risk Atlas, there is no information on the possible change of the climate envelope.
Image: Odd spot blue butterflies watching each others backs
The length of the forewings is 10–12 mm. The ground colour of the upperside of the wings is blue with blackish marginal borders. The underside ground colour is whitish grey. Adult males are often found watering inside the forest zone and near the presumed host-plant.
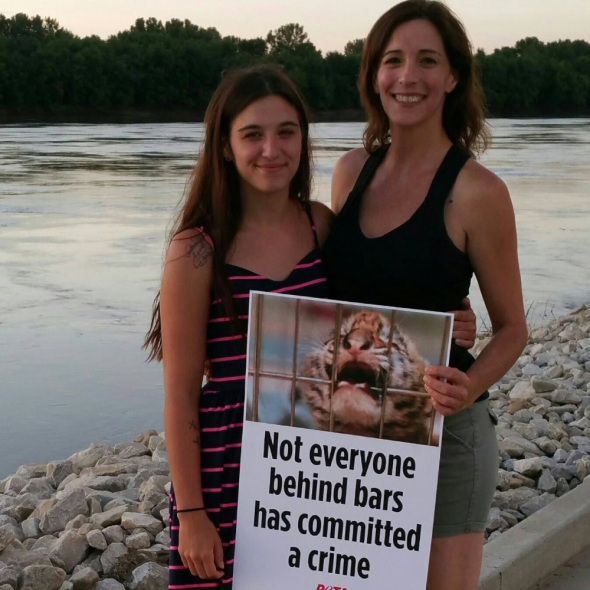
This Mondays (ESP) Endangered Species Watch post is dedicated to the early Mme Taylor Nicole whom sadly passed away last week. Herein are a few links to share, tag, and to learn to cope with sudden bereavement within the family environment.
I myself never met Mme Nicole or her mother Christina, however have spoken to Christina occasionally in relation to the work that I have undertaken in the past regarding the pet meat trade. I believe I owe a little gratitude to such a wonderful person.
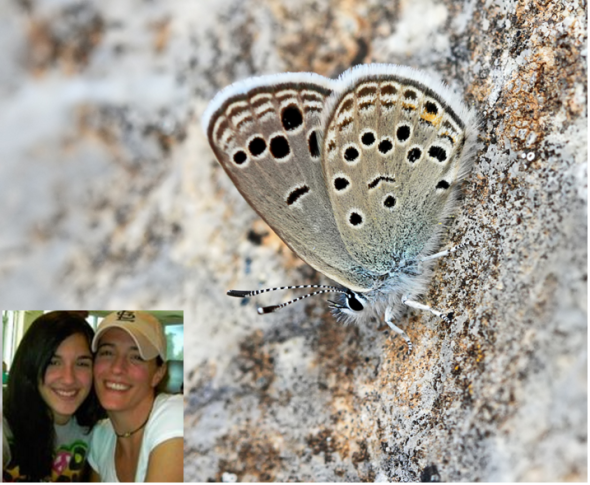
Image: Mme Christina Ann and Daughter Mme Taylor Nicole
Due to Mme Christina Ann’s daughter passing away suddenly, while Christina was on excursion on the continent of Africa, helping those within impoverished zones, and those with no voice, Mme Ann’s travel insurance would not cover the expenses of having to suddenly flying back home. Please be most kind to donate a small amount to help mother cover this charge by clicking the link hereto: https://www.gofundme.com/9nnawu5w
The link hereto https://www.compassionatefriends.org/Brochures/surviving_your_childs_suicide.aspx provides more details for parents on how to deal with sudden death. Compassionate Friends is a United States Not for Profit Organisation helping parents, relatives and friends dealing with the loss of a close loved one from suicide.
“The love between a mother and daughter is FOREVER”
Today’s Endangered Species Post (ESP) is dedicated to the Odd spot blue butterfly, Mother Christina Ann and Daughter Mme Taylor Nicole.
Thank you for reading.
Dr Jose Carlos Depre PhD. MEnvSc. BSc(Hons) Botany, PhD(NeuroSci) D.V.M.
Environmental, Botanical & Human Science
Chief Environmental Officer (CEO)
Endangered Species Monday: Papustyla pulcherrima | Special Report.
Endangered Species Monday: Papustyla pulcherrima
Manus Green Tree Snail - Very first invertebrate to be listed on the Endangered Species Act of the United States of America (2015) Endangered Species Post Special Report.
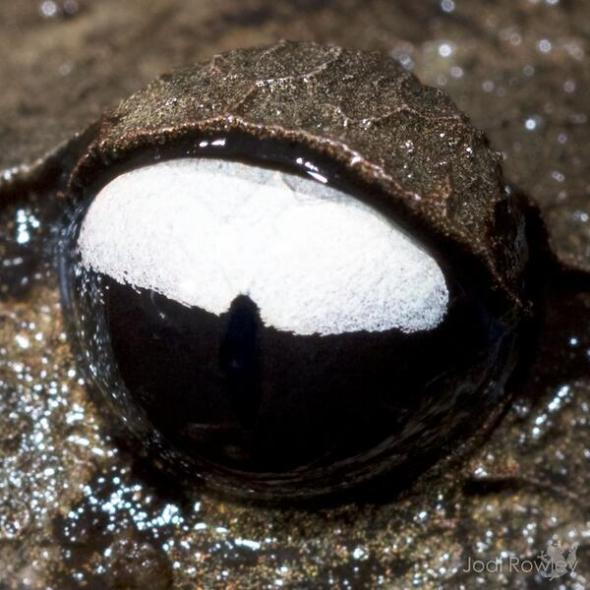
This Monday’s Endangered Species Post (ESP) I take a wee glimpse into the life of the Green Tree Snail, also commonly known by Papua New Guinea’s natives as the Manus Green Tree Snail. Image Credit: Stephen J. Richards.
Identified by Professor Rensch 1931, Rensch was born on the 21st January 1900 in Thale in Harz and died on the 4th April 1990 in Münster, (Germany), Professor Rensch was an evolutionary biologist, zoologist, ethologist, neurophysiologist and philosopher and co-founder of the synthetic theory of evolution. He was professor of Zoology and Director of the Zoological Institute at the Westphalian Wilhelms University in Münster. Together with his wife Mme Ilse Rensch he also worked in the field of Malacology and described several new species and subspecies of land snails.
The Manus Green Tree Snail is identified as Papustyla pulcherrima commonly known as the Emerald Green Snail. From 1983-1994 this particular species of snail was considered (extremely rare). Back in 1996 when scientists managed to again finally catch up with this stunning little mollusk, the species was then listed as (data deficient) of which to date there remains little information about this (rare) but beautiful snail.
P. pulcherrima is endemic to the Papa New Guinea northern island of Manus of which the species is listed as (near threatened), and has also been reported on the adjacent Los Negros Island. Environmental scientists have confirmed from villagers on the main Manus Island that the species is not located anywhere else. However there are some sketchy reports that the species “may be located on surrounding islands”, however there is no evidence to back these claims up.
Environmental scientists have confirmed for now that the species is located in only 12-13 areas of the Manus Island[s]. Further reports have confirmed that mature individuals are on the decline (which if not controlled could evidently see the species re-listed as vulnerable or endangered). The Manus Green Tree Snail is not believed to be living within fragmented zones. The species is restricted to forest and low intensity garden ‘type’ habitat. Declines have been noted within all 12-13 identified habitats on the Manus Island and adjacent Los Negros Islands. Population history is pretty much undocumented although has been shown to be slowly declining.
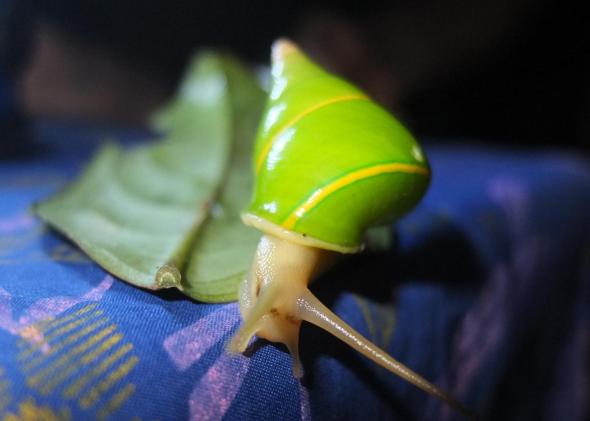
Image: Manus Green Tree Snail.
Back in 1930 when Professor Rensch identified the Manus Green Tree Snail, locals soon began collecting the species for trade thus seeing the mollusk now nearing endangered listing. Demand for the Manus Green Tree Snail has now drastically increased threatening the species furthermore. Locals continue to collect this rather unusual colored species shell for use within the jewelry trade. There are now “very serious concerns” that trade may eventually push the species into extinction.
Due to mass trade exploitation the Manus Green Tree Snail is the very first invertebrate to be listed on the Endangered Species Act of the United States of America. International trade has been controlled by export permit since 1975 under the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES) appendix II. Unfortunately this is not stopping locals from harvesting the species, and trade is still continuing despite it now a criminal offence under United States and some international laws.
“Overexploitation threatens the Manus Snail”
Market sales data collected from the Lorengau market, over a six day period suggest that annual sales at the market may approach 5,000 shells. Investigations by the Wildlife Conservation Society (WCS) reveal that large quantities of shells are still being attempted to be exported out of the country. Online searches revealed the sale of the shells, often marketed as antiques, occurring in open forums and internet market places based in New Zealand, Australia, and the United States of America (USA). International Animal Rescue Foundation has ran numerous traces online of which located yet again Ebay as being a number one trading site of the “threatened species”, please view the image below and click the image link that’ll direct you to that site.
“EBAY JAPAN IS A HOTBED FOR ILLEGAL TRADE OF THE MANUS GREEN SNAIL”

International Animal Rescue Foundation’s External Affairs Department and the Environmental Cyber Crimes Unit located many a sites trading the Manus Green Tree Snail’s shell which is illegal under some trade law, unfortunately the Ebay site listed above, located within Japan is one of many more that are trading (despite the species nearing extinction).
I.A.R.F’s Environmental Cyber Crimes Unit have since filed a complaint with Ebay, providing all the relevant data to now remove these species from their sites, however its likely to prove negative as the trader could very well state they harvested or purchased the shells before international laws were drafted. Furthermore a trace of the owner that owns this site above which is in violation of the United States and Cites laws (is located within the United States). So in regards to enforcement, breaking this link is going to be somewhat of a tough cookie. Further trade was witnessed here via what we can only believe is alleged “antiques”.
Further trade all of which is illegal has been recorded hereto - this site linked back to a Mr Rob West of 121 Henderson Road, Sheldon, Brisbane, Queensland 4157 Australia, Telephone: 610732061636. Mr West from Brisbane categorically states that he doesn’t own a shop, and is a one man band, yet clearly this link states otherwise. Further evidence revealed antique trade conducted on the Ebay site, see in the image below (illegal under United States law).
Click the image link below to view more.
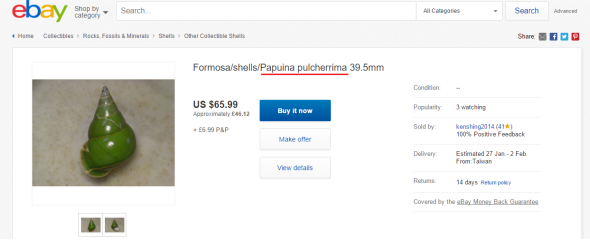
“Illegal to trade under the Endangered Species Act of the United States of America”
The environmental wildlife crimes investigation team linked to TRAFFIC and Cites stated:
It is possible the avoidance of conventional nomenclature is an attempt to avoid detection by authorities. In some cases, sellers on internet market places were based in CITES signatory countries (including: Australia, Italy, New Zealand, Singapore and USA) while others were not (e.g. Taiwan). Currently, volumes of shells on sale in such online market places appear low, suggesting that the existing controls on international trade maybe adequate. However, given that the online prices of shells were often orders of magnitude greater than market prices on Manus Island, vigilance will be required to insure that illegal international demand does not fuel a resurgence in snail collection.
Despite the massive trade on Manus Green Tree Snails online and within open Asian markets, its literally impossible to determine if this trade will eventually lead to the species being pushed into extinction. However it MUST be noted that there are currently only 12-13 identified habitats that the snail currently inhabits. And based on traces online conducted by the I.A.R.F’s External Affairs Department - trade is most certainly “out of control”, and not as Cites has reported (2012).
The shell of this species is a vivid green color, which is unusual in snails. The green color is however not within the solid, calcium carbonate part of the shell but instead it is a very thin protein layer known as the periostracum. Under the periostracum the shell is yellow.
MAJOR THREATS
The Manus Green Tree Snail is mostly threatened by habitat destruction through forest clearance: logging, plantation development (especially rubber) and to a lesser extent road developments. Increasing human population growth and an increasing cultural demand for deriving cash incomes from the land will likely see the rate of forest degradation increase in the future. Harvest occurs when trees are felled as part of traditional shifting cultivation and the snails, typically found in the canopy, suddenly become exposed. Such harvesting is not uncommon but it is likely to be of lower significance than the longer term habitat degradation caused by such agricultural practices.
While harvest for illicit international trade is occurring, the volumes are not “allegedly” thought to be large compared to historic rates, although they may approach levels seen in the legal domestic trade. However, given that the prices of shells internationally are often orders of magnitude greater than market prices on Manus Island, vigilance will be required to insure that illegal international demand does not fuel a resurgence in snail collection.
Notable deposits of gold have been found in central Manus and a mine operation will likely result in the next decade although no details of the plan have been released (as of 2014). The forests of Manus Island were badly affected by the 1997-1998 El Niño which resulted in a prolonged drought. Should climatic change result in increased rates of similar conditions this may constitute a future threat to the snail species, however, current predictions suggest that future incidence of drought in Papua New Guinea will decrease (Australian Bureau of Metrology and CSIRO 2011).
Despite the reassurances from Cites, WCS and the local wildlife organisations - evidence clearly points to large scale online trade legal and illegal. Furthermore there is no telling if shells online are antique or smuggled from the Manus Islands which is very concerning.
Manus Green Tree Snail is the first such snail to be listed on the threatened list of endangered species (USA). Research also explains to us that its likely the species will be plundered into extinction - very soon. Enjoy the video.
Thank you for reading, and please be most kind to share to create awareness and education.
Dr Jose C. Depre PhD. MEnvSc. BSc(Hons) Botany, PhD(NeuroSci) D.V.M.
Environmental & Human Science
Donate by clicking the link below:
https://www.facebook.com/Anti-Pet-and-Bush-Meat-Coalition-474749102678817/app/117708921611213/
Sign up here to our A.P.B.M.C news feed below here:
https://www.facebook.com/Anti-Pet-and-Bush-Meat-Coalition-474749102678817/app/100265896690345/
Follow me on Twitter here:
https://twitter.com/josedepre11
Sources:
IUCN, WWF, CITES, WCS, Ebay, Wikipedia, Australian Bureau of Metrology and CSIRO
Endangered Species Monday: Archaius tigris
Endangered Species Monday: Archaius tigris
This Mondays Endangered Species watch Post (ESP) I document on yet another African species of wildlife that hunting revenue is not helping to preserve. The Tiger Chameleon was identified back in 1820 by Dr Heinrich Kuhl (September 17, 1797 – September 14, 1821) was a German naturalist and zoologist. Kuhl was born in Hanau. He became assistant to Coenraad Jacob Temminck at the Leiden Rijksmuseum van Natuurlijke Historie. (Image: Credited to Henrick Bringsoe, A tigris).
In 1817 he published a monograph on bats, and in 1819 he published a survey of the parrots, Conspectus psittacorum. He also published the first monograph on the petrels, and a list of all the birds illustrated in Daubenton’s Planches Enluminées and with his friend Johan Coenraad van Hasselt (1797–1823) Beiträge zur Zoologie und vergleichenden Anatomie (“Contributions to Zoology and Comparative Anatomy”) that were published at Frankfurt-am-Main, 1820.
Commonly known as the Tiger Chameleon or Seychelles Tiger Chameleon the species is currently listed as [endangered] which is not uncommon as like many Chameleons within the Seychelles their range is shrinking by the year or being overrun by invasive botanical species.
Endemic to the Seychelles the species has been listed as endangered since 2006 of which populations trends are unknown. Much documentation often cites the species at “comparatively” low density, however one must not take this as factual until a true population count is seen. It has been alleged that for every [five hectares] there is possibly 2.07 individuals which isn’t good ‘if true’ since the island is only 455 km2.
From what we know the species remains undisturbed where there aren’t invasive Cinnamon trees identified as the Cinnamomum verum. However where C. verum is spreading the Tiger Chameleons habitat is under threat from this invasive plant. There is a negative correlation between Chameleon density and the presence of cinnamon, suggesting this invasion is detrimental to chameleon populations. Negative correlation is a relationship between two variables such that as the value of one variable increases, the other decreases.
The Tiger Chameleon’s main endemic range on the Seychelles islands is Mahé, Silhouette and Praslin. A historical record from Zanzibar (Tanzania) is erroneous. It occurs from sea level to 550 m asl, in areas of the islands that have either primary or secondary forest, or in the transformed landscape if there are trees and bushes present. Although they are currently estimated to have a restricted distribution on each island (following survey transects conducted by Dr Gerlach if anecdotal observations from transformed landscapes (e.g. degraded areas outside the areas surveyed) are valid, then the distribution would be larger than mapped at present.
To date the only [non-active] conservation actions that I am aware of are within the Vallee de Mai on Praslin which is currently not a protected national park. Fortunately the species is protected to some degree in the Morne Seychelles, Praslin and Silhouette National Parks. The primary threat within non-protected areas is as explained invasive Cinnamon which seems to be posing similar threats to both small reptilians, insects and birds on the islands and mainland Madagascar.
While the species has been in the past used as a trade animal it was alleged that there were no Cites quotes since 2000 - 2014. However from 1997 - 2013 a total of twelve live specimens were legally exported [despite the species threatened at risk status]. Cites allowed the twelve species to be exported for use within the pet trade which I myself find somewhat confusing. Two specimens were exported to Germany in 1981 with the remainder [10] sent to Spain. I am a little perplexed as to why these twelve specimens were legally exported, furthermore I have found no evidence or follow up data that would satisfy me in believing this export was even worthwhile for the species currently losing ground within their natural habitat.
From 1981 -2010 a further 98 dead specimens were legally exported for scientific zoological projects. Then in 1982 a single live specimen was legally exported with Cites permit for experimental purposes. While I cannot [again] locate any evidence or reason as to why this single specimen was exported alive - I must make it clear that Cites is sympathetic to Huntington Life Science’s and various other animal experimental laboratories. However this doesn’t prove that Cites has exported to anyone of these experimental research centers, it is merely my assumption.
Image: Archaius tigris
No other trade is reported out of the Seychelles, although re-export of specimens imported to Germany and Spain has been reported to Switzerland and South Africa, respectively (UNEP-WCMC 2014). This species is present and available in limited quantities in the European pet trade, and illegal trade and/or harvest may occur on a limited basis. ‘A’ report handed to myself from an [anonymous 2014] officer from the office of UNEP states that a population of some 2,000 specimens has been recorded [2014] however there is yet again no census historical data to back these claims/report up. I again must point out that if its proven there are no fewer than [2,000 Tiger Chameleons] remaining in the wild and, Cites is allowing export then Cites is going to come under immense pressure from International Animal Rescue Foundation Africa because exporting live animals for pet trade at such ‘alleged’ depressed populations - is neither helping the species nor supportive of conservation practices.
Threats
The main threat is habitat degradation as a result of the invasion by alien plants species, especially Cinnamomum verum, principally on Mahé and Praslin. Cinnamon is displacing other vegetation, it is present all over the islands and it is the fastest growing, heaviest seeding plant in most areas and is changing the composition of the forests. Currently it makes up 70-90% of trees in Seychelles forests, reaching >95% in some areas. For Archaius tigris, the cinnamon trees provide a normal structure of vegetation, but the invaded forests support a massively diminished insect population, somewhere in the region of 1% of normal abundance. This excludes invasive ants which are the only common invertebrates associated with cinnamon.
In addition, the cinnamon produces a denser canopy than native trees, giving deeper shade which excludes forest floor undergrowth (other than cinnamon seedlings), and this also is a factor in the reduced insect abundance. The Chameleons are found on cinnamon and in cinnamon invaded areas, as long as there is a wide diversity of other plants and a dense undergrowth. In fact, rural gardens can provide habitat for the Chameleons, because these tend to be more diversity in terms of flora, and therefore can support invertebrate fauna.
Dr Jose C. Depre
Environmental and Botanical Scientist.
















