Endangered Species Friday: Aceros nipalensis
Endangered Species Friday: Aceros nipalensis
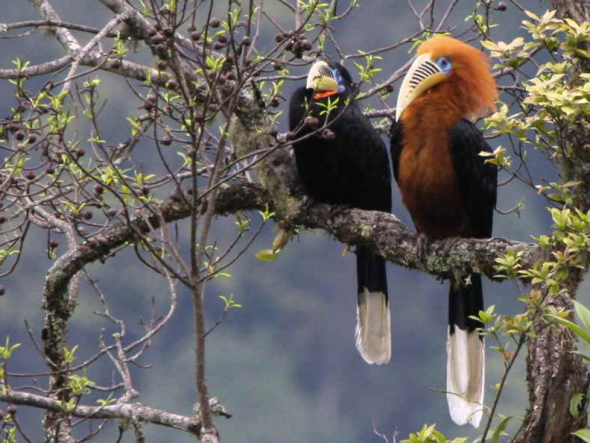
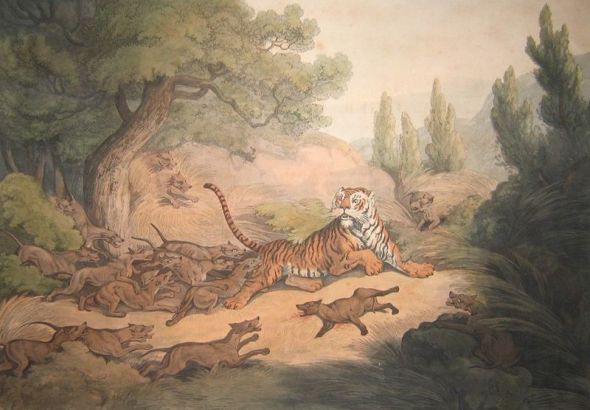
This Fridays (ESP) - Endangered Species watch Post I have chosen to document on this stunning species known commonly as the Rufous-cheeked Hornbill, because of large population declines throughout most of the birds historical range. More awareness needs to be created with regards to this particular bird specie due to their natural habitat declining and localized extinctions that have already occurred in the past decade. Furthermore extinctions are now likely to occur within Viet Nam and [west] Thiland where hunting is the primary threat to the species.. (Image credit Ian Fulton).
Identified back in 1829 by Mr Brian Houghton Hodgson (1 February 1800 or more likely 1801– 23 May 1894) was a pioneer naturalist and ethnologist working in India and Nepal where he was a British Resident. He described numerous species of birds and mammals from the Himalayas, and several birds were named after him by others such as Edward Blyth.
Listed as vulnerable the A. nipalensis is endemic to Bhutan; China; India; Lao People’s Democratic Republic; Myanmar; Thailand and Viet Nam. Unfortunately A. nipalensis has already been declared extinct locally in Nepal. Like many large birds within this region of Asia the Rufous-cheeked (or necked) Hornbill’s populations are declining quite extensively throughout their range of which deforestation and habitat degradation and, hunting is primarily to blame.
The species has been listed on Cites Appendix (I-II) of which an estimated population census count has determined there are no less than 2,500 birds but no greater than 9,999. A survey count back in 2001 by Bird-Life International concluded that from the [estimate] above the [true] population count is actually by far more lower than previously suggested, however few conservationists are now debating this due to the birds ‘alleged’ extensive range within South East Asia.
From the Bird Life International (2001) census the organisation stated there was no fewer than 1,667 mature individuals but no greater than 6,666, which is rounded to 1,500 to 7,000 mature individuals exactly. Since the last 2001 census its quite possible populations have increased and decreased to date.
A. nipalensis is known to inhabit the following ranges; Bhutan, north-east India, Myanmar, southern Yunnan and south-east Tibet, China, [west] Thailand, Laos and Viet Nam. The species has declined [drastically] and is no longer common throughout most of its known historical range. While we know the species is now regionally extinct within Nepal the next likely localized extinction may very well be within Viet Nam of which its populations have fallen to alarming rates.
Within [most] of Thailand where the species was quite common reports have sadly indicated the bird is no longer commonly seen, and like Viet Nam, Thailand could become the third county to see localized extinctions occurring too, the only known habitat within Thailand that A nipalensis occurs now is within west Thailand. To date reports have confirmed that within Bhutan A. nipalensis remains pretty much common of which Bhutan is known to the birds [largest] stronghold.
Healthy large populations have also been documented back in 2007 within Namdapha National Park, India, Nakai-Nam Theun National Biodiversity Conservation Area, central Laos and perhaps also Huai Kha Khaeng, [west Thailand], and Xishuangbanna Nature Reserve, China. Some conservationists have been led to believe that while populations are considered quite large within these strongholds that the species may very well be “more widespread than previously thought”. Meanwhile the species is known to inhabit north Myanmar, and there are recent records from West Bengal and Eaglenest Wildlife Sanctuary, Arunachal Pradesh, India.
Rufous-cheeked Hornbill commonly resides within broad-leaved forest, some reports have also indicated the species to be present within dry woodland too. Mating and nesting normally occurs from the months of March to June within large wide girth trees, the very trees that the species depends on though are being felled throughout most of the Hornbills historical range.
Image: Rufous-necked-Hornbill (Photographer unknown)
Major Threats
Its dependence on large trees for feeding and nesting makes it especially susceptible to deforestation and habitat degradation through logging, shifting cultivation and clearance for agriculture. Furthermore, viable populations require vast tracts of forest to survive, exacerbating its susceptibility to habitat fragmentation. These problems are compounded by widespread hunting and trapping for food, and trade in pets and casques. Hunting is the primary threat to the species in Arunachal, India. A report from the Wildlife Extra organisation details poaching incidents with regards to Hornbills.
Wildlife Extra stated:
The unique and intriguing breeding habits that caught Pilai Poonswad attention are central to the birds’ plight. Each hornbill pair seeks out a suitable hollow – 15 to 40 metres above the ground in the trunk or branch of a Neobalanocarpus, Dipterocarpus or Syzygium tree – in which to raise a single chick. When a suitable cavity is found, the female walls herself in, using mud supplied by her mate and regurgitated food, to hatch and rear her chick. The male feeds them for the next three months and, if he fails, both mother and chick may perish. The birds consume up to 80 different kinds of fruit, scattering the seeds over many hectares of forest. With other seed-distributing animals such as monkeys now scarce, the hornbill has become pivotal in maintaining the integrity of the forest. But the birds rarely spread the seeds of the trees in which they nest: if these disappear, the hornbills too will vanish – and the trees and plants they help propagate will soon follow.
Click the link above via the [report] to read more on this very fascinating conservationist.
My name is Dr Jose Carlos Depre, MD, B.Env.Sc, BSBio, D.V.M. I myself have been working within bird, tree kangaroo and pachydermata conservation, rescue and reporting for over fifteen years.
Within these unique, wonderful and exhilarating years I have witnessed one of my favorite species of animals [birds] declining to worrying levels that is now so concerning it has led to sleepless nights for many years. Should we continue to see such catastrophic population decreases of birds we’ll eventually witness alarming declines of plants and trees. The same applies with insects and herbivorous mammals too.
Like insects birds are incredibly important for both human and animal survival. The vast majority of all bird species rely on plants for their staple diet. On consuming fruits, leaves, flowers Etc, the very seeds within the birds diet of life needed to continue seed dispersal will be lost should all bird populations go extinct. Should this occur we selfish humans will then become the Planets seed disperses. Think about that next time you fell a tree or rip a plant up.
Dr Jose. C. Depre
Environmental and Botanical Scientist.
Thank you for reading and please share fare and wide to create as much awareness for all Hornbills as possible.
Embassy Day: For Cats and Dogs in the Horrific Meat Trade.
EMBASSY DAY: 17TH SEPTEMBER 2015 WWW.SAYNOTODOGMEAT.NET
Did you know on the 17th September 2015 from 11:00am the Australian organisation www.saynotodogmeat.net, registration 49 860 343 527 will be hosting peaceful demonstrations around the globe within nine major cities? Embassy Day forms the first (governmental) lobbying in relation to #OperationUnite 2016. Embassy Day will be the organisations second largest demo since April 4th 2015. Back in April Say No To Dog Meat made history by hosting the worlds largest anti pet meat demo in over twenty five countries.
On the 4th April 2015 the Say No To Dog Meat family hit the streets internationally in their thousands marching for dogs and cats in the horrific pet meat trade. The main April protests were non-governmental, however was a reminder that should the (eight governments) the organisation are lobbying not respond to the polite requests from the Aussie organisation. The next step would be Embassy Day, September 2015. Finally after Embassy Day, the organisation will then begin gearing up for phase two of Operation Unite 2016 that will be held October 2nd and 3rd 2016. Followed up with #OperationUnite comes the new #lovefamily campaign too.
Image: (SNTDM) supporter, #lovefamily campaign.
September 17th 2015 will see demonstrators lobbying South Korean embassies within Los Angeles, United States and Ottawa, Canada. Then in New York the Indonesian embassy, followed up with the Cambodian embassy in Seattle, United States will be demonstrated. Meanwhile within the United Kingdom the Vietnamese embassy will be peacefully protested in London, followed up with the Indian consulate in Belfast, Northern Ireland. The Nigerian embassy in Johannesburg, South Africa will follow soon after. The Thailand consulate within Perth and Philippines consulate in Brisbane, Australia will be peacefully lobbied too.
Donna Armes, campaign manager and director confirmed that all embassy consulate generals and ambassadors had been sent communications months before Embassy Day was planned. Furthermore the campaign manager stated a second electronic communication had been sent and received by embassy staff informing them about the peaceful protests, and why the organisation has been forced to lobby all nine embassies. Embassy staff, consulates and ambassadors have failed to acknowledge the Aussie organisations peaceful plans which is a little frustrating but then the organisation didn’t expect a reply anyway.
Say No To Dog Meat volunteers and directors will begin the ‘peaceful demonstrations’ with an up to date speech on current and past issues in relation to both ‘Asian and African’ dog and cat meat trade outside of each embassy. After the main speech the public can stay or depart of which the organisations volunteers and directors will then be handing into the embassies all data and petitions.
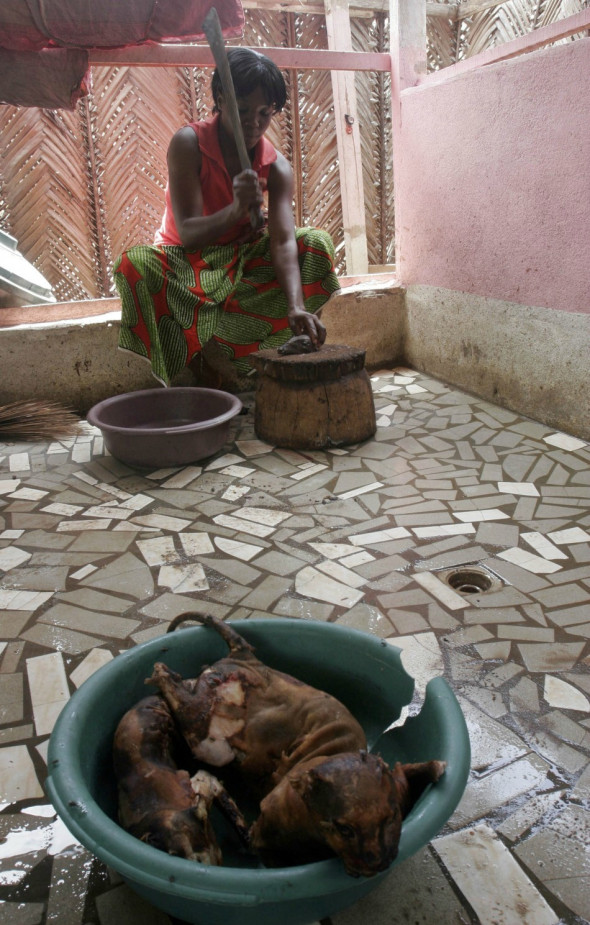
Image: Nigeria, woman prepares dog carcass for [404 joint delicacy, peppered dog soup].
Each petition contains from 10,000 to 200,000 signatures. Statistics on pet meat consumption death rates, virus and disease, regulations and violations of current standing law, predictive model data research, food hygiene violations will be handed into the consulate generals and ambassadors too. Presidential letters will also feature within the pack of which each government has a set six to eight months to respond. The organisation is not expecting an immediate or even positive response, of which OPERATION UNITE will continue to go ahead come October 2016.
For the very first time in history the Indian and Nigerian embassies will be lobbied by the organisation in relation to the Indian, Nagaland and Nigerian pet meat trades. Nigeria is the largest dog meat consuming country on the continent of Africa and third largest on the planet. Furthermore deaths from consumption of diseased or rabies infested pet meat has skyrocketed this year alone with some eighty people dead already. Meanwhile the Indian Nagaland state loses on average an estimated forty people a year via the direct consumption of rabies infested dog meat. Rabies is also on the rise in both pet meat consuming zones. India is where 85% of all human rabies deaths occurred between 1995 and 2004. Over this period there were 21404 rabies deaths a year there. Death rates for 2014 are yet to be seen.
“About 3.5 million dog bites are registered every year in India. The Government cannot give vaccine free of cost to all people. From 2006, the price of vaccine has increased…”
Despite many protests against the South Korean Bok Nal pet meat trade that began in June and ended in the first week of August. The South Korean government took no notice of expert knowledge, scientific data or petitions handed to them. Instead they allowed traders to continue the horrific disease riddled trade, and took little notice of their own laws and guidelines implemented to protect dogs and cats in meat trade. Dare we ask what the point is in introducing animal protection laws, just to allow native citizens to continue violating them?
From 2013-2015 Say No To Dog Meat has vainly lobbied the Viet Nam health minister and president Trương Tấn Sang to bring an end to the pet meat trade. On the 19th August 2014 reports issued by the (World Health Organisation) confirmed that deaths rates had increased slightly to forty (per year), however its estimated that some one hundred people die annually from rabies infection.
Despite the Aussie organisation sending more than enough scientific evidence to the Vietnamese health minister and president the trade continues. From 1995-2004 the then death rate from rabies in Viet Nam stood at some 1,550. Since 2004 the Vietnamese pet meat trade has increased. Death rates continue to increase within the country from the direct consumption of diseased pet meat, statistics from 2014 showed many of these deaths were infant related either bitten by dogs on private land or from consuming rabied infected dog and cat meat.
March 16th 2009 the Vietnamese government were handed third party data from; National Institute of Infectious and Tropical Diseases and the National Institute of Hygiene and Epidemiology in Hanoi, Viet Nam that stated; “Most Rabies deaths in Vietnam were from the direct Butchering and eating of either dog or cat meat”.
Vietnamese researchers confirmed;
“In Viet Nam, dogs with rabies have been detected in dog slaughterhouses and workers at dog slaughterhouses are vaccinated against rabies as part of the national programme for rabies control and prevention. However, the private slaughter of dogs is relatively common in the country which increases rabies infection rates”
“Vietnamese doctors already consider dog slaughtering to be a risk factor for rabies transmission, but it is important that other health care workers and policy makers, both in- and outside Vietnam, are aware of this risk factor”
Dog and cat meat trade is now finally illegal within Thailand, unfortunately this doesn’t stop traffickers from snatching dogs and transporting from Thailand into the Viet Nam. Yes the trade may indeed be illegal, but again our own investigative journalists have located street traders openly selling and smuggling unhygienic meat in rural communities.
Back in 2013 [Life With Dogs] stated; “In the past week, Cambodia, Laos, Thailand and Vietnam have signed a deal with the intention of ending the importation and sale of dogs to be used as food. This move was initiated by their governments because of the involvement of animal welfare group Asia Canine Protection Alliance. The ACPA is comprised of four notable animal groups: Animals Asia, Change for Animals Foundation, Humane Society International and Soi Dog Foundation.
We are now in 2015 and as yet [SpeakupFortheVoiceless] and [SayNoToDogMeat] have yet to witness any such decrease of trade within Cambodia, Vietnam and Laos. Trafficking and snatching of pet dogs and cats continues within Thailand feeding the trade within the Viet Nam and China. Why has it taken from 2013 to do nothing? One only has to walk the streets of Hanoi, Saigon, Hoi An and Ben Tre to witness dog meat traders more than active. On June 30 2015, police from Sakol Nakorn intercepted a truck carrying the butchered remains and carcasses of more than 100 dogs. The truck was heading for Tha Rae, [the traditional home of Thailand’s dog meat trade]. Yet trade is illegal!
Within the Philippines the government has introduced tough and stringent laws with regards to pet meat traffickers and peddlers (Please click the links to view current data from government). Say No To Dog Meat recognizes the Philippines as one of few Asiatic countries on the continent that has taken the pet meat trade seriously. Despite a law banning the killing and maltreatment of dogs (Animal Welfare Act of 1998), dog-eating and the industry that supplies it continues particularly in the northern part of the country. Back in June 23 2013, some 12 dogs were rescued in San Pedro Laguna, according to the Department of Agriculture (DA).
The Philippines government aims to eliminate the country’s dog meat trade by 2016, AKF Head and Legal Counsel Heidi Caguioa told Rappler [2014]. Eradication means no more dog meat traders and no more dog meat restaurants. Say No To Dog Meat will be lobbying the Philippines embassy within Brisbane, Australia calling on the government to strengthen the current Animal Welfare Act 1998 and Rabies Act 9482.
Finally Say No To Dog Meat volunteers will be lobbying the Indonesian embassy calling on the government to enact law and close down all known dog meat markets. The Indonesian dog meat trade is allegedly associated with the Minahasa culture of northern Sulawesi, Maluku culture and the Bataks of northern Sumatra, where dog meat is considered a festive dish, usually reserved for occasions such as weddings and Christmas. While Say No To Dog Meat and our comrades Animal Defenders Indonesia, Surabaya Tanpa Dog Meat, Bali Adoption and Rehabilitation Center would like to believe this, the trade on dog and cat meat actually occurs every day of the month.
This September 2015 please unite with Say No To Dog Meat this Embassy Day 2015. For more information please contact the organisation here via email: [email protected]
Image: Say No To Dog Meat, Team Perth.
Chief Executive Officer.
India: War on Poaching Intensifies.
India: War on Poaching intensifies.
Since early May 2012 the Indian State, Maharashtra government provided all of its rangers a shoot to kill licence directly aimed at “poachers” regardless of age, sex or religion. The shoot to kill order was given of which rangers are immune from prosecution due to high levels of Rhino, Tiger, Lion and, Elephant poaching within the country.
When International Animal Rescue Foundation India became aware of Maharashtra government’s demands they watched and waited for results of which back then were little however, since 2013 rangers have been actively involved in over one hundred and forty nine legal killings with a further eleven so far to date (13th June 2015). The number is believed to be a lot higher. Furthermore as poaching is not just confined to “animals” but also the sacred sandalwood, forestry rangers have been actively engaging sandalwood poachers and smugglers too.
April 4th 2015 forestry rangers and Police came under heavy gunfire in two separate locations within Tamil Nadu, Chittoor. Police and forestry guards tried to apprehend some twenty sandalwood poachers/smugglers of which took off into the sandalwood forests in Andhra Pradesh. The first shoot out saw some saw some nine smugglers shot dead in one area of the sandalwood forest that is unknown to us while a second saw a further eleven smugglers shot dead in what was described as a “heavy exchange” of bullets from both sides within Chittoor in Southern Andhra Pradesh. While some people have stated this action unjust we please ask you to continue to reading (to the bottom) for you to fully understand why the Police and forestry services may have took such action.
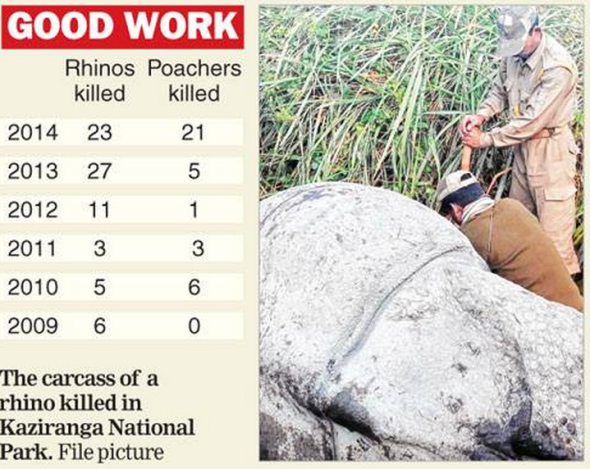
2015 has been quite a busy year thus far for forestry rangers and Police. At the start of the year, 15th January 2015 three Rhino poachers that were directly ordered to lay down their weapons aimed them at forestry guards opening fire. The incident that took place in the Kaziranga National Park, in the remote state of Assam prompted forestry guards to act quickly and professionally to preserve the sacred One Horned Rhino of which they shot the three poachers dead instantly. Fortunately no forestry guards or the Rhino were injured this time.
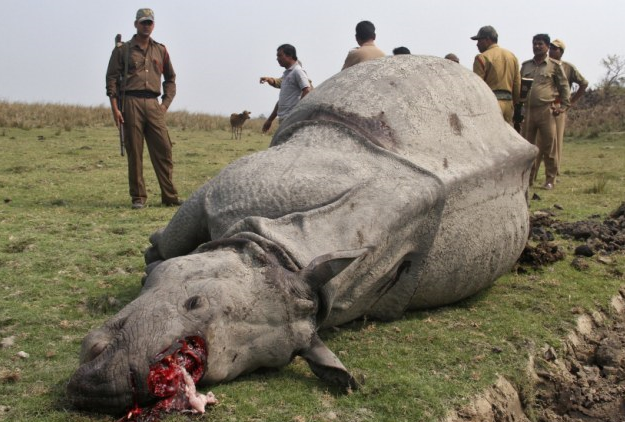
March 2015 a further three ivory poachers that were caught red handed slaughtering an Indian Rhino of which the Indian Rhino lost its life and was left in a pitiful state were shot dead immediately. We’ve included the image of that Rhino below for your information and to grasp why we and India have now had enough of this slaughter and will take the relevant steps required to support our men and women to secure our fauna and flora.
Image: Rhino killed by ivory poachers - poachers shot dead on site.
While poaching continues so does “hunting the poachers too” and so it rightfully should. International Animal Rescue Foundation India supported by its sister Africans Environmental company, began paying five “unnamed” forestry units within the shoot to kill zones larger cash incentives to hunt and take down any mammal or sandalwood poachers. The organisation has come under some fierce criticism from mainly European and American citizens most of which are devout church goers or, believe poverty is the first step that needs to be dealt with.
International Animal Rescue Foundation’s Indian Chief Executive Officer Vasvi Kanal stated “On consulting the Chief Environmental Officer back in 2012 when we were made aware of Maharashtra’s stance we knew we had to do something to support our brave men and women. After a meeting in New Delhi that following summer it was decided we should support the shoot to kill policy to send a a direct message out to poachers that you’ll no longer simply walk into our forests and parks and take what’s not rightfully yours”. Kanal went onto state “The shoot to kill policy had to be endorsed one way or the other and, I thank the Chief Environmental Officer Dr Jose Depre for wiring the funds directly to us that are now placed into the hands of these brave men and women to seek and kill poachers”.
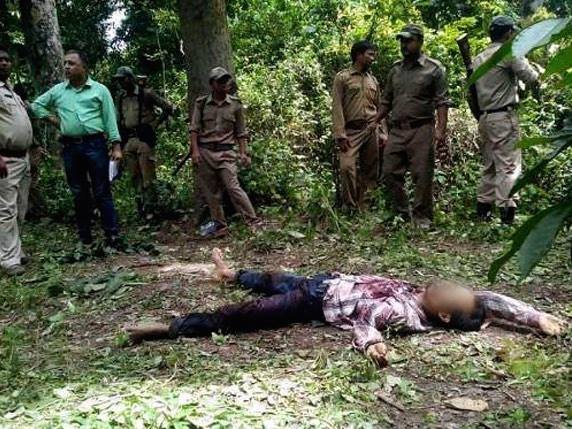
Image: Indian Rhino poacher shot dead on site.
Since the policy was enacted in 2012 in Maharashtra some seven states within India have since followed suite of Maharashtra’s firm stance and, since 2014 we’ve seen a staggering increase of poachers that have been caught trying to kill Rhino, Elephant, Tiger or illegally harvesting sandalwood shot dead on site. Furthermore many Indian press agencies have picked up the organisations support creating debate and stories on the subject that has encouraged more and more female and male citizens to come on board to protect and preserve our natural habitat and sacred heritage.
Soon after Maharashtra’s stance on “all animal and habitat poaching/destruction” took on a new positive twist, Nepal back in 2013 set their Anti Poaching Units into action - to hunt the - hunters. About 10 years ago, when the country was deeply mired in a civil war between government forces and Maoist rebels, there was hardly any focus on wildlife protection in one of Nepal’s most famous parks
The number of army monitoring posts in and around the park was reduced from 30 to seven as soldiers were shifted to anti-insurgency operations. In 2002, about 37 Rhinos were killed by poachers, triggering grave concern over the future of One-Horned Rhinos. Their numbers dropped from an estimated 612 in 2000 to less than 375 in 2005.
“According to our last rhino census in 2011 the number of Rhinos in the park has risen to more than 500,” said Kamal Jung Kunwar, a senior official at the Department of National Parks and Wildlife Conservation.
As the chief of the Anti-Poaching Operation from 2003 to 2007, Mr Kunwar played a key role in the conservation of Rhinos in Chitwan National Park. Spread over an area of more than 930 sq km, the park consists mostly of Sal trees and grasslands. Its flat lowlands are home to a variety of endangered animals like Royal Bengal Tigers, Rhinos, Leopards and Gharial Crocodiles. Crucial re-deployment: The successful conservation effort is attributed to a variety of initiatives, including tough action against poachers, enhanced intelligence and involving villagers living around the park in conservation efforts.
Image: Rhino poacher shot dead.
Meanwhile, while India strides forwards in its tough Anti Poaching operations poachers are still targeting rangers and police leaving their seriously injured on in many cases themselves killed. Deaths continue on both sides and rarely do the press and media overseas bother to print on the bravery of these men and women or, their tragic deaths.
Back in January 2014 poachers killed a female Rhino and a home guard at the Rajiv Gandhi Orang National Park, that Wednesday. Park officials said the home guard, Sushil, was killed during a gun battle with the poachers, who also managed to chop off the Rhino’s horn.
Rifles and ammunition were recovered from the spot. This is the second case of poaching at Orang which has about 100 Rhinos. The last Rhino was killed earlier in December, following which the park authorities announced a cash reward of Rs 50,000 for information on poacher Md Joynaluddin alias Junu. The authorities have also pasted Joynaluddin’s posters at several places in Darrang, Sonitpur, and Morigaon districts.
Back in 2014 a survey was undertaken on the number of rangers that are sadly murdered by poachers and killed by wild animals within the country according to the IBT. The results were shocking of which encouraged International Animal Rescue Foundation India to push more funding into local forestry units around Assam and the Ministry that supports guards financially. India loses more forest/Anti Poaching Guards than any other country on the planet.
Most of the Indian forest security men and women have been killed by poachers and wild animals, states the survey by non-profit organisation International Ranger Federation (IRF). In the past three years, as many as 72 forest rangers died in India, whereas in other countries in Asia, Africa and America, only less than 10 deaths of forest rangers have been reported, The Times of India reported, quoting the survey by IRF which strives to create awareness about forest rangers and security men.
It can be recalled that smugglers of red sanders killed several forest rangers in AP’s Tirumala forests in recent years. Notorious bandit Veerappan has also killed several forest officers and security men till a decade ago. The survey further stated that about 60 percent of the forest rangers’ killings, in the last three years, happened in Asia.
“We are extremely concerned that rangers continue to face high levels of violence and are being murdered at an alarming pace,” said IRF president Sean Willmore.
India lost 24 forest rangers in 2014, 14 in 2013 and 34 in 2012. India tops the list in the deaths of forest rangers during all three years. The report went onto state - That most rangers were killed by wild animals and poachers. Apart from animals and poachers, diseases such as dengue and malaria, forest fires and road accidents have also claimed the lives of rangers, the survey added.
In India, smugglers of wild animals and forest wealth like red sanders do not hesitate to kill rangers, if they are obstructed from committing the crime. In Seshachalam forest of Andhra Pradesh, about 200 smugglers attacked forest rangers and killed two officers in December 2013. The 200 smugglers first rained stones on the ranger sand then attacked them with batons. Rangers in India are often seen unarmed, making them vulnerable to the smugglers’ attacks.
The government of India has been dealing with wildlife poachers with an iron fist in the past one year with 30 poachers being gunned down in the Northeast alone. The number that figured in the data released by the environment ministry is the highest ever in the country. Most of the killings took place in the Kaziranga National Park, Assam. The KNP, Assam is the largest known “active poaching area” hence the largest amount of hits and is custodian to over 1000 endangered Indian one Horned Rhinos.
“The number shows our determination to eliminate wildlife traffickers and poachers. It is a big achievement of the Modi government,” environment minister Prakash Javadekar said recently.
Highly sophisticated arms were recovered from the poachers who killed Rhinos for horns smuggled to South-East Asia through porous Myanmar. Hunting down of poachers in Kharbi Anglong of Assam was undertaken by the Congress-led Assam government to save single-horn rhinos of Kaziranga and nearby areas.
Big cats at huge risk:
Wildlife in other parts of the country isn’t as lucky as the Rhinos. As many as 23 Tigers and 116 Leopards were poached in 2014 across India, with states like Uttarakhand, Maharashtra and Madhya Pradesh reporting a large number of cases.
“These are the cases that have been reported. There might have been cases where the poachers took the whole animal, without leaving a trace,” said Tito Joseph of the Wildlife Protection Society of India. Traffic, a non-government group monitoring wildlife trade, says that there has been no let down in illegal wildlife trade in India. It says the Northeast is turning into a hub of wildlife smuggling.
A report by the National Tiger Conservation Authority also indicates weak wildlife crime management in the country. It states that almost 40% of the forest guards do not have enough equipment to deal with highly organised wildlife crimes. “The states are not providing funds to modernize wildlife crime management,” a senior official said.
Concluding;
Despite some public criticism calling the organisation “dogs” and “disgusting” India’s tough stance on Anti Poaching must continue. International Animal Rescue Foundation India hopes to push a further $15,500 into the cash incentive jar to help equip rangers, police and forest guards. Furthermore the environmental company that has some one people working on the ground in New Delhi will be working with local communities in poverty stricken zones where poachers are known to originate from to help decrease poaching, improve poverty and hopefully decrease killing on both sides.
Lastly I wish to leave you with this video directed at those that believe Indian forestry guards and Anti Poaching Units are randomly picking off innocent people. Please watch the video to the end and undertake your own Google search on those brave men that sadly lost their lives fighting for animal and environmental freedom.
Thank you for reading.
Johan La Roux
Rhino Welfare Project Africa.
Endangered Species Monday: Cuon alpinus.
Endangered Species Monday - Cuon alpinus.
Dhole - Reckless and Daring.
This Monday’s endangered species article we focus on a rather undocumented species of wild dog in the family of canidae generically identified as the Cuon alpinus back in 1811 and commonly named as Asiatic wild dog, Indian wild dog or just Red dog.
The species was scientifically named by Berlin born Dr Peter Simon Pallas (22 September 1741 – 8 September 1811) was a German zoologist and botanist who worked in Russia. A number of animals were described by Pallas, and his surname is included in their common names, including: Pallas’s cat, Pallas’s long-tongued bat, Pallas’s tube-nosed bat, Pallas’s squirrel, Pallas’s leaf warbler, Pallas’s cormorant, Pallas’s fish-eagle, Pallas’s gull, Pallas’s sandgrouse, Pallas’s rosefinch, and Pallas’s grasshopper warbler. Also, he is honored in the specific epithet of scientific names of animals described by others, including: Pallas’s pika (Ochotona pallasi), Pallas’s reed bunting (Emberiza pallasi), and Pacific herring (Clupea pallasii). (Wiki).
The Dhole is currently listed as (endangered) of which its populations are still decreasing quite rampantly. Although declines are still being documented the species remains native to Bangladesh, Bhutan, Cambodia, China, India, Indonesia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Lao People’s Democratic Republic, Malaysia, Mongolia, Myanmar, Nepal, Russian Federation, Tajikistan, Thailand and finally Viet Nam.
Within central eastern Asia there still remains no confirmed reports of Dhole populations of which the species was once endemic to this range. However as the species has yet to be declared extinct within countries of eastern Asia we must continue to make public that the species may still be true to this region of south east Asia. Recent reports have stated the species was seen within Jiangxi district, south China, however, outside of this area no other confirmed sightings have been noted now for some years within the Tian-Shan Range.
Few sketchy reports have vaguely confirmed that the species was seen (2006) Qilian Shan in north-western Gansu Province. Meanwhile the Dhole still remains within Tibet of which forestry officers and locals confirm the species as “commonly viewed” which is at least a positive note despite populations declines over much of the species endemic range. North Korea was once known to hold Dholes however due to the communist states strict rules and no-go-areas its difficult to document or research on the species. If North Korea does indeed hold Dholes environmental research teams must be granted entry to secure the species from any localized extinction occurring.
South of the River Ganges, India Dholes are still very commonly viewed despite large human population increases, species displacement, human species conflict and, habitat fragmentation. Central, eastern and western India Dholes are still known to inhabit again, commonly. Research teams continue to pick the species up within north eastern India in the states of Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Meghalaya, and West Bengal too. Further reports place the species within the Ladakh area of Kashmir, which is contiguous with the Tibetan highlands in China.
In Bhutan, there have been recent press reports that Dholes have recovered from a government-initiated mass poisoning campaign in the 1970s and there have apparently been numerous recent incidents of Dholes killing livestock in the lower Kheng region. Two recent, independent, eye-witness reports identify Dholes in six protected areas in Bhutan. In some regions, Dhole predation on wild boar (Sus scrofa) may be viewed in a positive light by local people. Wild boars are known to injure and in some cases fatally wound the locals.
Reports still cannot confirm if the species is present within Bangladesh. In Indochina, Dholes probably ranged over all or almost all of Lao PDR, Cambodia, Viet Nam and Thailand, although reliable site-specific information is scarce. Present distribution is highly fragmented and large parts, particularly of Viet Nam and Thailand, are without any regular occurrence of Dholes, although they persist in a number of protected areas.
The species’ historical range probably included all or most of the Malaysian peninsula and the Indonesian islands of Sumatra and Java, but reliable information is scarce. Current distribution is poorly known but is thought to be highly fragmented. On the Malaysian peninsula, Dholes are known to occur in four sites in northern and central areas of the peninsula (from recent camera-trap surveys). On Java, Dholes appear to be most common in the protected areas at the eastern and western ends of the island. On Sumatra, very little is known, but Dholes are known to occur in major protected areas in the southern, central, and northern parts of the island (e.g., from camera trapping).. There is no reliable evidence of the presence of Dhole in Turkey.
Within some areas Dholes are known to inhabit the same areas as Tigers and Leopards however, due to increasing poaching attacks these areas are not being made public. Its quite likely though that poachers may use the Dhole as a point of interest to illegally monitor and poach Tigers and Leopards. Competition between the Dhole, Leopard and Tiger is mostly avoided due to differences in prey. Some reports have been duly noted of Dholes actually attacking Tigers causing them considerable damage and in two known cases Dhole packs have been documented as killing Tigers.
One would be led to believe that the Tiger has no real predators however, when a Dhole or Dhole pack confronts a Tiger the Tiger will on most occasions retreat up a tree or high rocky incline. Dholes are known to “mob” Tigers for a considerable time should they feel threatened or malnourished. Reports have shown that Dholes are more than able to fend off Tigers and in most cases will if threatened or in search of food maim or fatally wound the Tiger. Dholes are quite able to defend themselves too and have the canines to easily kill and take on Tigers in Tiger habitat. Interactions between the Dhole, Tiger and Leopard has been documented however very little eye accounts or video footage show such species species conflict.
One of the very earliest reports of “Indian wild dogs” attacking Tigers can be viewed below for your immediate attention and information.
Image: A Tiger Hunted by Wild Dogs (1807) by Samuel Howitt. This is one of the first illustrations of the species, featured in Thomas Williamson’s Oriental Field Sports. The depiction though is based on Williamson’s description of the animal as resembling the Indian pariah dog.
Threats
Depletion of prey base: Across almost all of Cambodia, Lao PDR, and Viet Nam, as well as within protected areas, ungulates occur at levels well below natural. All species of ungulate except muntjacs, pigs, and in some areas southern serow (Naemorhedus sumatraensis) are ecologically or fully extinct across extensive parts of the region. Only a few of the largest wildernesses support nearly intact species assemblages and even in these, the larger species (Bos spp., Cervus spp., hog deer Axis porcinus) are very rare.
This situation will likely hinder any possibility of recovery by the region’s Dhole populations, even if the other issues could be addressed. While not as depressed as in Indochina, prey levels in Indonesia also exist at levels much below carrying capacity (because of illegal hunting and habitat degradation). In protected areas in southern and central India, where Dhole numbers are stable, prey densities are high. In north-east India, prey densities are very low in protected areas with Dholes.
Habitat loss and transformation: Currently, extensive areas of natural or semi-natural vegetation remain in Lao PDR and Cambodia, some areas encompassing many hundreds of square kilometres of potential Dhole habitat. However, habitat conversion and fragmentation are proceeding apace. In Viet Nam, very few natural areas of over 50 km² remain. Habitat loss and fragmentation is a major threat to protected areas in Indonesia, particularly those on Sumatra. Habitat loss and degradation are also serious threats to Dholes in South Asia and the disappearance of Dholes from many of the forested tracts in India has been attributed in large part to loss of habitat.

Persecution: This certainly occurs in Indochina, although it is unclear how often. In Indonesia, too, it is a threat but again its significance is unknown. In India, such persecution can play a serious role in limiting local populations. Dholes living outside or on the edge of core protected areas are particularly vulnerable to human kleptoparasitism, snaring (non-selective) and direct persecution. For example, during a radio-tracking study in 2000, in the buffer zone of Kanha Tiger Reserve, central India, at least 16 out of 24 Dholes in one pack died from a sudden strychnine poisoning. In southern India, such persecution is moderate to low and often occurs indirectly when cattle graziers and others inadvertently go close to Dhole dens and disturb adults and pups, disrupting breeding and rearing. “By-catch” in snares and other traps is probably a significant threat to Dholes across Indochina at least.
Competition with other species: Apparently, free-living dogs have been seen and/or camera trapped in many parts of Indochina, but there is no evidence for existence of large populations. Undoubtedly, the main competitor for prey species in Indochina is people. There is no evidence that feral dogs are significant competitors with Dholes in Indonesia. In many parts of their range, Dholes are sympatric with Tigers and Leopards and so the potential for significant interspecific competition for prey exists, especially if the prey populations are reduced as a result of hunting by people.
Disease and pathogens: Particularly those transmitted by feral and/or domestic dogs (e.g., mange, canine distemper, parvovirus and rabies). The significance of disease is unclear in Indochina, but diseases are a significant threat in South Asia and probably in parts of Indonesia. There is no widespread exploitation for fur or other purposes, though medicinal use should be investigated in China..
Thank you for reading.
Dr Jose C. Depre
Chief Environmental and Botanical Environmentalist (CEO)
www.speakupforthevoiceless.org
www.saynotodogmeat.net
www.saynotodogmeatevents.info
www.international-animalrescue-foundation.org.uk
Licence to Kill - Welcome to the Future of Conservation.
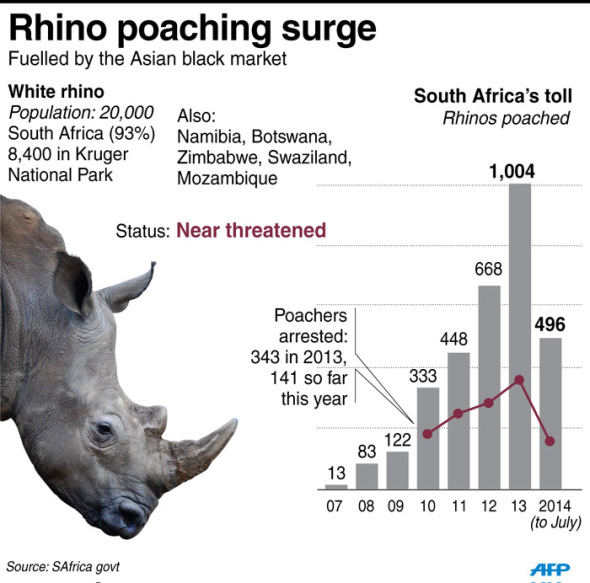
Rhino and elephant poaching on the African continent has again raged out of control this year, and as we near the end of 2014 statistical data shows that near to 1200 rhinoceros have been poached for fake medicine and thousands more elephants killed for meat and their ivory. Its expected by the end of 2014 we will have lost some 1400 rhino. Data models have also shown that by the end of 2015 we look set to loose a staggering 2,009 rhinos with thousands more elephants too.
The poaching pandemic within South Africa custodian to the worlds largest populations of Rhinoceros isn’t decreasing, nor are any forms of anti poaching actively working to at least stem the poaching rate. From 2010 we lost 333 rhinoceros of which some 165 people were arrested. 2011 poaching and arrest statistics increased again that saw some 448 rhino butchered and 282 poachers arrested. From 2012 poaching statistics shot up yet again seeing some 668 rhinoceros killed and 297 people suspected or known to have poached arrested. 2013 over 1004 rhino were slaughtered of which a further 298 people suspected of poaching were arrested.
Statistics for 2014 to date place arrest rates at some 344 with some 1100 rhinoceros bludgeoned to death to provide the Asian medicine market with fake medicinal cures and to show wealth among the rich within the countries of Viet Nam, Laos, China and Thailand.
India has had its fair share of poaching too although poachers do play Russian roulette when they wish to poach rhinos, tigers or elephants within the Indian national parks. Statistics show some 37 one horned rhinoceros poached since the start of the year which is a little over last years poaching records. Arrest rates are up that see some 45 people arrested. Deaths of poachers has increased from last years statistics that was 5 poachers killed compared to this years kill rate that stands at 27 poachers killed within the national parks of India.
Please note the Rhino poaching stats for 2014 are incorrect - to date over 30 Rhinos have since been poached.
While arrest rates are increasing within South Africa [see pic below] with regards to rhino poaching very few poachers are actually brought before the courts with many given bail just to commit the same offence again or flee back over the border from which they remain untouchable just to re-offend again.
Back in early December 2014 International Animal Rescue Foundation Africa and India launched a public debate focusing on [Shoot to Kill] - a method of wildlife preservation now active in the majority of wildlife parks in India that sends a clear and precise message to poachers - yet within South Africa is barely practiced as rangers and farm security either face red tape court and legal action or haven’t even the weapons to shoot to defend or kill poachers. Red tape or legal action is not seen within the states of India where a one shot to kill poachers has been authorized.
Kaziranga National Park hosts plenty of tigers being the worlds highest density and fleets of endangered one-horned rhinos. (More than two-thirds of the remaining population.) And, since 2010 a take-no-prisoners anti-poaching policy that allows rangers to shoot on sight. Welcome to the future of conservation.
Indian wildlife poacher Naren Pegu briefly became famous back in 2010 with regards to the Indian shoot to kill policy. Poacher Naren Pegu was shot dead on the morning of December 13th 2010 after anti poachers could take no more. Naren Pegu had decimated many rhino and tiger populations making thousands from animals parts and providing an illicit trade to South East Asia.
Time to Get Tough on Poaching;
The fall of India’s most notorious poacher.
Pegu was a member of the Mishing tribe, one of Assam’s many indigenous groups that, like their equivalents everywhere, have lost land and livelihoods. Mishing villages line the park boundary, their inhabitants pressed against it like kids at a candy-store window. If you can’t pay $50 for a jeep safari, you can’t get inside. Growing up here, Pegu learned to sneak past the border; he knew the park like his own backyard. He’d come and go undetected by the forest guards—India’s version of wildlife rangers. Poaching ran in Pegu’s family; his father was a poacher before him. In all due respects Pegu was “allegedly” poaching to provide a stable income for his family of which poachers within Africa of which some opportunistic poachers are merely doing the same. If countries such as Viet Nam, Laos and China were not using tiger, rhino and other animal parts for trade its most likely that Pegu and his family members would either have to resort to other violent crime to feed and provide income to family members or die from extreme poverty.
Most Mishing involved in the trade are content to serve as illegal guides for the bigger regional guns—sharpshooters and brokers from Nagaland—whom they lead in and out of the vast park, taking a small cut. But Naren Pegu was enterprising. He taught himself the rules of the trade, cutting deals in seedy hotels. Learned where to get black-market .303 rifles from the separatists who control the Nagaland hills. He thought big. Typically, poachers blow any money they come into, but not Pegu: he’d saved enough to invest in three vehicles, a big house, even a plot of land, where he was starting his own tea garden in some sort of psychological stab at legitimacy. While Pegu was bringing down more than $20,000 per year through poaching, his Mishing relations scrabbled to earn $200 a year in the rice paddies.
Pegu had every right to feel cocky as he and an accomplice slipped into Kaziranga on the evening of December 12, waiting out the night munching on rotis and precooked rice; a fire would have given them away. At dawn, rhinos scatter across Kaziranga to feed on the rich grasslands, and Pegu was ready. He came upon a mother rhino feeding with her calf. Got out his rifle. Shooting a rhino is like shooting a barn: when you take aim, they stop and stare, deciding whether to charge. Pegu shot the mother dead, hacked off her horn, and left the baby standing there. The park border, his village, and a payday in Nagaland were not far away.
Pegu should have been home free. He knew the landscape, and Kaziranga employs only about 500 forest guards to cover more than 300 square miles of tall grass and jungle—on foot. What were their chances of finding him? Yet, unbeknownst to Pegu, before he even fired his shot three forest guards had entered the area, searching for him. As soon as he fired, they closed on the spot. Unlike most guards in most parks in India, they were armed. And they had license to kill.
Pegu saw the guards first and opened fire. Missed. The guards took cover. As the shooting continued, one guard calmly raised his antique .303 Lee Enfield rifle to his shoulder, lined up Pegu in his sights, and blew his head off.
Pegu’s accomplice was shot in the hip by another guard. An hour later, he, too, had died “from his injuries,” according to the park’s report. Pictures from that day show the two men lying on the forest floor. The accomplice has dried black blood around his eyes, nose, and ears. Pegu’s head is split open like a watermelon.
The photography we have on Pegu and his accomplice is to graphic to include within this article however one can Google it by searching in the Punjabi language.
Licence to Kill - Smack in the Face to South Africans…
Indian rangers and forestry guards are paid an extra allowance should they locate and shoot dead poachers. While some may not believe this is actually helping to deter poachers - it actually is. India has the lowest rhino poaching rate compared with Africa of which to date over 1100 South African rhinos have been poached dead this year alone [2014]. 91.74% of voters agreed this year that a shoot to kill policy should be drawn up within South Africa. 6.46% of people stated a shoot to kill policy should not be given to rangers while 1.73% stated they were unsure. Either way this is desperate times and desperate times calls for some serious defensive measures. No mater what legislation the South African government is bringing in - its not working, This year alone as explained over one thousand rhinos have been bludgeoned to death. Something has to give and now we know poachers are feeling somewhat afraid to enter Indian National Parks the same sense of fear must apply to African poachers that wish to rid Africa of rhinos and other large fauna.
India is quite a poor country however they take wildlife crime as serious. Back in 2012 In addition, the government in Maharashtra reserved a fund of 5 million rupees ($90,000), to be used to reward people who can give information about alleged poachers. This year alone within rhino and tiger reserves alone we have seen an increase of poachers being shot dead and government handing out cash rewards. We must also reiterate that India has stated no legal action will be brought against those whom kill poachers. So why the same practice is not being adopted within South Africa is quite baffling. Are certain government ministers in on the poaching?
Indian forestry teams mostly now print on how they have shot dead poachers - rather than arrest them. Back in November 2014 yet another shoot out entailed the seventh for that month that left two rhino poachers dead and yet another message sent to the poaching community that wildlife crime will not be tolerated. Sadly since November to December we’ve lost a further seven rhinos however a four poachers out of them seven incidents were shot dead.
The two poachers were killed in an encounter with forest guards [picture below] in the Kaziranga National Park, famed for its one-horned rhinoceros. Acting on a tip-off, forest guards spotted the duo in a forest area between Diffloo and Borbhag camp in Burapahar range in Nagaon district and an encounter ensued in which the poachers were killed, a senior forest official said. The forest guards also recovered a .303 rifle, eight live cartridges, seven empty cartridges, some foodstuff and a mobile handset. The slain poachers have since been identified and their bodies have been sent for postmortem. A total of 14 poachers have been killed this year in Kaziranga National Park.
Poachers had arrived into the park in search of the endangered one horned Rhinoceros.
While some may agree hunting the poachers is extreme, its unfortunately the only [extreme] method of preserving our wildlife. Human Rights Organisations have yet to really speak out on the issue however are monitoring the increasing death rate of poachers within India. Their argument is poachers are trying to support their families financially.
Tiger and rhino populations within India are at their lowest though and while still extant their presence brings in revenue from tourism which helps to secure parks, pay wages, and decrease poverty within areas that border the main rhino and tiger parks. So in all the government is trying its hardest not only to protect its wildlife but also impoverished communities. Taking Indian wildlife poacher Naren Pegu case to hand too - while some journalists have stated he was only poaching to secure his families welfare, the vast majority of money was being used to fund his lavish lifestyle. While Naren Pegu was funding his own way of life, meanwhile on the border of Kruger National Park, South Africa “poachers that derive from poverty stricken Mozambique” are living the life of Riley. Poaching African rhino and living off the funding that is generated from the sales of the cut down horn. It truly is disgusting and a complete smack in the face to all Africans.
In Western Mozambique a now not so tiny nor impoverished village named as Kabok is now known as Mozambique’s millionaires rhino row. Poverty stricken individuals that are [untouchable] have for the past several years been wandering over the non-secure South African-Mozambique border taking down rhinoceros left right and center. While many face arrest and in some rare cases have been short dead [when a shoot out occurs] the village is growing and so too is its greed for Kruger’s Rhino horn and the wealth such horn trade brings in. Mansions and new vehicles can clearly be seen along the border to the disgust of anti poaching units and rangers alike.
In neighboring South Africa, these mansions would be called matchboxes. Most are flat-roofed, single-storeyed structures. Some look similar to RDP houses [public housing]. But what separates these homes from the usual reed houses in Kabok is that they are made from brick.
This part of Mozambique is dirt poor and the remnants of the civil war scar the landscape and the psyche of the people. War amputees wander the dirt roads. The new Kabok has been built on the horns of the hundreds of rhinos slaughtered just kilometres away in Kruger National Park. It is not alone – there are other towns spread along the border that lines Kruger National Park. They are the staging posts for rhino poachers.
There was a time when the bordering Corumane Dam supplied the community with its main source of income – fishing. Now, under the silvery full moon, fishermen ferry poachers across the lake, rowing them up the Sabie River and dropping them close to the Kruger fence. In South Africa Kabok has long had the reputation of being a haven for robbers and hijackers who take refuge across the border. Rhino economics filters through the town, the anti-poaching officer explains. Everyone gets a piece of the pie, builders are paid to construct those houses. Spaza shops have sprung up, some built with rhino money. The funeral industry, it appears, gets its cut too. Mozambique has in the past year acknowledged rhino poaching as being a crime and is actively helping to reduce communities along the border of the Kruger National Park. Sadly while the Mozambique government have acknowledged rhino poaching its still seen as a misdemeanor offence rather than a punishable offence. In all this is a smack in the face to all South Africans and our wildlife too.
Rules of Engagement - African Rangers can Face Legal Action;
Member of the SANDF Anti Poaching Unit patrolling the Kruger National Park
While the Indian Government has actively authorized in tiger and rhino reserves a shoot to kill policy of which forest guards are immune from legal action, in South Africa the rules of engagement are somewhat more cloudy of which there have been few cases where rangers and Anti Poaching Operatives have faced the wrath of their own government taking legal action against them for protecting their own wildlife. Animal rights activists must also remember when screaming and shouting at conservation units to shoot poachers - there are rules that must be obeyed at all times. These very rules are what International Animal Rescue Foundation Africa are now going to challenge in the wake of last months rhino poaching statistics and intelligence that has pinpointed South Africa as being the next country to be hit hard by elephant poachers. Activists must also remember that the vast majority of South African Anti Poaching Units are just that and not members of SANDF - South African National Defense Force that have the capability and authorization to take a shot at poachers and are 99.9% of the time armed while many Anti Poaching Units that consist of volunteers and/or rangers are lacking basic equipment or in some cases one unit only has one shooter. Least forgetting do not have the authorization to just kill poachers.
Unlike soldiers in combat, rangers pursue criminals, not enemy combatants. Rangers enforce national laws and work under specified rules, and in South Africa and elsewhere, they’re permitted to fire only in self-defense. That need for restraint can be stressful, states the now retired Major Jooste. “Here’s this [ranger], tracking poachers in 45 degrees [Celsius, or 113 degrees Fahrenheit] for many days. He gets a sighting, but he cannot shoot at the person. He must now stalk the person.” Yet the thick bush hinders tracking. When the ranger finally finds his quarry, “then he must challenge the poacher. Only when that person picks up his rifle may he defend himself. And that is taxing.”
According to Jooste, in 2013 SANParks rangers engaged in 65 firefights, but they recorded 108 sightings of poachers. “Because we’re law abiding, they get away. Because they run away into the bush, [the poachers] have the advantage.”
In addition, when a ranger in South Africa kills a poacher, the ensuing police investigation puts pressure on the ranger and his or her family—even if the case is dismissed. “You’re on the defensive all along,” Jooste says. “You know that when you sight them, in a split second you’ll have to make a decision whether to defend yourself, and there will be consequences.”
The consequences can range from legal action from the poachers themselves or from families against rangers of which is time consuming, taxing on the already impoverished country and sees rangers time taken up in courts rather than where they should be operating - in the fields.
Murder - Rangers risk their lives in the fields for pittance;
“Many who become game rangers go into it knowing that the position goes with many dangers of wild animals, dehydration, irritating insects, never mind the poachers—and most are the type of tough personality that can handle the rigors of the job,” says Kevin Bewick, head of the Anti-Poaching Intelligence Group of Southern Africa.
A recent ranger recruitment drive for Virunga yielded 1,800 applicants for 112 spots, despite the high death toll in the park during the past decade. For many, the attraction is the promise of a job, but that’s not the only, or even the main, factor.
Picture above - KWS monument in honor of Kenyan Wildlife Rangers killed on active duty.
“Being a ranger was not a choice but a calling,” says Stephen Midzi, whose base is Shangoni Post in Kruger. “I was born for this, so had to fulfill what has already been written in my book of life.” Zakouma’s Ndotoingar says simply, “I’m proud of my work.” “Not a single guy has quit,” SANParks’ Jooste notes, adding that without the rangers like Midzi, poaching statistics would be a lot worse. “Look what would happen if we weren’t here.”
Every four days in Africa and around the world a ranger or Anti Poaching Operative is killed in their line of work. Many either face a quick death, are killed by contract shooters or tortured to death. The risks are endless yet wildlife security forces still risk their lives despite pittance [very little monetary income].
As explained International Animal Rescue Foundation Africa is challenging the South African government on shooting to defend of which the organisation wants a clear and precise “shoot to kill” law introduced for wildlife rangers and Anti Poachers not just SANDF. Furthermore I.A.R.F.A. calls on the government to not only authorize rangers to adopt this method of conservation but implement a NO conviction No Legal action clause within contract. Training and more equipment to be supplied to rangers too and rangers with no firearms to be equipped without delay.
International Animal Rescue Foundation Africa doesn’t stand alone either when it comes to such licence to kill policy. Over 90% of South Africans questioned agreed that a shoot to kill policy must be enforced to send a clear and precise message to poachers and king-pins that poaching will not be tolerated within the country. Should the organisation win it could see rangers in other countries authorized a licence to kill. Kenya is one such country on the continent of which KWS - [Kenyan Wildlife Service rangers] not only face death from poachers but are also heavily outnumbered by poachers that are slaughtering rhino and elephants.
The Peoples Verdict - Licence to Kill;
Back in November International Animal Rescue Foundation Africa and India started a public debate with regards to the shoot to kill policy. The debate has thus far seen quite a prolific response from which can be read below. Quite astonishingly we counted a mere dozen or more responses that were against the shoot to kill policy, whereas over 2,000 responses based from our Indian and South African debates called for a shoot to kill policy to be implemented.
Below is a handful of extracted responses for you all to read. You can join the debate by logging onto Facebook and clicking the link below. Alternatively you vote via our poll that will be the second third poll this year of which we will collect all results and begin passing these on to the government and ministries throughout Africa.
Roxanne Cochran stated - I am from South Africa. I agree fully with this notion. If they’re willing to take a life, they should be prepared to be shot down dead too. It’s very sad to see that most rhinos here have had there horns cut down for protection. It’s not natural and it breaks my heart that we have to go to such extremes to protect these beautiful creatures.
Gavin Hastings stated - Hello all, I am a serving soldier of the SANDF; I am just back from my 3rd deployment of 6 months from the Kruger. The problem id like to address is not man power or resources, it is the government of the country of South Africa and Mozambique who are now collaborating in the elimination of the species of rhino thanks to the bureaucratic impasse given to poachers of rhinos. As a soldier I am now “arresting” poachers. It is very difficult to maintain success and morale if you capture a person and he is extradited to re-do his killing the next week. I ask the international community to pressure my government. We need legislation to properly take care of the species survival and give the killers their fair due.
George Chimbai stated - In my country Malawi rhinos were once extincted and were re-introduced in the 1990s with rhinos from South Africa, without that Malawi wouldn’t have been boasting of having the BIG FIVE in its national parks and game reserves. South Africa as a supplier of endangered species to countries where they’re facing extinction I welcome and support the SHOOT TO KILL POLICY of these poachers.
Leisa Cope stated- I agree with shoot to kill only because I don’t see any other option. The consequences of killing animals not only brutally but into extinction needs to be this intense to at least make poachers think twice about what they are doing. If poachers choose to risk their lives then this is their own decision. How sad it is when it comes to this form of action.
Berdine Helderberg stated - Definitely shoot to kill - although, a warning shot might be needed first? (Legal wise..) Poachers know what they are doing, they know it is wrong and because they know they are untouchable, they continue committing these horrible horrible crimes. They simply do not care about the intense suffering of the animals and sometimes the babies too. If you can do it to a defenseless, helpless animal, you will do it to a human being too. Lastly, they will shoot any person that comes in their way, not thinking twice.
Kerryn Hay stated - Shoot to kill definitely. I have no sympathy for poachers even if they are disadvantaged/uneducated and trying to put food on table as some of you have argued - they are making the decision to brutally murder helpless animals and every action has consequences. Kill these criminals! why are we even considering giving them rights when animals have none. If it’s working in India then we must try it because nothing South Africa has done has helped thus far and time is running out while we debate the rights of ruthless criminals! I would prefer to see them die as slowly and painfully as the animals that they murder but let’s shoot to kill and make an example of them!
Heather Smith stated - These poachers are killing innocent animals, so why shouldn’t they expect the same treatment. Rangers are shooting to save these animals lives, poachers are shooting purely for money. You have my support all the way. Shoot to kill!!! Just as the poachers do.
Debbie Olivier stated - South Africa wake up! Allow our rangers to shoot to kill - no questions asked. We have entrusted our wildlife to them - we need to trust them with this too as they are well trained.
Donny De Mars stated - Why shouldn’t there be a shoot to kill law? I mean what makes you think these poachers would not do the same for any unarmed ranger who tries to bring them in. They are no better than drug traffickers and deserve even more severe punishment! A life for a life.
Robert Cates stated - I think a shoot to kill policy/law should be enacted not only to stop dead the ones doing it now, but also to SHOW/deter others thinking about doing it. I don’t think it should be even controlled by the police department… I think it should be an open season sort of policy… that should really put the scare in them.
Whoozie Blue Marlene stated - If you were running away from a bank having stolen a rare pink diamond the. The police would shoot you down dead. Are our rhinos not rare enough, aren’t they our beautiful pink diamonds?. Telling a poacher to stop or else does not work and if it does they are back in business chop chop. If this was installed it would work simply because no one wants to die. God left these animals in our care, so far the care has not been good enough I’m afraid. Protect our Rhino please because enough is enough !!
James Kipterem stated - I agree! Because rangers too are being targeted by these evil minded poachers. Even poachers, they have the same thought of “shoot to kill” whenever they meet rangers. So shoot to kill is the only remedy to a poacher, because, why break the law which we were passing together? that, ‘it is illegal to kill wild animals’. Instead of defending the law you break it. That is very bad. Always law defenders are more than breakers.
Jannette Slabbert stated - Any bad behavior must have real and costly consequences or you will never change it prison is obviously not enough of a penalty so if loosing your life is the price then so be it. It has proven effective in India then I say put the policy in SA too.
Russell Gordon stated - Future generation will blame us for not doing enough to have prevented the total extinction of the Rhino. So to address this now to preserve the Rhino for our future generations poachers and their ring leaders need to feel pain and by that I mean the ultimate sentence, the death penalty.
Laurian Knop stated - I vote shoot to kill poachers in self defense. Poachers are always armed and chose to kill the helpless and innocent. How many rangers have lost their lives to poachers? Self defense is not murder. Protecting those unable to defend themselves is not a criminal offense. Poachers are a scourge that need to be wiped out as they facilitate a bigger epidemic of terrorism, trafficking of drugs and children and general corruption. Why is this even being second-guessed? Do those opposed have something to lose should it be implemented?
Chris Switzer stated - I believe the continuity of a species, far outweighs any issues that might be brought up with regard to a shoot to kill policy. Poaching an endangered species, many of which on the brink of extinction, should be punishable by death.
Annmarie Botelho stated - I think that south Africa should have shoot to kill laws… if it keeps going the way it is we are going to lose are elephants and rhino …. it’s such a cruel trade and there really isn’t any need for it.
Gillian Curley stated - I don’t like the shoot to kill as the poachers are just doing what they are told to do and feed their families BUT something has to be done and if we can’t get the leaders and the buyers then yes sadly I agree to shoot to kill.
Marisol Davila stated - A policy of shoot to kill poachers will be a deterrent for the poaching business. Due to lax policies wildlife numbers are in the brink of extinction. Many economies depend on the tourism that wildlife attracts. Therefore, a harsh policy against poachers and their customers is key if any country wants to strengthen it’s economic survival in the long run. The message need to be loud and clear zero tolerance to poaching, no bits or ifs allow.
To take part in the debate that International Animal Rescue Foundation Africa is running you can comment by clicking here alternatively you can also hit the poll button below and tell us what you want. Please be aware that the poll expires one week from the date of this article of which we will not run another poll.
BEFORE voting please view the video below.
Conclusion;
International Animal Rescue Foundation Africa last year created data models that indicated their worst fears regarding wildlife poaching based on poaching deaths, natural deaths, gestation, deaths of unborn fetus, decreased populations of other larger fauna such as elephants and more. Model data has already shown that South Africa’s poaching rate will continue to increase and has provided very worrying numbers of final statistics supported by defense organisations working hard to stem the flow of poaching.
While none of us wants to see, read or hear of any living creature death - We must send a more stronger and decisive message into Asia and African poaching communities, and while tackling poaching is one thing we’ve also poverty to engage that will take the temptation away from individual opportunistic poachers that kill to fend for their families. Its these very communities that Asian traffickers and king-pins target as they know they are easy prey.
Look at it simply like this. If your living with no food, no electricity, no sanitation and require health support, are barely feeding your family or even yourself and living within a country that is doing little to decrease poverty then you will snap the chance up at anyone given moment to make money. Conservation organisations and leaders of Africa and world leaders must do more to decrease poverty around wildlife parks.
Failing this Data Models have shown that the white rhino will be verging near endangerment by 2017 of which the black rhino could be extinct in under five years within the wild [despite populations increasing]. Furthermore while the continent of Africa is still custodian to thousands of elephants, elephant populations are becoming more fragmented. Yesterday I.A.R.F.A reported a massive decline in South Sudan elephant populations that now stand at some 2,500. Giraffe populations are now at some 40,000 for the entire continent of Africa.
Bottom line is should Africa lose vast swathes of her wildlife then tourism will be affected too. Tourism brings in billions for the entire continent of Africa of which Africa’s wildlife is seen as the number one tourist attraction. A large number of countries depend on tourism for the economic growth. A recent study done for DFID concluded: “While poor countries only command a minority share of the international tourism market, tourism can make a significant contribution to their economies.
Eighty percent of the world’s poor (below US$1 a day) live in 12 countries. In 11 of these, tourism is significant and/or growing. Of the 100 or so poorest countries, tourism is significant (accounting for over 2% of GDP or 5% of exports) in almost half the low income countries and almost all the lower-middle income countries.” Using these same criteria and 1996 data, tourism is “significant” in an impressive number of African countries: Benin, Botswana, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, Comoros, Djibouti, Eritrea, Ethiopia, Gambia, Ghana, Kenya, Madagascar, Mauritius, Namibia, Niger, Senegal, Sao Tome & Principe, Seychelles, Sierra Leone, South Africa, Swaziland, Tanzania, Togo, Uganda, Zimbabwe. Zambia and Mali just missed the cutoff in 1996.
According to the World Tourism Organization (WTO), Africa as a whole attracts just fewer than 4% of total world tourists and accounted for 2.0% of international tourism receipts in 1997. Of the Sub-Saharan countries, only South Africa is listed in the top forty tourism destinations worldwide, where it was 26th in 1997. The WTO calculated [1996] that Africa had just over 3% of world accommodation capacity (796,000 beds). The Africa region showed the strongest expansion in arrivals of any world region in 1997, up 8.1% over 1996. Furthermore, during the 1988-97 decade, Africa had an average annual growth of 7.2% in visitor arrivals, only slightly lower than East Asia/Pacific, which had the highest growth rate of all regions though from a much higher base than Africa. The average annual growth rate for tourist arrivals worldwide has averaged 5.0% for the past decade.
However - the number of tourists now arriving in SSA has grown over 300% since 1990, with 2012 marking a high of 33.8 million tourists who visited the region. Income generated from tourism has also climbed: Receipts from hotels, tours and other attractions in 2012 amounted to over US$36 billion and directly contributed just over 2.8% to the region’s GDP, according to the report issued by the World Bank back in 2013.
Wild animals are probably one of the first things people think of when asked about Africa. Seeing all the documentaries on television, we can only wonder and watch in awe as these mighty creatures roam the plains and jungles. Many are now protected in reserves and tourists can venture out on varying safaris to watch them in their nature habitats. What an incredible experience for both the amateur and professional photographer! Zambia holds the most natural of parks because the area is not accessible between November and March due to the waterways. Since the animals, plants, birds, and other natural elements are left alone, the area is truly spectacular when viewed each year after this rejuvenation period.
Safari rates as number four on many tour guide questionnaires when asking tourists why they wish to visit Africa. So in all if we continue to see such a vast decline in wildlife and lack of hard core enforcement we’ll most certainly see a copious decline in tourism revenue. I don’t need to explain what that will spell either.
International Animal Rescue Foundation has been challenged by only Humans Rights Christian Organisation of which stated we should not lobby or enforce a licence to kill poachers. All that can be said to the Human Rights players is that when there are no animals left, and revenue is seen as shrinking because of this then the Human Rights organisations can visit Africa and tackle more violent crime, lack of any employment, rape, murder, and more.
The time to act is now and not tomorrow. Stand by International Animal Rescue Foundation and help us enforce a shoot to kill policy within South Africa, Kenya and Tanzania.
Thanks
Board of Directors for External Affairs - Ead
Chief Executive Officer of Environmental Projects Africa - Michael L. Rooste
Chief Environmental Officer & CEO Dr Jose C Depre
Chief Environmental Registrar Europa - J. F. Williamson
External Affairs and Lead Investigation Officer - Vincent Van der spuy
You can help us by donating, to donate click the picture below that will take you to our donation application on Facebook. Alternatively you can donate to our communications site listed hereto at
www.international-animalrescue-foundation.org.uk
Auschwitz begins wherever someone looks at a slaughterhouse and thinks: they’re only animals.
“Could a being create the fifty billion galaxies, each with two hundred billion stars, then rejoice in the smell of burning goat flesh?”
Sacrificial animal slaughter for religious reasons and beliefs is cruel and barbarically outdated. Back in 2012 in Sri Lanka I was disgusted to see a mass killing ritual involving hundreds of mainly men and young boys decapitating goats and other small mammals to the sheer delight of the baying crowds. Since my visit a Sri Lankan court has allegedly banned any sacrificial killings for religious purposes as of 29 August 2013. The cruel and inhumane practice still goes on though.
A complete list of religions across the world that involve animal sacrifice would be impossible to compile, as it is still a part of a variety of indigenous practices. However, in the West, very few religions involve animal sacrifice. Animal sacrificial killings take place all over the world and documenting on them all would take a life time.
Back in 2009 in Benin I was somewhat shocked to see a practice of animal sacrifice known as Santeria, shocking and nauseating Santeria is a syncretic faith that blends traditional West African magic and practice with Caribbean tradition and Roman Catholicism. There are more than 250,000 practitioners of Santería in the world but only two Santeria temples, neither of which is in the continental United States. Thus, home sacrifice is not only the norm, but a crucial aspect of Santería, without which Santería would effectively cease to exist.
Nothing is more grotesque though than the Hindu Gadhimai animal sacrificial festival. The world’s largest practice of animal slaughter of which only four legged animals are allowed to be slaughtered under religious practice of which some 500,000 animals ranging from pigs, buffalo (being the most common), goats, chickens and even dogs are barbarically slaughtered to please the o-holy great Gadhimai. Gadhima is the name of one of the Hindu goddesses of power, though the term usually refers to the world’s biggest animal sacrifice conducted at the Gadhimai temple area in central Terai of Nepal.
Animals are sacrificed as part of the Hindu festival, with the hope that the sacrifice will lead to the fulfillment of wishes by the goddess. It is estimated that more than 250,000 animals were killed during the period of sacrifice in 2009 while 5 million people visited Gadhimai during the festival. This centuries-old tradition is observed every five years in Gadhimai premises located in the village of Bariyapur of Bara District of Nepal near the border with India.
Male domestic Asian water buffaloes (Bubalus bubalis) (locally called “PaaDa”) are the preferred species to offer to the goddess. Several other species including male goats (Boka), chickens (Kukhura), Pigeons (Parewa), Ducks (Hansh) and some rats (Moosa), are also killed.
Several animal-rights activists protest against this event before and during every Gadhimai festival. The 2009 event drew the attention of celebrities like Maneka Gandhi and Brigitte Bardot, who raised their voices against the killings. Nepal government officials say they cannot stop the centuries-old tradition, despite opposition from animal-rights activists from Nepal and India. Animal rights activists say they are not looking for the practice to end overnight.
Is Gadhimai the worst festival though known to exist? I have viewed some “cultural traditions” that are by far more barbaric and gut wrenching than the Gadhimai. For instance we have Qurbani which in Islam is the sacrifice of a livestock animal during Eid-ul-Adha. The word is related to the Hebrew qorbān “offering” and Syriac qurbānā “sacrifice”, etymologised through the cognate Arabic trilateral as “a way or means of approaching someone” or “nearness”. In Shariah Udhiyya would refer to the sacrifice of a specific animal, offered by a specific person, on specific days to seek Allah’s pleasure and reward. The word qurban appears thrice in the Quran and in once in Sura Al-Ma’ida in reference to animal sacrifice. In the other two places the Quran speaks of sacrifice in the general sense, referring to any act which may bring one closer to Allah. Other appropriate terms are Dhabihah, Udhiyah and Nahar. A fifth term Zabah refers to normal Islamic slaughter outside the days of Udhiyah.
WARNING THE FOLLOWING VIDEO MAY UPSETTING VIEWERS - 18+ IS ADVISED.
Moving back to Africa a rather unpleasant traditional sacrifice occurs every year known as Ukushwama ritual. I was invited to this festival back in 2007 by a Zulu family that I had been talking to that previous week. On seeing the actual abuse and torture the bull went through I was almost brought to throwing up my previous meal I had that night. The Ukushwama ritual is performed by the Zulu’s of which has been outright condemned by many African animal rights groups. The festival was almost banned back in 2009 however to the dismay of those that fought hard to ban this repulsive tradition it still goes on to this very day.
Back in 2009 Animal Rights Africa tried to sue Zulu King Goodwill Zwelithini on the grounds that the Ukweshwama ceremony in which a bull is killed is cruel. Activists apparently met with Zulu King Goodwill Zwelithini on the chance that the ceremony would be banned. President Jacob Zuma known for his rather unpleasant public activities that involve the wearing of animal skins to killing magnificent fauna species has also been known to attend Ukweshwama ceremony.
It is alleged the history of sacrifice begins with Adam (sws). According to the Qur’an, when two of his sons, Abel and Cain, presented their offerings to the Almighty, one of them was accepted and the other was not (27:5):‘إذْ قَرَّبَا قُرْبَاً فَتُقُبِّلَ مِنْ اَحَدِهِمَا وَ لَمْ يُتَقَبَّلْ مِنَ الَآخَر.
Adam lay with his wife Eve, and she became pregnant and gave birth to Cain. She said, ‘With the help of the LORD I have brought forth a man’. Later she gave birth to his brother Abel. Now Abel kept flocks, and Cain worked the soil. In the course of time Cain brought some of the fruits of the soil as an offering to the LORD. But Abel brought fat portions from some of the firstborn of his flock. The LORD looked with favor on Abel and his offering, but on Cain and his offering he did not look with favour. (Genesis 4:1-5).
Objective of sacrifice;
The objective of sacrifice is to express gratitude to the Almighty. When we offer our life symbolically to the Almighty by offering the sacrifice of an animal, we are in fact expressing our gratitude on the guidance of submission which was expressed by Abraham (sws) by sacrificing his only son. On this occasion, the words uttered to declare the exaltedness and oneness of the Almighty are done so for this very objective. The Qur’an has explained this directive in the following words:
لَن يَنَالَ اللَّهَ لُحُومُهَا وَلَا دِمَاؤُهَا وَلَكِن يَنَالُهُ التَّقْوَى مِنكُمْ كَذَلِكَ سَخَّرَهَا لَكُمْ لِتُكَبِّرُوا اللَّهَ عَلَى مَا هَدَاكُمْ وَبَشِّرِ الْمُحْسِنِينَ (37:22)
The flesh and blood [of your sacrificed animals] does not reach God; it is only your piety that reaches Him. Thus has He subjected them to your service so that you may give glory to God for guiding you. [This is the way of the righteous] and [O Prophet!] give glad tidings to these righteous. (22:37).
WARNING THE FOLLOWING VIDEO DEPICTS HORRIFIC LEGAL ANIMAL ABUSE - VIEWERS ARE ADVISED TO PROCEED WITH CAUTION - FOOTAGE MAY BE UPSETTING.
The Shari‘ah regarding Animal Sacrifice;
The Shari‘ah regarding animal sacrifice that has reached us through the consensus and perpetual practice of the Ummah can be stated thus;
All four legged animals which are cattle can be sacrificed.
Sacrificed animals should not be flawed and should be of appropriate age.
The time of animal sacrifice begins after offering the ‘Id prayer on the 10th of Dhu Al-Hajj (Yawm Al-Nahr)
The days fixed for animal sacrifice are the same as have been appointed for the stay at Mina once the pilgrims return from Muzdalifah. In Surah Hajj, the words ‘أَيَّامٍ مَّعْلُومَاتٍ (some appointed days (22:28)) allude to these very days. In religious parlance, they are called ‘The Days of Tashriq’. Besides animal sacrifice in these days, one is also required to declare the ‘Takbir’ at the end of each congregational prayer. Being an absolute directive, the words of the ‘Takbir’ have not been fixed.
The meat of sacrificed animals can also be eaten without any hesitation by those have had them slaughtered and can also be used to feed others. The words: ‘فَكُلُوا مِنْهَا وَأَطْعِمُوا الْقَانِعَ الْمُعْتَرَّ’ (So eat from it your selves and also feed those who are content and those who ask (22:37)) explicitly point to this conclusion.
Picture depicts Russian Muslims sacrificing cattle.
This is the Shari‘ah of animal sacrifice. The Prophet (sws) has also explained some of its aspects:
i. Animals should be sacrificed in all circumstances after the ‘Id prayer. It will not be regarded as the sacrifice of ‘Id if it is offered before the ‘Id prayer; it will be a mere animal sacrifice that one may offer to eat meet.
ii. The appropriate age for a sacrificed sheep or goat is at least one year, for that of a cow, it is at least two years and for camels, male or female, it is at least five years. If these animals are not available, a ram can be sacrificed. It will suffice even if it is six months old.
iii. More than one people can share the sacrifice of camels and cows. These shareholders can even go up to seven. There are some narratives which mention that at one instance in the presence of the Prophet (sws), ten people shared one camel for sacrifice and he did not stop them.
iv. Animal sacrifice can also be offered as an optional act of worship other than on ‘Id. Consequently, when people asked about the ‘Aqiqah, the Prophet (sws) replied: ‘Anyone who wants to offer an animal for sacrifice on the birth of a child can do so.
So just because the Holy Qur’an and Bible state that animal sacrifice is accepted does it give one the right to then brutally slaughter any four legged animals? No it doesn’t, and this brutal practice must end as the torture involved in such culturally accepted traditions is out dated, extreme, abusive and totally immoral. Least forgetting the pain these animals go through is no different to that of any human abusing illegally any animal within the western world. Such abuse would see the perpetrators thrown into prison or given a hefty fine. Abuse is abuse no matter what you call it or how it’s practiced.
WARNING THE FOLLOWING DOCUMENTARY DEPICTS LEGAL ANIMAL ABUSE - VIEWERS MAY FIND DISTURBING.
Recently within the Animal Rights Community camels have been displayed brutalised in Islamic traditional practices. There are 21 references to camels in the first books of the Bible, and now we know they are all made up. So if they are all made up – meaning such practices are indeed nothing more than a hoax then surely governments locally and internationally that allow such slaughter to continue must now begin to end such horrific animal torture.
Some of them are quite startlingly verisimilitudinous, such as the story of Abraham’s servant finding a wife for Isaac in Genesis 24: “Then the servant left, taking with him 10 of his master’s camels loaded with all kinds of good things from his master. He set out for Aram Naharaim and made his way to the town of Nahor. He made the camels kneel down near the well outside the town; it was towards evening, the time the women go out to draw water.”
But these camels are made up, all 10 of them. Two Israeli archaeozoologists have sifted through a site just north of modern Eilat looking for camel bones, which can be dated by radio carbon.
None of the domesticated camel bones they found date from earlier than around 930BC – about 1,500 years after the stories of the patriarchs in Genesis are supposed to have taken place. Whoever put the camels into the story of Abraham and Isaac might as well have improved the story of Little Red Riding Hood by having her ride up to Granny’s in an SUV.
How can you tell whether a camel skeleton is from a wild or tamed animal? You look at the leg bones, and if they are thickened this shows they have been carrying unnaturally heavy loads, so they must have been domesticated. If you have a graveyard of camels, you can also see what proportion are males, and which are preferred for human uses because they can carry more.
All these considerations make it clear that camels were not domesticated anywhere in the region before 1000BC. The entire “cultural tradition is based upon a mocked lie”. So now we know this tradition is most certainly complete rancid nonsense of which has been scientifically proven is it right to state that God in both Christianity, Islamic and other faiths is not real? I will leave you to agree or disagree.
Lidar Sapir-Hen and Erez Ben-Yosef, the scientists who carried out the research, point out that the domestication of camels was hugely important economically, because they made trade possible over much larger regions of the Arabian Peninsula. But that is not what has provoked excitement about their claim.
Obviously it has upset fundamentalists. Everyone else has known for decades that there is even less evidence for the historical truth of the Old Testament than there is for that of the Qur’an. But the peculiarly mealy-mouthed nature of the quotes they gave the New York Times (which is not much concerned with the feelings of Christian fundamentalists) shows where the real problem is.
The history recounted in the Bible is a huge part of the mythology of modern Zionism. The idea of a promised land is based on narratives that assert with complete confidence stories that never actually happened. There are of course other ways to argue for the Zionist project, and still further arguments about the right of Israelis to live within secure boundaries now that the country exists. But although those stand logically independent of the histories invented – as far as we can tell – in Babylonian captivity during the sixth century BC, they make little emotional sense without the history. And it is emotions that drive politics.
FACT - Sacrifice, commonly known as Qurbani, means slaughter of an animal in the name of Allah on the 10th, 11th or 12th of the Islamic month of Zil Hijjah. FALSE – In the name of Allah (God) all religious stories surrounding such animal sacrificial events are non-factual.
Animals used and not preferred for sacrifice -
Animals NOT to be used in sacrificial rituals.
- Castrated four legged animals are the most preferred for animal sacrifice.
- Sheep aged six months to a year, but do not resemble a year old sheep
- Sheep a day under six months are not allowed
- Goat that is a day under one year. Cow, ox or buffalo a day under two years. Camel a day under five years
- Undomesticated, wild animals e.g. wild bull
- Any other animal beside domesticated goat, sheep, cattle and camel is not allowed for sacrifice?
- A blind animal or a sunken eye or an animal with its eye sticking out
- A cross eyed animal
- A frail weak emaciated animal
- An animal born without ears
- An animal with more than one-third of its ear cut off
- An animal that does not have any teeth and is unable to graze. However if it is able to graze it will suffice for sacrifice.
- An animal with the horns broken at the root and the brain is visible
- An animal that walks on three legs and does not take support from the lame leg. However if it takes support from the lame leg, it will suffice for sacrifice
- An animal with skin disease such as scabies or mange
- An animal that is deeply wounded
- An animal with cut teats or dried teats
- A cut-nosed animal
- An animal that is hermaphrodite (both sexual organs exist)
- An animal with damaged udders
- More than one-third of the tail is cut off
Animals acceptable for sacrifice
- An animal which has two-third vision
- An animal with a slit ear
- An animal born with no horns, or its horns are broken at any point above the skin/ wool
- A barren animal
- An animals that gets injured during the actual slaughter process is acceptable for sacrifice. It is important to ensure that an injured animal be slaughtered very quickly since the injury can cause infection rendering the animal not fit for consumption
- An animal with two-third of the tail intact
Animal abuse;
Back in 2009 a study challenged whether animals suffered more pain within sacrificial slaughter practices to that of (animals killed in slaughter houses). There has long been tension between animal activists and religious adherents over the sacrificing of live animals. Jewish and Muslim leaders have long argued that the sacrifices are not any more painful than what occurs in slaughter houses.
WARNING THE FOLLOWING VIDEO known as Qurbani, means slaughter of an animal in the name of Allah. THE VIDEO DEPICTS LEGAL ANIMAL SLAUGHTER/ABUSE - PROCEED WITH CAUTION.
Animal protection laws in the UK required the stunning of animals before slaughter but exempt live religious sacrifices. Both Islamic halal and Jewish kashrut law require that animals are slaughtered by having their throats cut. The animal must be alive to allow blood to drain freely — a relatively slow death for the animal. Conversely, the Sikh ritual – chatka – is a fast death caused by a sword. It has been alleged that the Jewish slaughter of animals via sacrificial killing has been stopped. This is not as factual as made out to be though.
WARNING THE FOLLOWING VIDEO DEPICTS GRAPHIC LEGAL ANIMAL CRUELTY.
UK law requires that all livestock be stunned prior to slaughter – with the exception of those animals intended for consumption by members of certain religions. Islamic halal and Jewish kashrut law require that animals are slaughtered by having their throat cut – a relatively slow means of death. The Sikh ritual – chatka – is much quicker when done correctly, involving a clean sword strike to the neck. A practitioner of ritual slaughter say the animal must be alive to facilitate the draining of blood – and that throat slitting is humane.
But the new research suggests otherwise. Dr Craig Johnson and his colleagues at New Zealand’s Massey University reproduced the Jewish and Islamic methods of slaughter in calves. The calves were first anaesthetised so although their pain responses could be detected, they wouldn’t actually feel anything. They were then subjected to a neck incision. A pain response was detected for up to two minutes following the cut, although calves normally fall unconscious after 10 to 30 seconds.
Johnson told the New Scientist he thought this work was “the best evidence yet that [ritual slaughter] is painful”. However, he observed that the religious community “is adamant animals don’t experience any pain so the results might surprise them”.
The findings have earned Johnson the inaugural Humane Slaughter Award from the Humane Slaughter Association. Dr James Kirkwood, the charity’s chief executive, said: “This work provides significant support for the value of stunning animals prior to slaughter to prevent pain and distress.”
Adam Rutherford, an editor of Nature, wrote on the Guardian website: “It suggests that the anachronism of slaughter without stunning has no place in the modern world and should be outlawed. This special indulgence to religious practices should be replaced with the evidence-based approaches to which the rest of us are subject.”
Some European countries, such as Sweden, require all animals to be stunned before slaughter with no exception for religions. But such a ban in Britain would be hugely controversial – and would draw inevitable comparisons with the ban on kashrut enacted by Nazi Germany in 1933.
Sacrificial slaughter elsewhere in the world;
Before (anyone) starts condemning the Far East we must also look at ourselves. Back in 2011 in the United States of America (USA) Massachusetts William Camacho was arrested and charged under the animal welfare act for practicing sacrificial animal killings. He stated that the closure of his shop by city officials and police was a “violation of his Afro-Caribbean” belief surrounding the sacrificial slaughter practice known to the “Palo religion”.
Chickens, pigeons and roosters – including one dead bird – were found in the basement of Bad Boyz Cutz, surrounded by religious paraphernalia.The owner of the barbershop, William Camacho, told officials that the birds were for animal sacrifices and claims that closing his shop amounted to religious discrimination.
The animals were found in an inspection of the building by New Bedford Animal Control following an anonymous tip complaining of loud poultry-type sounds coming from the building. The birds — three chickens, two pigeons and four roosters — were penned in wire cages and a cardboard box. They were found in a room with an ornate alter with candles and statues near a wall illustrated with hand-drawn religious symbols.
No cutting implements or evidence of violence was found in the room, Scott Langley, mayor of New Bedford, told ABCNews.com Officials initially thought the animals were being kept as a cock fighting ring, but Camacho, 41, said they were being to be used for animal sacrifice as part of his religion, which incorporates elements of Afro-Caribbean rituals.
“It’s called Palo Mayombe . It’s actually working with the dead and working with the spirits. We use the roosters to sacrifice so that the spirits can eat. That’s the way they eat. It’s a tradition,” he told ABC affiliate WLNE.
Concluding;
Animal sacrifice within the religious community must now come to an abrupt end. Inhumane slaughter must be abolished and replaced with “humane slaughter”. Although we do not recognize “inhumane slaughter” as a form of animal kindness we have to adopt some form of approach that will eventually see all animals globally given some form of “non-painful” death. As much as we despise all forms of animal slaughter within the meat industry and sacrificial slaughter community we will never see an end to such meat eating practices. So we must therefore continue challenging these communities and countries that fail to adopt such (inhumane slaughter and sacrificial) laws to now impose them based on scientific research tried and tested.
Take action today - share this document - create awareness - sign the petitions.
http://www.change.org/petitions/end-animal-sacrifice-in-nepal
http://www.change.org/petitions/stop-animal-sacrifice-gadhimai-festival-nepal-mass-animal-sacrifice
https://www.change.org/en-GB/petitions/indonesian-embassy-in-the-uk-stop-animal-sacrifice
http://www.petitiononline.com/ifa646b/petition.html
http://forcechange.com/63001/ban-torture-of-bulls-in-south-african-festival/
Thank you for reading;
Environmental and Botanical African and Asia Director
Dr Jose Calos Depre PhD, EnVstu, Ba, D.V.M
“Auschwitz begins wherever someone looks at a slaughterhouse and thinks: they’re only animals.”