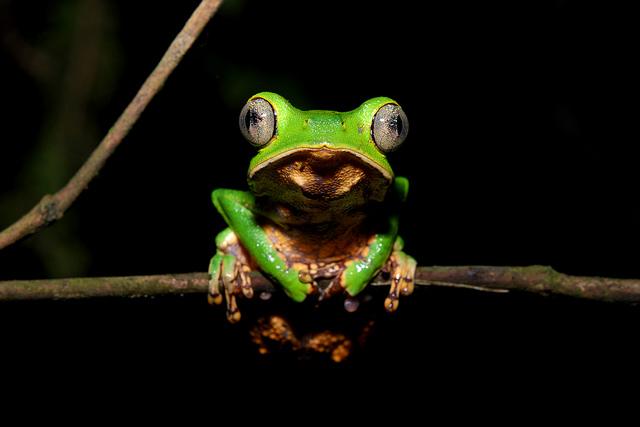
Endangered Species Monday: Tremarctos ornatus
Endangered Species Monday: Tremarctos ornatus
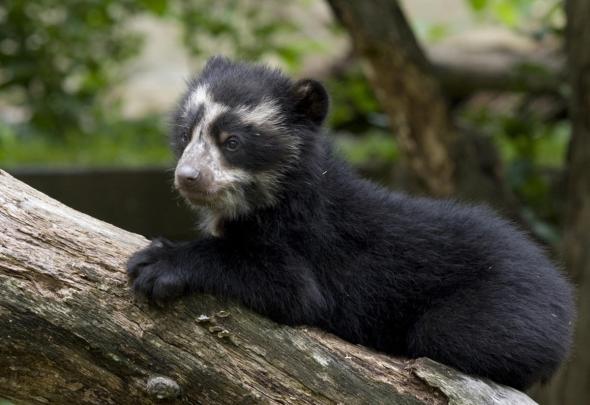
This January’s (2016) Endangered Species Watch Post is dedicated to the Tremarctos ornatus, commonly known as the Andean Bear or Spectacled Bear. The species was identified by Dr Jean Léopold Nicolas Frédéric Cuvier back in 1825. Dr Jean Léopold Nicolas Frédéric Cuvier lived from (23 August 1769 – 13 May 1832), known as Georges Cuvier, was a French naturalist and zoologist, sometimes referred to as the “Father of paleontology”. Cuvier was a major figure in natural sciences research in the early 19th century and was instrumental in establishing the fields of comparative anatomy and paleontology through his work in comparing living animals with fossils.
From 1982 to 1996 the Andean Bear has been listed as (vulnerable), of which its main threats are habitat loss and major poaching for the animal parts trade. Within the past thirty years populations have declined by a staggering 30% which qualifies the bear as being listed as (vulnerable). Habitat loss continues at a rate of 2-4% per year, which as yet doesn’t look set to decline. Furthermore identified threats do not look set to decrease anytime soon which could see this stunning animal pushed into extinction very soon.
Poaching is one of the main problems that can be controlled if (anti poaching enforcement) is increased within the bears habitat, unfortunately this is easier said than done. Furthermore, continued habitat destruction and illegal logging will see forest tracks opened up within the bears natural habitat, thus allowing poachers to walk freely into the bears home environment, thus seeing poaching occur. Anti poaching enforcement is a must, and needs to be taken seriously by all international (non-governmental organisations) that are working to sustain this animals welfare, and habitat.
Endemic to Bolivia, Colombia; Ecuador; Peru, and Venezuela, populations of the Andean Bear are now known to be decreasing rapidly, however populations are not reported to be (fragmented). Back in 1998 it was estimated by Dr Peyton that there was a mere 20,000 Andean Bears remaining. A 2003 survey, however estimated that there was in between 5,000 to 30,000 Andean Bears remaining. Andean Bears are now commonly located within the eastern Andes of which bear populations exist from the snowline down to 300 m asl in the Tapo-Caparo National Park in Venezuela. Andean Bears can also be located at high altitudes in Ecuador, Peru, Bolivia, and Columbia.
Andean Bears are “omnivores”, meaning that they feed exclusively on plant matter, fruits, bark and occasionally will consume meat of other animals, the bears preferred diet though is reported to be species of flora from the Bromeliaceae and Arecaceae. Activity patterns range from strictly diurnal for wild bears in Bolivia to mixed diurnal and nocturnal for reintroduced bears in Ecuador.
“EXTINCTION BY 2030 IS POSSIBLE”
As food is available year-round in all parts of their range, Andean bears do not hibernate. Based on the first few individuals of this species to be monitored using ground telemetry in Bolivia and Ecuador, home ranges overlap to a high degree and minimum home range sizes vary from 10 to 160 km² (although these are underestimates, as the bears were regularly out of range of radiotelemetry in both studies).
The Andean Bear stands at around 5ft to 6ft tall, and weighs in at around 220, 330lbs. The markings on the Andean bear’s face, neck and chest are exactly like human finger prints (unique to each and every individual Andean Bear). Andean bears are very timid and shy and prefer to live in isolated cloud forests, of which they are “mainly nocturnal” however will at times feed, live and socialize in daylight (although this is considered rare). Favorite foods are cacti, berries and of course honey.
Andean bears are quite typically solitary animals, and will only be seen in pairs during mating season. Females normally give birth to (1-2 cubs), cubs are normally mobile after one month, however will remain with their “mother” for up to eight months, mothers will often be seen with little cub hitching a ride on the back on the mothers back. Population studies state today that there may be no fewer than 3,000 Andean bears in the wild., which if true could soon see the species nearing extinction by 2030.
ANDEAN BEAR THREATS
Habitat loss and fragmentation, poaching, and the lack of knowledge about the distribution and status of the Andean Bear are the principal threats to this species. Much of the range of the Andean Bear has been fragmented by human activities, largely resulting from the expansion of the agricultural frontier. In some areas, mining, road development and oil exploitation are becoming a greater menace to Andean Bear populations as well as to local communities, due to land expropriation, loss of habitat connectivity, and water and soil contamination.
Many Andean Bear populations are isolated in small to medium-sized patches of intact habitat, particularly in the northern part of the range. The situation tends to improve towards the southern range, with some large patches of wilderness still remaining. Nevertheless, human population growth and national development plans throughout the Tropical Andes continue to be an important cause of habitat fragmentation and to threaten the connectivity among remaining wilderness patches.
Poaching is a serious threat throughout the Andean Bear range. Bears are often killed after damaging crops, particularly maize, or after purportedly killing livestock. Also, Andean Bear products are used for medicinal or ritual purposes and at some localities Andean Bear meat is highly prized. Live bears are also sometimes captured and sold.
Human induced mortality endangers the viability of small remnant populations. Lack of knowledge about the distribution and status is a problem throughout the region. In many areas, information about the status of Andean bears is outdated or, particularly in the southern portion of the range, simply non-existent. The absence of knowledge makes it difficult to develop realistic management plans for the conservation of this species, or to monitor changes in its distribution (reflective of changes in population status).
It is without a doubt the Andean Bear is facing “imminent extinction”, and from studies that are being conducted by various organisations including the International Animal Rescue Foundation Brazil, its very likely this animal is going to be pushed into extinction very soon.
Thank you for reasding the first part of this years (2016) Endangered Species Watch Post, and please feel free to scroll through 2014-2015’s posts below via the automatic scroll new feed bar.
Dr Jose C. Depre PhD. MEnvSc. BSc(Hons) Botany, PhD(NeuroSci) D.V.M. Environmental & Human Science
Chief Environmental Officer and Director
Donate today and help us continue our worldwide anti-wildlife trade enforcement operation continuing. Please click the DONATE button below.
DONATE BUTTON
Endangered Species Monday: Phalacrocorax carunculatus.
Endangered Species Monday: Phalacrocorax carunculatus
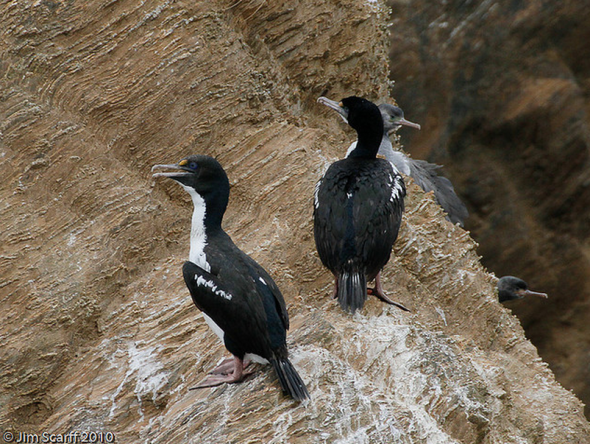
This Mondays (ESP) Endangered Species watch Post is dedicated to the Rough Faced Shag, scientifically known as Phalacrocorax carunculatus. Identified back in 1789 by Professor Johann Friedrich Gmelin (8 August 1748 – 1 November 1804) was a German naturalist, botanist, entomologist, herpetologist and malacologist. (Image credited: Jim Scarff 2010)
Listed as (vulnerable) the Rough Faced Shag doesn’t appear to be listed on either appendix (I) or (II). This Monday I have chosen to document on P. carunculatus as the species is incredibly rare. Thankfully conservation efforts and improvements in relation to protection of habitat have finally stabilized the birds population count. For once in many of my articles I can finally write on a bird that’s populations are not in decline. However, as explained the species is considered one of New Zealand’s rarest specimens.
Endemic to New Zealand the species derives from the family of Phalacrocoracidae. Locals commonly refer to the species by other names such as; New Zealand King Shag or King Shag. P. carunculatus qualified for the listing of vulnerable due to its very small (stable) population size where its restricted to four islands only.
From 1992 to 2002 the estimated number of birds living on all four islands stood at a mere c645 individuals (Est). A further 100-130 breeding pairs were counted too, which is equates (roughly) to 299-1000 ‘mature individuals’. Taking all individuals and breeding pairs into consideration followed up with the last census, it concluded that some 375- 1500 individuals remain on all four islands. Had drastic conservation measures not been implemented the species could have gone extinct.
Conservation practices on all four islands have been undertaken extremely well despite the fact populations are depressed. I personally applaud the New Zealand Government and Department of Environment for their efforts, and thank them for continuing future conservation and bird management projects.
Image: Rough Faced Shag small colony.
92% of the population resides on White Rocks, Sentinel Rock, Duffers Reef and Trio Islands, in the Marlborough Sounds, with two smaller colonies off D’Urville Island. Furthermore surveys on islands have confirmed that populations have remained stable over the last fifty years.
Breeding normally occurs on small rock stacks and islets, the primary diet component is said to be left eyes flatfish. However the Rough Faced Shag will also feed on other marine aquatic specimens too.
Colonies now reside within wildlife sanctuaries that are clearly signposted on the islands reminding tourists and any wannabe poachers to stay clear of Rough Faced Shag habitat. Bird watchers are also reminded to stay clear of habitat, especially when breeding occurs due to the species being very sensitive to human disturbance. I am somewhat concerned as to how a tourist has been able to edge so close the colony within the image above. This isn’t good and as such enforcement teams must remind tour operators of the (code of conduct).
Conservation actions that are now underway include a census count every five years and, monitoring of vessels that can/do cause habitat disturbance. Furthermore development of techniques to establish new colonies of Rough Faced Shags elsewhere for future survival. A code of conduct has been established to (remind commercial boats, fishing-people and tour operators) of their obligations and duties to ensure Rough Faced Shags are not pressurized by human disturbance.
Protection of all breeding grounds has most likely been sought since last documentation on the species (2012). Prevention of marine farming next to ‘any’ colonies breeding or non-breeding and responsible fishing programs have been rolled out minimize by-catch thus ensuring the birds food source requirements are not depleted or harmed in anyway.
Threats
In the 1800s, collecting by ornithologists and hunting for the fashion trade may have affected numbers. Human disturbance (boats, aircraft and scuba divers) can cause desertion of nests and subsequent predation by gulls. New interest from tour operators in the region may increase the problem. Set-nets are sometimes placed very close to colonies and present a major risk. Birds are occasionally illegally shot. Probably the largest threat now is that of tourists or fishermen disturbing breeding and non-breeding colonies. Hence why conservation measures have been put into practice to remind and keep tourists and fisherman away from all inhabitant islands.
Thank you for reading.
Dr Jose C. Depre
Environmental and Botanical Scientist.
Endangered species Friday: Acinonyx jubatus
Endangered Species Friday: Acinonyx jubatus
This Fridays endangered species I speak up about the now (not co common Cheetah). Endangered Species Watch Post (ESP) tries to limit the amount of commonly known specie on the platform, however due to recent declines we’ve now included the specie within the (ESP).
Listed on the ‘threatened list’ of (endangered species) as vulnerable, the common Cheetah was formally identified by Johann Christian Daniel von Schreber (1739 in Weißensee, Thuringia – 1810 in Erlangen), often styled I.C.D. von Schreber, was a German naturalist. (Image Cheetah, photographer unknown).
Identified back in 1775 there remains a total of some five sub-species known that inhabits north, south, west and east Africa. The sub-species A. j. venaticus is known only to inhabit Iran. Some very contradictory reports state there may or may not be populations living within Central India too.
From 1996 to 2002 A. jubatus populations haven’t increased of which this amazing hunting cat commonly known as the Cheetah or (Hunting Leopard) continues to sit at (vulnerable listing). Further population declines will most certainly see the specie qualifying for the category of (endangered). Should this occur the African Cheetah will become the first specie of big cat within the new millennium to hit endangered level.
Cheetahs have disappeared from some seventy six percent of their known historical range which now overtakes that of the Panthera leo (Lion). African populations are considered ‘widely common’ however still known to be sparsely populated. Meanwhile in Asia the Cheetah has practically vanished which is why we must do more to protect the last known remaining Africans populations before further extinctions occur. Cheetahs were known to be quite common throughout Mediterranean and the Arabian peninsula, north to the northern shores of the Caspian and Aral Seas, and west through Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan, Afghanistan, Pakistan into central India However this is no longer the case.
One reason for for Asiatic Cheetah population declines was due to live captures of the animal which were trained to hunt other fauna. Unfortunately that was not the main reason why the specie spiralled into near extinction. The primary threat was Cheetah prey decline. This same problem has also been noted as effecting other big cats within Africa and Asia too. Agriculture, over-unregulated-hunting, over-culling, urbanization and habitat destruction via humans, has all played a significant role pushing the species furthermore into the realms of near extinction. Within Iran the sub-species A. j. venaticus is known to be (critically endangered)
In Tunisia Cheetahs were known to roam freely, however there are no known populations remaining within the country. The El-Borma region, near the Algerian boundaries, was probably among the areas where Cheetahs have last been seen in 1974 and documented. Reports compiled back in 1980 now tell us the specie is incredibly rare (if not regionally extinct already). Recently hunters yet again stated that (hunting) has never impacted on the species whatsoever. That’s a complete barefaced lie by members of (PHASA) Professional Hunting Association of South Africa and (DSI) Dallas Safari International.
Cheetahs became extinct from most of the Mediterranean coastal region and easily accessible inland habitats of El-Maghra and Siwa oases one decade after being widely distributed in the northern Egyptian Western Desert until the 1970s. The main reasons explaining cheetah extirpation have been attributed to (extensive and uncontrolled hunting and the development of coastal lands). Please view images lower down the article.
“The main reasons explaining cheetah extirpation have been attributed to (extensive and uncontrolled hunting and the development of coastal lands)”…
Current data on Cheetah population within Eritrea, Sudan and Somali is unknown. Populations within these three countries could very well already be extinct. Reports conducted within most “known Chad Cheetah zones” have sadly concluded the species is no longer present within the of much African country either, 2008 surveys did pick up few roaming species within Southern Chad though. Few populations remain within Central Sahara although to what extent is again unknown.
 Image: Hunter, Canada - 7,000 to 10,000 Cheetah remain and this is allowed by Cites.
Image: Hunter, Canada - 7,000 to 10,000 Cheetah remain and this is allowed by Cites.
Within the African countries of Cameroon, Central African Republic, Congo, and Democratic Republic of Congo again population counts are not known. (Its’ quite possible that the species has already gone extinct). Cheetahs are already officially extinct within Burundi and Rwanda. Reports have sadly confirmed the species is also extinct within Nigeria. Poaching and over-hunting have wiped all populations out within the three central African countries. A 1974 study ‘suggested’ that few populations may be occupying both Cameroonian boundaries and Yankari Game Reserve. This report is though mere speculation and not confirmed evidence.
EXTINCTIONS TO DATE
Regional Extinctions
Extinctions have already occurred within; Burundi; Côte d’Ivoire; Eritrea; Gambia; Ghana; Guinea; Guinea-Bissau; India; Iraq; Israel; Jordan; Kazakhstan; Kuwait; Oman; Qatar; Rwanda; Saudi Arabia; Sierra Leone; Syrian Arab Republic; Tajikistan; Tunisia; Turkmenistan; United Arab Emirates; Uzbekistan and Yemen.
Possible Extinctions
Afghanistan; Cameroon; Djibouti; Egypt; Libya; Malawi; Mali; Mauritania; Morocco; Nigeria; Pakistan; Senegal, Uganda and the Western Sahara.
Known Endemic Zones
Algeria; Angola; Benin; Botswana; Burkina Faso; Central African Republic; Chad; Congo; Ethiopia; Iran; Kenya; Mozambique; Namibia; Niger; South Africa; South Sudan; Sudan; Tanzania, United Republic of; Togo; Zambia; Zimbabwe. (Updated 2015)
2015 WILD POPULATION COUNTS
(Please note the following populations below are wild and not captive nor farmed)
Reintroductions of Cheetah populations have taken place within Swaziland however to what extent the populations are within Swaziland is unknown.
What we know to-date is that populations within the “Southern Africa” (not just South Africa) hosts the largest populations at roughly some 5,000+ mature individuals. Botswana and Malawi holds roughly 1,800 mature individuals. Populations are unknown within (Angola) and ‘considered possibly extinct’. Mozambique holds some 50-60 mature individuals, Namibia 2,000. SOUTH AFRICA holds some 550 mature individuals, Zambia some 100 mature individuals, Zimbabwe 400. A large proportion of the estimated population lives outside protected areas, in lands ranched primarily for livestock but also for wild game, and where lions and hyenas have been extirpated. So we do question why trophy hunting and unregulated hunting still persists out of farmed areas.
Ethiopia, southern Sudan, Uganda, Kenya and Tanzania holds an estimated (2,500 mature individuals) however due to intense hunting pressure, poaching and habitat destruction this number could be much lower. (There is NO evidence that hunting within any of the ‘legal zones’ has increased Cheetah populations whatsoever”. Furthermore I challenge all hunting organisations within the legally allowed hunting areas to prove myself wrong? The largest population (Serengeti/Maro/Tsavo in Kenya and Tanzania) is estimated at 710.
Kenya hosts some 790+ mature wild individuals, Tanzania 560+ to 1,100 individuals. Uganda, Gros and Rejmanek (1999) estimated 40-295 with a wider range in the Karamoja region, whereas now Cheetahs have been extirpated and just 12 are estimated to persist in Kidepo National Park and surroundings. North-West Africa the species stands at no fewer that 250 mature individuals (if that).
Within Iran the ‘sub-species’ of Asiatic Cheetah - A. j. venaticus (if still extanct) stands at some 60-100 mature individuals. We do like the fact the conservation trustee is a known hunter allegedly supporting Cheetah conservation. We’ve yet to see an real improvement of Iranian Cheetahs in the country (more money talk)…
The overall “known Cheetah population” for Asia and Africa is by far more threatened that the Lion. To date there are some 7,000 known mature individuals remaining within the wild but no greater than 10,000. This sadly make the Cheetah by far more threatened than Panthera leo. African Lion populations stand at some 15,000 to 13,000 maximum. As the Cheetah population will not likely exceed 10,000 individuals - the species therefore qualifies for (vulnerable status).
Nowell and Jackson stated that Cheetah populations in the past have undergone some alarming declines, now it would seem that history is re-repeating itself (this time the specie may not survive). The Cheetah exhibits remarkable levels of genetic diversity in comparison and compared to other wild felids, so there could be a high chance the species may make it back from the near brink of extinction within the wild.
Problem is poaching and over-hunting then wasn’t as prolific as it is today. Scientists stated that interbreeding among other individuals had saved the species from bottleneck declines in the past. This history dated back some 10,000 years. Sport hunting then wasn’t an issue as it is today, so in all fairness the species could be hunted into extinction illegally or legally (with much thanks to Cites on the ‘legal part’). So in all honesty we may lose the Cheetah before the Lion.
While the causes of the Cheetah’s low levels of genetic variation are unclear [back then], what is clear is that large populations are necessary to conserve it. Since Cheetahs are a low density species, conservation areas need to be quite large, larger than most protected areas. Major areas of the African continent are being overtaken by humans, agriculture to cope with human expansion and deforestation. No longer is it a case of ‘if’ rather than ‘when’….
MAJOR THREATS
Cheetahs are ‘hunted for sport and trophies’, as well as handicrafts products. Live animals are also traded - the global captive Cheetah population is not self-sustaining. Pest animals are also removed.
In Eastern Africa, habitat loss and fragmentation was identified as the primary threat during a conservation strategy workshop (2007). Because Cheetahs occur at low densities, conservation of viable populations requires large scale land management planning; most existing protected areas are not large enough to ensure the long term survival of Cheetahs. A depleted wild ungulate prey base is of serious concern in northern Africa. Cheetahs which turn to livestock are killed as pests. Conflict with farmers and depletion of the wild prey base are also considered significant threats in parts of Eastern Africa.
In Iran, the Asiatic Cheetah A. j. venaticus is threatened indirectly by loss of prey base through human hunting activities. In addition, most protected areas are open to seasonal livestock grazing, which potentially places huge pressure on the resident ungulate populations through disturbance and potential competition. Additionally, domestic dogs accompanying the herds present a likely threat to both Cheetahs and their prey. An emerging threat is the possibility of fragmentation into discontinuous subpopulations as a result of increasing developmental pressures (mining, oil, roads, railways); this is particularly the case in Kavir N.P., currently the north-western limit of the Asiatic Cheetah’s range.
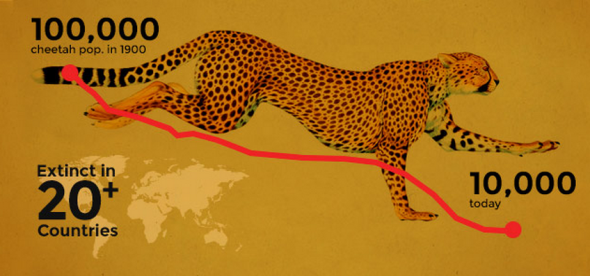 Image: Cheetah populations are more threatened than Lions.
Image: Cheetah populations are more threatened than Lions.
Conflict with farmers and ranchers is the major threat to Cheetahs in southern Africa. Cheetah are often killed or persecuted because they are a perceived threat to livestock, despite the fact that they cause relatively little damage. In Namibia, very large numbers of Cheetahs have been live-trapped and removed by ranchers seeking to protect their livestock (from government permit records, Nowell [1996] calculated that over 9,500 cheetahs were removed from 1978-1995). While removal rates have fallen, in part due to intensified conservation and education efforts, many ranchers still view Cheetahs as a problem animal, despite research showing that Cheetahs were only responsible for [3% of livestock losses] to predators. Although Cheetah in Iran have been killed because of predation on livestock, since 2003, there has been no direct evidence of killing Cheetahs, though it is likely most incidents go unreported.
“Cheetahs are also vulnerable to being caught in snares set for other species”.
Another threat to the Cheetah is interspecific competition with other large predators, especially lions. On the open, short-grass plains of the Serengeti, juvenile mortality can be as high as 95%, largely due to predation by Lions. However, mortality rates are lower in more closed habitats.
CITES [allows legal trade in live animals and hunting trophies under an Appendix I] quota system (annual quotas: Namibia - 150; Zimbabwe - 50; Botswana - 5). This was accepted by CITES as a way to enhance the economic value of Cheetahs on private lands and provide an economic incentive for their conservation. The global captive Cheetah population is not self-sustaining; Cheetahs [breed poorly in captivity] and in 2001 [30% of the captive population] was wild-caught. While analysis of trade records in the CITES database shows that these countries have reported almost no live exports since the late 1990s, Conservation groups are concerned that there is a substantial illegal cross-border trade in live animals.
There is also concern about illegal trade in skins, as well as capture of live cubs for trade to the Middle East. There is an increasing trade in cubs from [north-east Africa into the Middle East], but there is currently little trade in cubs from the Sahel region, where it was previously considered a major problem. Cheetahs are active during the daytime and there is concern that they can be driven off their kills by [tourist cars crowding around, or mothers separated from their cubs]. Burney (1980) conducted a study and concluded that [tourist cars did not seem to harm cheetahs, and in fact sometimes helped, as cheetah chases more often ended in a kill when there were cars around, distracting prey, providing cover from which to stalk, or otherwise waking Cheetahs up to notice prey in the area]. However, [tourist numbers have risen sharply by then, and its potential impact on cheetahs remains a concern].
The Eastern African Cheetah conservation strategy identified four sets of constraints to mitigating these threats across a large spatial scale. Political constraints include lack of land use planning, insecurity and political instability in some ecologically important areas, and lack of political will to foster Cheetah conservation. Economic constraints include lack of financial resources to support conservation, and lack of incentives for local people to conserve wildlife. Social constraints include negative conceptions of Cheetahs, lack of capacity to achieve conservation, lack of environmental awareness, rising human populations, and social changes leading to subdivision of land and subsequent habitat fragmentation. These potentially mutable human constraints contrast with several biological constraints which are characteristic of Cheetahs and cannot be changed, including wide-ranging behaviour, negative interactions with other large carnivores, and potential susceptibility to disease.
Disease is a potential threat to the Cheetah, as its reduced genetic diversity can increase a population’s susceptibility. However, the most serious disease mortality thus far documented in wild Cheetahs was from naturally occurring anthrax in Namibia’s Etosha National Park; Cheetahs, unlike other predators, do not scavenge carcasses of ungulates killed by anthrax, and thus [had no built-up immunity] when they preyed upon springbok sick with the disease. The Cheetah’s low density may offer some measure of protection against infectious disease; for example, Cheetahs were not affected by an outbreak of Canine Distemper Virus in the Serengeti National Park which [killed over 1/3 of the Lion population]. Serological surveys of Cheetahs on Namibian farmland indicate some exposure and survival of the disease.
We are losing the Cheetah faster than the specie of Lion. Although some regulations are in place with the species listed on Appendix I (Cites) its quite likely we’ll lose wild populations should hunting, poaching and unregulated hunting not stop now.
Thank you for reading.
Dr Jose C. Depre
Environmental and Botanical Scientist.
Sources; Cites, Red List, Wiki, Wild Forum, DEA, CCG, DSI, PHASA, Cambridge University, Oxford University.
Endangered Species Monday: Alouatta belzebul.
Endangered Species Monday: Alouatta belzebul
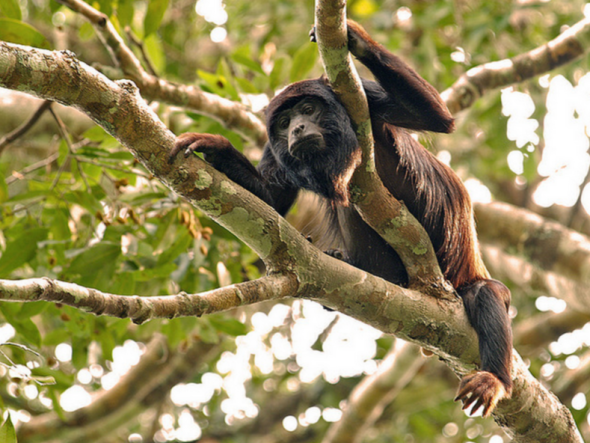
This Monday’s endangered species article from the (Endangered Species Watch Post) focuses on the Red Handed Howler Monkey of which is listing near to endangerment. (Image Red Handed Howler Monkey)
Generically identified as Alouatta belzebul back in 1766 by Professor Carl von Linnaeus (1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after his ennoblement as Carl von Linné was a Swedish botanist, physician, and zoologist, who laid the foundations for the modern biological naming scheme of binomial nomenclature.
Listed as vulnerable the species is endemic to Brazil (Alagoas, Maranhão, Pará, Paraíba, Pernambuco, Rio Grande do Norte, Sergipe and Tocantins). Populations are currently on the decline of which its very likely the species will be re-categorized as endangered within the next five years, if not sooner.
A. belzebul is said to be extremely common in some areas such as Marajó however is noted as rare within the Atlantic Forest portion of the range known as; Rio Grande do Norte, Alagoas, Paraíba and Pernambuco. Last survey census’s reported the species to be inhabiting at least ten isolated locations of which two hundred individuals remain in each plot.
International Animal Rescue Foundation Brazil have for the past three years been conducting surveys within the area will be submitted to the (IUCN). Furthermore the Environmental Protection Unit now re-based in Londrina are working with local communities, hunters and farmers within the A. belzebul range to preserve commonly known species of monkey, birds, amphibians and flora within the region.
IARFB are also currently conducting investigations to locate where sugar cane is being exported too and used within from the A. belzebul’s region. Its believed that America, Mexico, South America, and Europe are purchasing large sugarcane exports from the region. Tesco, J.S Sainsbury’s, Cooperative Food Group, Asda, Walmart, Woolworths and Spar have all been noted on suppliers exports from the regions. Aldi, Lidl, Quick-Save, Budgens have been ruled out. We are least impressed though with J.S Sainsbury’s name written on export documents of sugar cane from the region.
Within the ten isolated locations six populations are known to reside in Paraiba, two in Rio Grande de Norte, one in Pernambuco, and one in Alagoas. The largest population in the Atlantic Forest is in Pacatuba in Paraiba with about 80 animals. There have been five registered local extirpations from forest fragments in the last 50 years.
Little known conservation actions are under way within their endemic region and as explained populations are decreasing and nearing endangerment. A. belzebul is listed within the family of Atelidae which is one of the very first five of new recognized ‘new world monkeys’. Its quite likely that new sub-species of the Red Handed Howler Monkey may be located as well as newer species of ‘new world monkeys’ too within the coming years. Only five years ago did scientists locate over 100,000 new species within the Yasuni National Park, Ecuador so in reality anything is possible.
The Atelidae family host howler, spider, woolly and woolly spider monkeys (the latter being the largest of the New World monkeys). They are found throughout the forested regions of Central and South America, from Mexico to northern Argentina.
When the species is not foraging on the ground floor they can normally be found resting in the canopies of trees at a height of some sixty feet. Social groups normally consist of seven to twenty members that will host mature males, females juveniles and infants. Males normally take lead of the pack or (troop).
These large and slow-moving monkeys are the only folivores of the New World monkeys. Howlers eat mainly top canopy leaves, together with fruit, buds, flowers, and nuts. They need to be careful not to eat too many leaves of certain species in one sitting, as some contain toxins that can poison them. Howler monkeys are also known to occasionally raid birds’ nests and chicken coops and consume the eggs.
Image: Adult Red Handed Howler Monkey.
Howlers are the only New World primates which regularly include mature leaves in their diet, although softer, less fibrous, young leaves are preferred when they are available. Their folivory and ability to eat mature leaves is undoubtedly one of the keys to their wide distribution and the wide variety of vegetation types they inhabit.
Mature fruit is the other important food item, especially wild figs (Ficus) in many regions, but they also eat leaf petioles, buds, flowers (sometimes seasonally very important), seeds, moss, stems and twigs, and termitaria. The diet of two A. belzebul groups in the Caxiuanã National Forest was studied by Souza et al. (2002). They were largely folivorous but would switch to fruits whenever available, especially during the wet season.
Size:
Adult male weight 7.27 kg (n=27),
Adult female weight 5.52 kg (n=26)
Adult male weight 6.5-8.0 kg (mean 7.3 kg, n=27),
Adult female weight 4.85-6.2 kg (mean 5.5 kg, n=26) .
Threats
Listed on Cites Appendix II there are few threats associated with the species. Nevertheless they still remain and if left unchecked can rapidly increase placing the new world monkey in danger of extinction.
In the Amazon, the species is widespread, although they are hunted. The Amazon populations have suffered severely from forest loss throughout their range in southern Pará over the last decade. In the Atlantic Forest population, the major threat is the fragility of the remaining small forest patches to stochastic and demographic affects (habitat loss and fragmentation has been mainly due to sugar-cane plantations).
Please share and make aware the Red Handed Howler Monkey’s plight. Tip: Check sugar products from local shops and hypermarkets to ensure your not aiding the destruction of their natural habitat via your sugar purchase. Check your local candy and other shopping supplies. If necessary contact companies politely asking where they are obtaining the sugar products from. Never give up.
Thank you for reading.
Dr Jose C. Depre.
Environmental and Botanical Scientist.
Chief Executive Officer
Endangered Species Friday: Ailurops ursinus
Endangered Species Friday: Ailurops ursinus
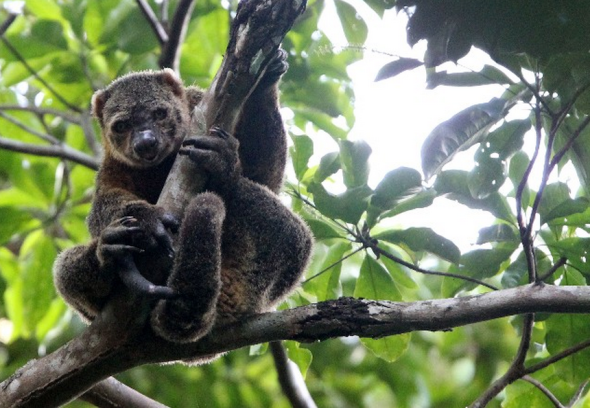
A. ursinis was identified back in 1824 by Dutchman Dr Coenraad Jacob Temminck - (31 March 1778 – 30 January 1858) was a Dutch aristocrat, zoologist, and museum director. Listed as vulnerable the species is endemic to Indonesia on the island of Sulawesi of which there remains limited data on this rather fine specimen of marsupial that resides in the family phalangeridae. (Image: Young Bear cuscus)
Populations of the (Bear cuscus) as its commonly known continue to steadily decline even though there are limited - conservation measures in place protecting the species (There remains as yet no data on population size). The Bear cuscus has practically gone extinct within the Tangkoko-DuaSudara Nature Reserve of which a staggering 95% decline has been recorded within the region alone of which the primary threat within the nature reserve is hunting and trade for pets.
North Sulawesi has also seen a staggering decline identical to the population decreases documented within the Tangkoko-DuaSudara Nature Reserve too. Yet again hunting and the illegal pet trade are very much responsible, and may very well within the next five to ten years lead to a complete extinction occurring.
As much as I myself hate to say it I am pretty certain from viewing statistical data past and present that extinctions are going to occur even sooner than predicted. Should extinctions occur it proves yet again that poaching is having a disastrous effect onto just about every African and Asian species known.
Habitat loss and forest clearance are all playing a pivotal roll at decreasing populations of this beautifully attractive marsupial. As a conservation and botanical scientist sometimes I wonder to oneself why we even bother to help species of animals and flora when some governments show no support, or respect whatsoever in our quest to protect and serve. Then I remember, my children and their children’s heritage is just as important as mine and the teams fight to protect.
Bear cuscus are known as arboreal marsupials meaning, they mostly thrive and spend the majority of their peaceful and playful lives within trees and dense forest. Unfortunately these forests and trees are slowly dwindling in size primarily for land clearance to support local farms and communities and, not forgetting slash and burn activities. I cannot begin to imagine what these creatures think and feel when destructful and greedy humans destroy their homes and pastures. The feeling of not-knowing-when such harm is to be inflicted must be terrorizing for them.
The genus contains the following single species that is known to be related to the Bear cuscus; Ailurops melanotis that inhabits the Salibabu Island listed as (critically endangered) and endemic to Indonesia on the island of Sulawesi. Typically found in undisturbed tropical lowland moist forests, this species does not readily use disturbed habitats, thus it is not usually found in gardens or plantations. It is a largely diurnal and as explained a arboreal species that is often found in pairs. Diet usually consists of a variety of leaves, preferring young leaves, and like many other arboreal folivores it spends much of its day resting in order to digest similar to the Koala bear of Australia.
Image: Bear cuscus relaxing in the canopy of Tangkoko
The only known conservation actions that are taking place are within in few protected areas, that include: Tangkoko-DuaSudara Nature Reserve, Bogani Nani Wartabone National Park, Lore Lindu National Park, Morowali National Park, and a host of forest reserves. This species is nominally protected by Indonesian law. Unfortunately even though the species is protected the illegal pet trade still continues of which I myself have on many occasions located small pet shops in Indonesia selling Bear cuscus from rusty, cramped cages.
Threats
The species is threatened by habitat loss due to clearance of forest for small-scale agriculture and through large-scale logging. It is also heavily hunted by local people for food, and collected for the pet trade. Cuscus hunting forays are often planned before special occasions (e.g., birthday celebrations) in order to provide future guests with the greatly appreciated meat. (These inferences are based on some six months of residence among Alune villagers in 1993–95, which included participation in forest activities and standard ethnographic data collection.)
Thank you reading.
Dr Jose C. Depre
Environmental and Botanical Scientist.
Please donate by clicking the link below and help the board of directors establish their Viet Nam pet and wildlife rescue and rehabilitation clinic today. Without your help we cannot take dogs, cats and small bush meat animals of the streets and into safety. No donation is to small and all donations are greatly and kindly appreciated.
Please donate here:
https://www.facebook.com/SayNoToDogMeat/app_117708921611213
Stay up to date with our SNTDM newsletter:
https://www.facebook.com/SayNoToDogMeat/app_100265896690345
Thank you.
Stay up to date with African and international environmental and animal welfare affairs here:
https://www.facebook.com/pages/International-Animal-Rescue-Foundation-World-Action-South-Africa/199685603444685?fref=ts











