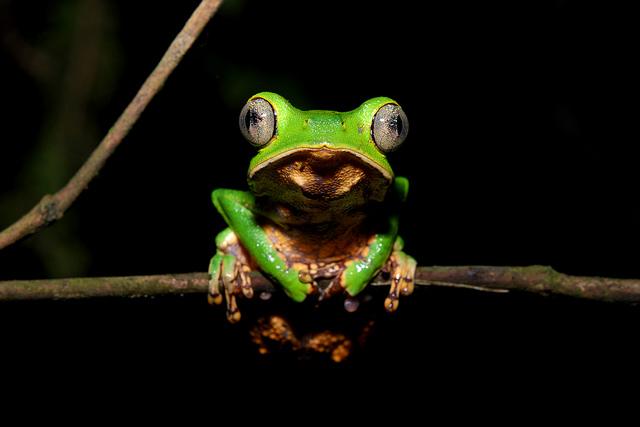
Endangered Species Friday: Gastropholis prasina
In this Fridays Endangered Species Watch Post (ESP), I focus briefly on this rather elusive species of Green Keel bellied Lizard, that’s endemic to the continent of Africa. I’ve long adored our African reptilians, unfortunately they’re own habitat like many larger species of fauna is under threat… (Image credited: S. Spawls) Green Keel bellied Lizard.
Listed as (near threatened) the species was primarily identified by Dr Franz Werner (15 August 1867 in Vienna - 28 February 1939 in Vienna) was an Austrian zoologist and explorer. Specializing as a herpetologist and entomologist, Werner described numerous species and other taxa of frogs, snakes, insects, and other organisms.
I thank Dr Werner (despite not being alive today), for his truly amazing journeys all over the African continent of which he located many hundreds of different reptiles, snakes, frogs, worms, and an assortment of other mammals. Had Dr Werner not followed on from his fathers footsteps its quite likely the Green Keel bellied Lizard wouldn’t be known today (among many other animals this amazing man identified).
Gastropholis prasina was originally identified back in 1904, then re-classified by Dr Loverbridge back in 1936 as (Bedriagaia moreaui ). However today this is not the species true name, G. prasina remains the true identity. Endemic to Kenya and Tanzania, the species is commonly known found along the eastern arc of Kenya and Tanzania’s coastal plain.
Localities are: Watamu, Arabuko-Sokoke Forest, Amani in the Usambara Mountains, Tanga, Zaraninge Forest, and the Nguru Mountains. The reptilian probably also occurs in Kenya’s Shimba Hills, however this has yet to be fully confirmed.
Populations are known to be “severely fragmented”, which has led to concerns that the species may soon be re-listed as (vulnerable or even endangered). Current historical data records show no evidence of a mean population count sparking more concerns that the species may be more “threatened than has been led to believe”. For now we can only assume (but not estimate) what the population count may be based on location and trapping (see image below). (updates to follow). Please view the map below of which details where the highest abundance of Green Keel bellied Lizard habitats remain today.
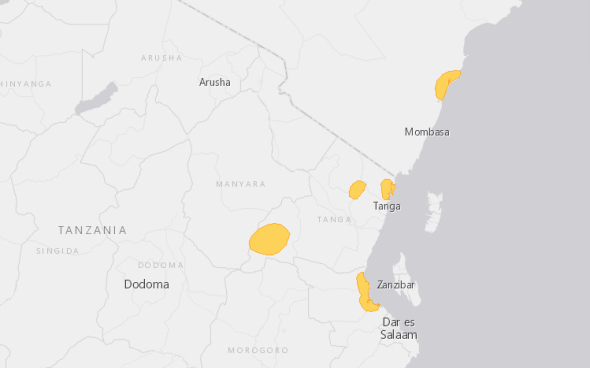
Image: Identified habitat locations of the Green Keel bellied Lizard.
Past records state the species is either “rare or considered very rare”, however I must point out that this historical data is from 1989 and a further assessment dated 2002. Vast swathes of habitat has been lost since the 1980’s and early millennium, habitat destruction is rife within Kenya and Tanzania, poaching, bush meat trade and land conversions are also increasing annually.. So in all honesty, none knows for sure if the species is now (to date rare or very rare), as records are out of date, which is an observational fact!
Unfortunately the species is neither listed on (Cites appendix I or II) despite the fact the reptilian is near (vulnerable). There remains no evidence that the Green Keel bellied Lizard is used within trade, or the Traditional African Medicine Trade (TAM). However there is evidence that the reptilian is collected during large scale tree felling for displays in local snake farms. Its quite possible the species “may be collected to feed snakes too” which if true could be seriously detrimental to the wild populations that are still unknown.

Image credit: Torsten Kunsch
Green Keel bellied Lizard is diurnal (either comes out during the day or not). The reptilian is also known to be quite secretive and arboreal (living mostly in or among trees), which could explain why the reptilian is at the best of times difficult to locate and study, especially if the animal wants to come out only at night. Environmental scientists are in a sense playing cat and mouse when it comes to studying that is.
Despite the species living primarily among trees, there is no evidence that the animal lives high up among the canopies either, (confusing I know). Specimens have been located mainly close to the ground or next to the base of trees, as seen within the images above (1-2). Further studies have shown that the reptilian can live as high as 12 meters from base level within the tree, but not exactly the canopy.
Investigations haven’t really shed much light as to whether the species is indeed affected by habitat disturbance. However where cashew nut farms are being grown within the animals habitat of which these farms have turfed up the animals natural homes, there does appear to be some evidence that proves the Green Keel bellied lizard cannot tolerate this type of habitat disturbance, so we’ll need to be looking into this more closely, followed up with surveys in relation to intensive logging and species collection.
While the Green Keel bellied Lizard is not listed on either of the appendixes, the reptilian is known to inhabited ‘protected parks’ being that of Arabuko-Sokoke Forest and the Amani and Zaraninge Forest.
Major Threats
Coastal forest is rapidly disappearing within this species’ range, and is thought likely to represent a threat to the lizard. While it has been recorded from cashew plantations, it is thought to require continuous tree cover. Expanding human populations along the fertile East African coast, and associated agricultural development, are the major threats to forest in this region (2014). Much of the species’ coastal distribution is, however, within well-protected areas, and its largest distribution centre is inland in the Nguru Mountains.
It’s uncertain what the future holds for this rather secretive lizard, furthermore its evident that threats while minimal are still present and increasing, we still don’t know what the actual true population count is neither. More studies need to be conducted to determine the exact population, and where required the necessary protection plans and (listing on either Appendix I or II) applied.
Video: Green Keel bellied Lizard in Captivity
Thank you for reading and please follow me on Twitter for more great news updates by clicking the link below… Have a Great Weekend.
https://twitter.com/josedepre11 < Follow me on Twitter here.
Did you know you can also follow us on Facebook here:
https://www.facebook.com/InternationalAnimalRescueFoundationAfrica/
Dr Jose C. Depre PhD. MEnvSc. BSc(Hons) Botany, PhD(NeuroSci) D.V.M.
Environmental, Botanical & Human Science
NB: Don’t forget that every Monday, Wednesday and Friday’s editions of environmental news, vegan and vegetarian recipes, endangered species Monday and Friday, and much more. You can subscribe for free via entering your email address into the “follow me” drop box on the right hand side of this page. Its free, and you’ll be emailed direct all new media around the world every week directly from the International Animal Rescue Foundation’s Environmental News and Media Team and myself.
January 22, 2016 | Categories: You must be the change you want to see in the world | Tags: (ESP) International Animal Rescue Foundation Africa, Africa, Amani, Arabuko-Sokoke Forest, Cashew Farming, Cites, Dr Franz Werner, Dr Jose Depre, Endangered Species Watch Post, Fridays Animal, Frogs, Gastropholis prasina, Green Keel bellied Lizard, Insects, IUCN, Kenya, Lizard, Near threatened, Nguru Mountains, Organisms, Reptiles, Reptilians, S.Spawls, Snakes, Tanga, Tanzania, Torsten Kunsch, Usambara Mountains, Watamu, Zaraninge Forest | Leave a comment

Endangered Species Friday: Dyscophus antongilii
This Friday’s endangered species article I focus on yet another Africans frog that is listing near endangerment. In fact this frog species is so threatened should conservation actions not improve we’re likely to see extinctions occur within the next decade. (Please note: the image above depicts the frog in threatened state - colors do differ)
Commonly known as the Tomato frog the species is one of three within the genus Dysophus. Scientifically identified as Dyscophus antongilii this particular genus is the only genus known to be at threatened status while the other two sub species are in fact listed as least concern.
Identified back in 1877 by Explorer Alfred Grandidier (20 December 1836 – 13 September 1921). Explorer Grandidier was a French naturalist and explorer. From a very wealthy family, at the age of 20, he and his brother, Ernest Grandidier (1833–1912), undertook a voyage around the world. At first they were led by the astronomer and physicist Pierre Jules César Janssen (1824–1907), but when Janssen fell sick and had to return to France after about six months, the brothers continued the journey.
They visited South America in 1858 and 1859 and in particular the Andes, Peru, Chile, Bolivia, Argentina and Brazil. During this voyage they gathered a significant collection of specimens which were analyzed, in 1860, by Ernest.
Conservation actions did improve the species back in the late 1990’s of which the D. antongilii was then listed as vulnerable. Since this time though conservation actions have improved to some degree leading to the species to then be re-listed back in 2002 as (near threatened). Unfortunately due to this particular genus being only native to the Africans island of Madagascar where habitat fragmentation, destruction, urbanization, species/human displacement, slash and burn operations are increasing only reduces frog habitat furthermore. Main causes of declines though are trade and pollution of water bodies.
D. antongilii is known to be abundant, however populations of this particular genus are currently unknown on the island. Locals have stated D. antongilii is most commonly seen within the Maroansetra region on the island of Madagascar. Unfortunately when environmentalists undertook surveys and census counts within the area with regards to the locals knowledge of the species, it was found that populations are actually declining quite rapidly. One such problem that has been noted by International Animal Rescue Foundation Africa was the increasing tropical pet trade.
International Animal Rescue Foundation Africa and International Animal Rescue Foundation England located a broad range of pet suppliers within England and America. Despite D. antongilii classified as “near threatened” and in overall decline one can purchase this exact genus within the United States for as little as $29.99. Meanwhile within the counties of Manchester, Nottingham, London, Kent and Wales pet suppliers were trading for around £30.99.
On researching a pet supplier within the United States not only did we locate evidence of D. antongili on sale, other species of threatened and “endangered” animals were also on sale. A search of their Facebook social media page also aroused suspicions of which they have since closed down. Pet Solutions, Beavercreek based in Ohio can be located here: http://www.petsolutions.com/C/Live-Frogs/I/Tomato-Frog.aspx meanwhile their Twitter account can be viewed hereto: https://twitter.com/petsolutions

Image: Tomato frog in normal relaxed mode shows their unique tomato coloring.
The species lives in primary rain-forest, coastal forest, secondary vegetation, degraded scrub, and highly disturbed urban areas. It is a very adaptable species, but possible declines in Maroansetra indicate that there might be a limit to the extent that it can persist in urbanized habitats. It appears to be localized to sandy ground near the coast, and breeds in ditches, flooded areas, swamps, and temporary and permanent still or very slowly flowing water.
Tomato frogs breed in February to March following heavy rainfall; the sounds of males calling to attract females can be heard around small water bodies in the dark Malagasy night. Following copulation, females will lay a clutch of 1,000 to 15,000 eggs on the surface of the water. Tadpoles hatch from these small black and white eggs about 36 hours later; they are only around six millimetres long and feed by filter-feeding. Tadpoles undergo metamorphosis into yellow juveniles and this stage is completed around 45 days after the eggs were laid.
Ambushing potential prey, adult tomato frogs feed on small invertebrates, such as beetles, mosquitoes, and flies. When threatened, these frogs can inflate themselves, giving the appearance of greater size.
Threats
Pollution of water-bodies is a potential threat, and in the past this species was subject to collection for international trade, although this is now largely under control and restricted. Despite trade allegedly being restricted - it seems this is not the case as International Animal Rescue Foundation Africa have located over 34 suppliers in the last week, many of which have ties back to Asia and Africa. International trade is indeed taking off again, and with a population in decline - international trade must cease immediately.
This colorful species is much in demand by herpetological hobbyists. Captive breeding, in addition to CITES listing, has effectively halted the trade in wild-caught specimens. However it must be noted that captive breeding cannot always be proven within the private industry, and scrutiny must always be used to conclude if any breeder is following the relevant procedures and laws in place.
Research into captive breeding techniques for the tomato frog has been carried out by Baltimore Zoo in the United States in an effort to boost the currently small and genetically deprived captive population that exists in that country.
A consortium of U.S. zoos that form the Madagascar Fauna Group (MFG) have established an exhibit at the Parc Zoologique Ivoloina, Madagascar in an attempt to help educate local people about this attractive member of their natural heritage. Very little is known about the tomato frog and further research into its distribution, behavior and potential threats is urgently needed before effective conservation measures can be put into place.
It is currently listed on Appendix I of the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species (CITES), but this move has been criticized by some authors as an ineffective strategy and one that has undermined the status of the unlisted D. guineti. Furthermore, research is needed to determine if D. antongilii is in fact a separate species or merely a variant of D. guineti.

Thank you for reading and taking the time to educate yourself and others about this amazing reptile.
Dr Jose C. Depre
Chief Environmental Officer/ CEO
Botanical and Environmental Scientist.
July 3, 2015 | Categories: You must be the change you want to see in the world | Tags: Africa, Alfred Grandidier, Dyscophus antongilii, Endangered species, IARF, IARFA, IARFE, IUCN, Madagascar, Maroansetra, Near threatened, Pet Solutions, Red, Reptiles, Tadpoles, Tomato, Tomato Frog | Leave a comment








