Endangered Species Monday | Tasmanian Devil | Sarcophilus harrisii.

ENDANGERED SPECIES MONDAY | TASMANIAN DEVIL
This Mondays endangered species watch post (ESP) is dedicated to the Tasmanian devil, an endangered carnivorous marsupial that’s roughly the same size as a small domesticated canine. (Image credits: Bicheno Tasmania tourism)
The Tasmanian devil was formally identified back in 1841 by ‘French’ Dr Pierre Boitard (27 April 1787 Mâcon, Saône-et-Loire – 1859) whom was a French botanist and geologist. As well as describing and classifying the Tasmanian devil, he is notable for his fictional natural history Paris avant les hommes (Paris Before Man), published posthumously in 1861, which described a prehistoric ape-like human ancestor living in the region of Paris. He also wrote Curiosités d’histoire naturelle et astronomie amusante, Réalités fantastiques, Voyages dans les planètes, Manuel du naturaliste préparateur ou l’art d’empailler les animaux et de conserver les végétaux et les minéraux, and Manuel d’entomologie etc.
Listed as (endangered), and scientifically identified as Sarcophilus harrisii. Back in 1996 conservation scientists undertook further research on the species thus concluding the species was of ‘lower risk’. Unfortunately since 1996 - things have changed dramatically on the Australian continent. From the middle 1990’s conservationists estimated the mean mature individual total as being - 130,00-150,000 mature individuals.
Spotlighting sightings of Tasmanian devils across the state have declined significantly since the emergence of Devil Facial Tumour Disease (DFTD) in the mid-1990s: by 27% by early 2004, by 41% by early 2006, by 53% by early 2007, and by 64% by early 2008. The decline was significantly sharper in regions where DFTD had been reported earliest, such that in north-east Tasmania, mean sightings have declined by 95% from 1992-1995 to 2005-2007, with no indication of recovery or plateau in decline.
Comparison of mark-recapture results in the same area from the mid-1980s and 2007 supports this finding. At the Freycinet peninsula, on the east coast of Tasmania, where the population has been monitored through trapping from 1999 to the present, the population has declined by at least 60% since the disease was first detected in 2001 and the adult population still appears to be halving annually. Other indicators of devil abundance, such as road kills, predation on stock, and carrion removal, also support this conclusion of a substantial decline.
Surveys conducted back in 2007 ‘estimate the (mature) Tasmanian devil populations to be standing 25,000 being the highest estimate’; this equates to around 50,000 individuals. However back in 2004 conservationists stated the (mature populations) could be as low as 21,000 mature individuals. Conservationists have confirmed that due to the rapid spread of Devil Facial Tumor Disease, and other threats such as road accidents and predator kills - acknowledging these provisos, the best estimate of total population size based on current evidence thus lies within the range of 10,000-25,000 mature individuals. Based on threats, gestation, life span this therefore qualifies the species to be entered into [endangered category].
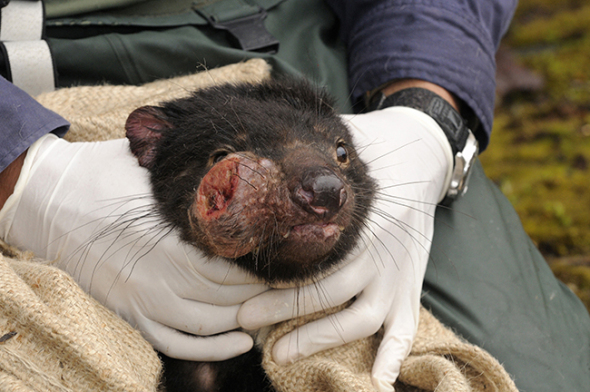
13 Feb 2011, Cradle Mountain-Lake St. Clair National Park, Tasmania, Australia — Tasmanian Devil (Sarcophilus harrisii) being treated by scientist for DFTD, Devil Facial Tumor Disease. This is a cancer that is spread by biting or physical contact from one animal to another, Cradle Mountain, Tasmania, Australia. — Image by © Dave Wattsl/Visuals Unlimited/Corbis.
In North-Western Australia Tasmanian devil populations are estimated to be standing at between (3,000-12,500 individuals). Meanwhile - in Eastern South Western Australia populations are said to be standing at 7,000 12,500 individuals.
Other trapping work by the Department of Primary Industry and Water (DPIW) Save the Tasmanian Devil Program broadly support these predictions for DFTD-free regions. However, in central and eastern regions, marked population declines have been detected, in association with the earlier reports of Devil Facial Tumour Disease (DFTD), subsequent to the time of the Jones and Rose survey. The north-west region is thus now thought to support the highest population densities.
The species is not known to be seriously or severely fragmented, however populations on the decline and fast, primarily due to Devil Facial Tumor Disease.
THREATS
Current evidence suggests that DFTD is an infectious, widespread disease, so that any attempt to delineate boundaries between affected and unaffected locations is likely to be outdated swiftly. DFTD has been associated with local population declines of up to 89% since first reported (Hawkins et al. 2006, McCallum et al. 2007), indicated by long-term spotlighting data, widespread trapping and laboratory results. The declines, and the prevalence of the disease, have not eased off in any monitoring sites, and DFTD is present even in very low density areas.
It is estimated that the adult population is approximately halving annually on the Freycinet peninsula with extinction predicted at this site 10-15 years after disease arrival. Declines were most marked in areas where the disease had been reported earliest, in north-eastern and central eastern Tasmania.
Mean spotlighting sightings of Tasmanian devils per 10 km route, obtained from across the core Tasmanian devil range (eastern and north-western Tasmania), have declined by 53% since the first report of DFTD-like symptoms in 1996. The most immediately threatened location is thought to be the region where DFTD was reported prior to 2003: across 15,000 km² of eastern Tasmania.
By 2005, the Devil Disease Project Team had confirmed DFTD in individuals found across 36,000 km² of eastern and central Tasmania. DFTD is now confirmed across more than 60% of the devil’s overall distribution, and there is evidence for continued geographical spread of the disease, so that Tasmanian devils across between 51% and 100% of Tasmania may be, or have already been, subject to >90% declines in a ten-year period. The currently affected region covers the majority of the formerly high-density eastern management unit, involving what was perhaps around 80% of the total population.

Image: Tasmanian devil killed by car/with suspected DFTD.
DTFD has resulted in the progressive loss of first the older adults from the population and then the younger adults so that populations are comprised of one and two year old’s. As female devils usually breed for the first time at age two, they may not successfully raise a litter before they die of DFTD. An increase in precocial breeding indicates some compensatory response, but as yet this appears to have been insufficient to counter mortality.
DFTD behaves like a frequency-dependent disease, probably because the majority of the injurious biting, which is the type of contact most likely to lead to disease transmission, occurs between adults during the mating season. Frequency-dependent diseases, which are typically sexually transmitted, can lead to extinction. Because transmission occurs between the sexes at mating irrespective of population density, these types of diseases lack a threshold density below which they become extinct.
Cannibalism is considered fairly common in Tasmanian devils and renders the species particularly vulnerable to disease transmission. However, modes of transmission of DFTD are not as yet known.
ROAD KILLS:
A recent three-year study of roadkill frequency on the main roads of Tasmania estimated 2,205 Tasmanian devils are killed on roads annually. This suggests that 2-3.% of the total Tasmanian devil population are killed on roads (based on an estimated population of 60,000–90,000 individuals at the time of the survey). The roaded parts of Tasmania closely match the core distribution area for Tasmanian devils.
Roadkill was attributed as the cause of up to 50% and 20% of Tasmanian devil death during a recording period of 17 months at Cradle Mountain and 12 months at Freycinet National Parks, respectively. Local extinction and a similar rate of population decline at Cradle Mountain indicates that roadkill can cause local extinction, in which the road becomes a local sink. Future impact is likely to remain at the same level.

Image: Paper cutting relating to 3 year study of fauna road kill.
DOG KILLS:
Reports of about 50 devils killed per year by poorly controlled dogs are served from about 20 dog owners. There is no obligation or incentive for such reports, and generally some hesitance even among those providing them, so the real figures are more likely of the order of several hundred devils killed by dogs each year.
FOXES:
There have been spasmodic, small-scale introductions of the Red Fox (Vulpes vulpes) into Tasmania since early European colonisation. Early incursions were sometimes efforts at acclimatisation and others for short-term hunting. More recently, there has been at least one accidental incursion (from a container ship in 1998) and credible reports of a concerted, malicious campaign of introduction.
Hard evidence (confirmed scats, carcasses) of foxes has been found in the north-west and northern and southern midlands. Credible sighting reports have come from most of the eastern half of the State including the central highlands and the far north-west, mostly areas where Tasmanian devil populations are suppressed by DFTD.
A commonly held view has been that the abundance of Tasmanian devils has prevented fox establishment through interference competition, either aggressive exclusion or predation on denned juveniles. Red Foxes and Tasmanian devils share preferences for den sites and habitat, and are of a similar size. Tasmanian devils abundance is likely to slow, if not prevent, fox establishment.
It is possible that foxes have been present in Tasmania for many decades at sub-detectable levels, and that a degree of ecological release has occurred due to DFTD, with foxes increasing to detectable numbers. The current impact of the Red Fox has been quantified, and it is unlikely that fox numbers are currently at a level to impose a measurable impact.
A decline in Tasmanian devils number may create a short to medium-term surplus of food, for example carrion; ideal for fox establishment. Fox establishment may cause both direct and indirect effects on Tasmanian devils. Direct effects include (reciprocal) killing by then abundant foxes of then rare juvenile devils at dens while the female forages.
Fox establishment may also cause ecosystem disruptions through changes in other species - a feature of foxes on mainland Australia and something that might then also indirectly affect Tasmanian devils. Tasmania has the potential to hold up to 250,000 foxes (based on modelling of habitat preferences and densities in south-east mainland Australian) which could replace most medium- to large-sized marsupial carnivores.
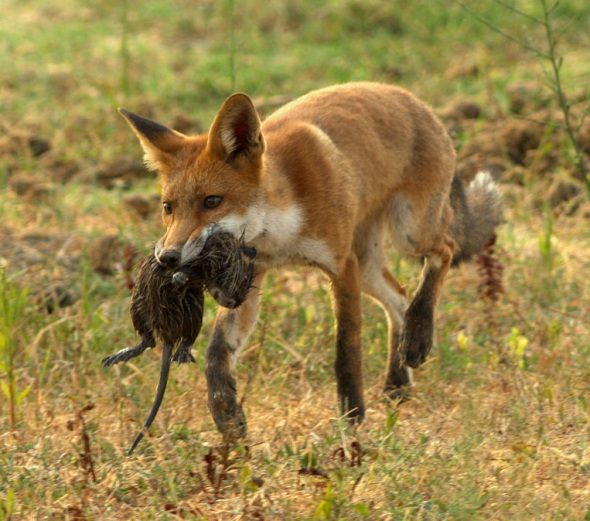

Image: Red foxes have been reported to prey on Tasmanian devils/Other Marsupials.
PERSECUTION:
In the past, persecution of the Tasmanian devil has been very high throughout settled parts of Tasmania, and is thought to have brought about very low numbers at times. Through the 1980s and 1990s, systematic poisoning in many sheep-growing areas (particularly fine-wool with its reliance on merinos) was widespread and probably killed in excess of 5000 devils per year. In the 1990s, control permits were occasionally issued to individuals who were able to argue that Tasmanian devils were pests (e.g. killing valuable lambs).
Current persecution is much reduced, but can still be locally intense with in excess of 500 devils thought to be killed per year. However, this is reducing since devil numbers have declined. While the small amount of current persecution is likely to persist it is unlikely to constitute a major threat unless the Tasmanian devil population becomes extremely small and fragmented.
LOW GENETIC DIVERSITY:
Dr Jones in 2004 found the genetic diversity of Tasmanian devils to be low relative to many Australian marsupials as well as placental carnivores. This was consistent with an island founder effect, but previous marked reductions in population size may also have played a role. Low genetic diversity can reduce population viability, and resistance to disease.
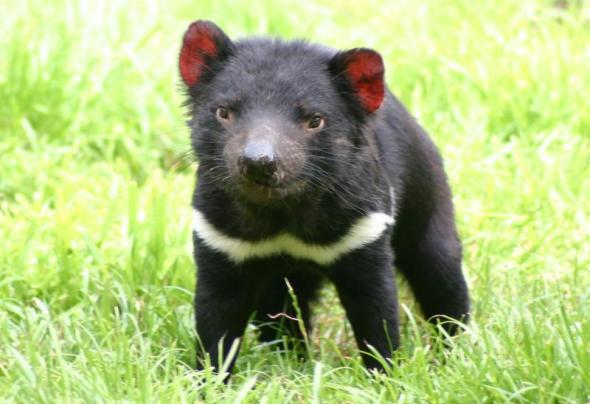

Image: Tasmanian devil (photographer unknown).
Tasmanian devils normally eat birds, snakes, fish, reptiles and insects. Furthermore its not uncommon to witness the species feasting on dead carrion. Female devils will mate with dominant males, who fight to gain their attention. Three weeks after conception, the females ‘can’ give birth to up to FIFTY BABIES, called joeys, although some reports state between 20-30 joeys. These extremely tiny joeys scramble to attach themselves to one of the four available teats in the mother’s pouch. Gestation is around 21 days.
For now the future is uncertain with regards to the Tasmanian devil. The species hosts a large number of natural threats, as well as roadkill accidents, human persecution and (DFTD). For now populations are considered to be generally high, although not that high for the species to qualify as vulnerable, or even near threatened. There are a number of Australian marsupials facing many threats, despite the continent being inhabited at some 10% by humans, or to be precise - 768,685 km2.
While I myself cannot state for certain what the future may hold for the Tasmanian devil - for now based on the large number of threats and continued population declines - its highly likely that come 2026 we’ll be seeing yet another Australian extinction occurring under our noses, and that is the sad reality of life from which our wildlife is facing today.
One thing is for sure though - never underestimate the DEVIL - they’re not called devils for nothing and have a rather cute temper too. Welcome to the planets largest carnivorousness marsupial. The Tasmanian devil
Thank you for reading.
Dr Jose C. Depre PhD. MEnvSc. BSc(Hons) Botany, PhD(NeuroSci) D.V.M.
Master Scientist of Environmental, Botanical & Human Science
Endangered Species Monday | Potorous gilbertii - Back From The Brink Of Extinction.
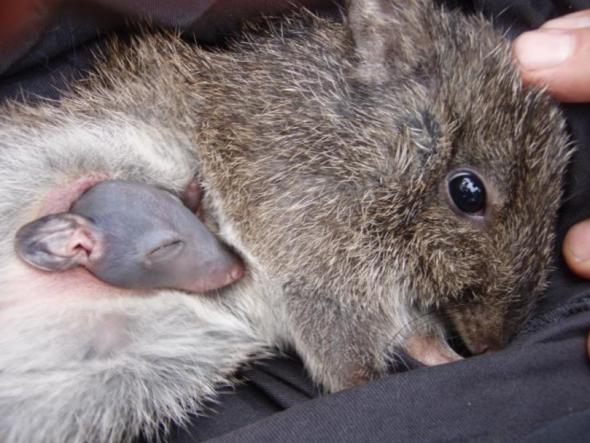

Endangered Species Monday | Potorous gilbertii
This Monday’s (ESP) post, I’ve decided to document a little more on Australia’s wildlife. This Monday I have dedicated this post to one of Australia’s most endangered marsupials. Commonly known as the Gilbert’s Potoroo. (Image Credit Parks and Wildlife Australia).
Identified as the worlds ‘rarest marsupial’, the species is scientifically known as the Potorous gilbertii. Listed as (critically endangered) the species was primarily identified back in 1841 by Dr John Gould FRS - 14 September 1804 – 3 February 1881) who was a British ornithologist and bird artist. He published a number of monographs on birds, illustrated by plates that he produced with the assistance of his wife, Elizabeth Gould, and several other artists including Edward Lear, Henry Constantine Richter, Joseph Wolf and William Matthew Hart.
Dr Gould has been considered the father of bird study in Australia and the Gould League in Australia is named after him. His identification of the birds now nicknamed “Darwin’s finches” played a role in the inception of Darwin’s theory of evolution by natural selection. Gould’s work is referenced in Charles Darwin’s book, On the Origin of Species.
Life hasn’t been at all easy for the P. gilbertii. It was only back in 2012 that conservation and environmental scientists (rediscovered) the species of which it was believed the marsupial had gone completely extinct within the wild. Endemic to Australia there is very little known in relation to when threats came about, increased and decreased. However I can state now; as small as populations are known - P. gilbertii’s populations are ‘currently stable within the wild’.
While though populations are stable, there are only thirty to forty actually known to be living within their endemic wild, so there is still a large amount of concern for the worlds most endangered marsupial. Back in early 1980’s the species had been listed as (completely extinct within the wild after studies from the 1800’s turned up nothing). Fortunately though environmental scientists went on the prowl and were not under any circumstances ready to write this species off whatsoever. They were technically looking for an animal that hadn’t been seen since the 1880’s-1990’s. Their work though eventually paid off.
“THEN CAME A BREAK THROUGH IN 1994”
Environmental scientists come 1992-1993 were ready to write the species off, call off all explorations and projects that were aimed at hopefully rediscovering the species. Fortunately though the Australian Parks and Wildlife Service persisted - and come 1994 a spotting was recorded. After so many years believing the Gilbert’s Potoroo had gone extinct, scientists discovered an extremely small population - to the joy of many. Finally there was hope, and today the species remains under full governmental protection.
Native to South-western and Western Australia the remaining populations was taken by three collectors between 1840 and 1879 in the vicinity of King George’s Sound (Albany), but exact locations are unknown. Skeletal material is common in cave deposits between Cape Leeuwin and Cape Naturaliste. Sub-fossil skeletal specimens have been located in coastal sand dunes between these localities. It is currently restricted to Mt. Gardner promontory in Two Peoples Bay Nature Reserve.
The entire population (consisting of 30-40 mature individuals) as explained above remains inhabits the Two Peoples Bay Nature Reserve of which they enjoy protection from the local parks wildlife board. While populations are identified as extremely small, mother will give birth to either 1-2 babies every year, normally its 2 babies. Like kangaroos the species has the ability to keep a second embryo in a state of diapause while the first embryo is growing. If the first baby does not go to term, a second baby starts growing right away.
Check out the Gilbert’s Potoroo Action Group by clicking this link
Diapause is considered a rare phenomena - especially in kangaroos, although its been witnessed quite a lot over the past few years by European, British and Australian Zoologists. The last diapause event (that I’m aware of) was witnessed at the Taronga Zoological Gardens in Australia. You can read the story >here.< The gestation period for Gilbert’s potoroo is unknown, but is estimated to be similar to the long-nosed potoroo at 38 days.
Since so few are alive today, much of the reproductive cycle for Gilbert’s potoroo remains unknown. However, the main breeding period is thought to be November–December with similar breeding patterns to those of the long-nosed potoroo. Scientists have tried to breed them in captivity, but recent attempts have been unsuccessful, citing diet, incompatibility, and age as possible factors that influenced the lack of reproduction. Reproduction in the wild is thought to be progressing successfully as many females found in the wild are with young.
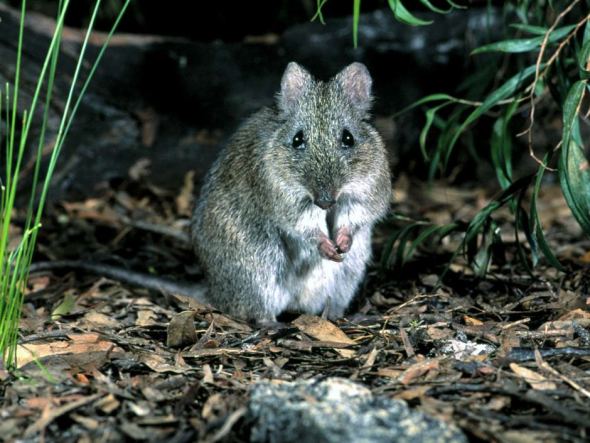

Image: Gilbert’s Potoroo. Photographer Mr Dick Walker.
In 2001, the Gilbert’s Potoroo Action Group was formed to help in the education and public awareness of the potoroo. The group also helps with raising funds for the research and captive-breeding programs for Gilbert’s potoroo. In efforts to protect the remaining population, three Gilbert’s potoroos (one male and two females) were moved to Bald Island in August 2005, where they are free from predation. Since that time, an additional four potoroos have been sent to establish a breeding colony.
THREATS
Fire is the critical threat (present and future) to this species as the Mt. Gardner population is in an area of long unburnt and extremely fire prone vegetation, and a single fire event could potentially wipe out the species (except for the few individuals in captivity and on Bald Island). This species is in the prey size range of both feral cats and foxes, and both are known to exist in the Two Peoples Bay area, thus this species is likely threatened by these predators.
Maxwell et al. (1996) states that the reasons for the decline of the species are unknown. Predation by foxes has probably been significant. Changed fire regimes may have altered habitat and/or exacerbated fox and cat predation by destroying dense cover. Gilbert’s notes record it as “the constant companion” of Quokkas, Setonix brachyurus
Unlike Gilbert’s Potoroo, the Quokka, although declining, persists over much of its pre-settlement range. The difference has not been explained. Maxwell et al. (1996) and Courtenay and Friend (2004), suggest that dieback disease caused by Phytophthora cinnamomi threatens persisting populations by eliminating plant symbionts of hypogeal, mycorrhizal fungi which are the principal food of Gilbert’s Potoroos. Altering vegetation structure and eliminating plants that provide food are direct threats to this species.
For now and based on various accounts, research and up to data documentaries. The species is still in danger. As explained above a single large and sporadic fire within the species habitat - could kill off the entire identified populations, which would be a catastrophe. While there is minimal threat from predators such as foxes and feral cats - this could change. So the need for persistent monitoring is a must. Finally we have disease, with populations being so small at around 30-40, any single disease could like fires wipe the entire species out within a single week.
Within the article above I’ve included various links for your immediate attention and information, as well as a link to the main working group that is helping (and doing all they can) to preserve the species. Furthermore I’ve included a donation link for you to donate to the Gilbert’s Potoroo Action Group. While I’m not entirely sure whether you can volunteer, there is a link on the main website below (highlighted: Volunteer Today). Just click the link, follow the instructions and, I’m confident someone will get back to you as soon as possible.
Volunteer Today
Thank you for reading, please don’t forget after reading to share this article, and hit the like button too.
Dr Jose Carlos Depre Depre PhD. MEnvSc. BSc(Hons) Botany, PhD(NeuroSci) D.V.M.
Environmental & Human Science
Endangered Species Monday: Dasyurus maculatus
Endangered Species Monday: Dasyurus maculatus
This Mondays Endangered Species Watch Post (ESP) I focus a little attention onto the Spotted-tailed Quoll. D. maculatus was identified back in 1792 by Dr Robert Kerr (1755 – 11 October 1813) Dr Kerr was a scientific writer and translator from Scotland. Dr Kerr was born in Roxburghshire as the son of a jeweler. He studied medicine at the University of Edinburgh and practiced at the Edinburgh Foundling Hospital as a surgeon. (Image adult Quoll)
Dr Kerr translated several scientific works into English, such as Antoine Lavoisier’s work of 1789, In 1792, he published The Animal Kingdom, the first two volumes of a four-tome translation of Professor Linnaeus’ Systema Naturae, which is often cited as the taxonomic authority for a great many species. (He never did start the remaining two volumes.) Please note, the Spotted-tailed Quoll is described as ‘two subspecies’ and will be noted as such during this short article.
Listed as near threatened, D. maculatus has been wrongly named by some writers as the ‘Tiger Quoll’. The species shows no resemblance to that of a Tiger nor shows any familiar behavioral traits too. There is no mention of a ‘Tiger Quoll’ within conservation literature too. So I wish to put that name to bed now.
From 1996 the species [and sub-species] was listed as vulnerable, a further 2008 evaluation of the carnivorous marsupial saw conservation NGO’s submit data to the Red List of which the Spotted-tailed Quoll now qualifies for the criteria of (near threatened). Endemic to the island of Australia the species exists as explained as two sub-species.
Sub species (1) Dasyurus maculatus maculatus was formerly distributed in south-eastern Queensland (as far north as Bundaberg and as far west as Chinchilla), eastern New South Wales, Victoria, South Australia, Tasmania (including some of the Bass Strait Islands. Maxwell et al. (1996) reported that in south-east Queensland this particular sub-species has undergone a range contraction indicated to be in excess of 30% over the last 25 years and is now rare in most areas.
Sub species (2) D. m. gracilis formerly occurred throughout the latitudinal range of the Wet Tropics World Heritage Area of north Queensland. It is now apparently extinct from the Atherton and Evelyn Tablelands, and there are few sightings south of 17o45’S. This represents a decline in extent of occurrence of approximately 20%.
Populations are decreasing of which there remains an estimated ‘20,000’ mature individuals. Populations in south-east Queensland, western Victoria (Otways and far south-west of Victoria), and coastal areas of southern New South Wales are known to be declining too. Populations in north-eastern Queensland are small, fragmented, and are <1,000 individuals. Tasmanian population numbers appear to be stable.
There is some evidence of a decline in distribution or in numbers in remaining suitable habitat (e.g., in the Otway Range), and the species is mostly uncommon (although it is present in good numbers in some areas, such as the Marengo and Chaelundi Forests).
Image: Spotted-tailed Quoll (juvenile)
Threats
The reasons for decline of D. m. maculatus are a combination of habitat loss and fragmentation, possible disease at the beginning of the 20th century, competition with foxes and feral cats, predation by foxes and dogs, and impact of widespread strychnine baiting for dingoes.
Most recently threats include non-target mortality from trapping and poisoning (there is a long-standing concern that Quolls are being killed by the use of 1080 poisoning, but this has not been confirmed and is currently the focus of a number of investigative trials).
Direct persecution is significant as they are attracted to caged birds and do not necessarily take flight when discovered. Estimated forest loss as a result of clearing within its former range in south-east Queensland is over 70%, with the majority of loss occurring over the last 20 years.
The species uses a large number of den sites throughout the year and activities that reduce the number of den logs are likely to be significant. In Tasmania this taxon is naturally rare, possibly as a result of competition with D. viverrinus, Sarcophilus harrisii, and feral cats. Road mortality could be a significant factor where high speed roads and good habitat coincide, as Quolls are attracted to feed on the carcasses of road-killed animals.
D. m. gracilis is susceptible to factors which increase juvenile and/or adult mortality, or which otherwise decrease breeding success. Such factors may include habitat clearance, logging, introduced species including cane toad, and direct killing at chicken pens, at houses, and on roads.
Conservation actions are underway with more planned soon that will work to evaluate the current species size, habitat loss, food sources and protective areas needed Etc.
Spotted-tailed Quolls are generally nocturnal and rest during the day in dens. However, juveniles and females with young in the den can be seen during the day and may leave their dens when it is light out. Quoll dens take the form of underground burrows, caves, rock crevices, tree hollows, hollow logs, or under houses or sheds. Quolls move by walking and bounding gaits. Trails are not particularly important for Quoll, although they forage and scent mark along runways and roads.
Facts
Size of the Quoll depends on the species. They can reach 14 to 29.5 inches in length and 3 to 15.4 pounds of weight.
Quoll is covered with coarse coat that can be grey, brown or black in color. Basic color of the fur is enriched with prominent white spots. Quoll has pointed snout and pink nose. Its powerful jaw is equipped with sharp teeth. Tail is long and bushy. Quoll has sharp claws on the front and hind feet that are used for holding the food, climbing and digging underground burrows.
Quolls are nocturnal animals (active during the night). Even though Quolls are agile climbers, they spend majority of their life on the ground. Quolls can consume both animals and plants. Diet is mainly based on small mammals (such as rabbits), small birds, snakes and insects. They occasionally eat fruit and nuts.
Main predators of Quolls are crocodiles and snakes. Quolls live in the underground burrows, inside the hollow trees or caves. Quoll is territorial animal.
Male’s territory overlaps with territories of several nearby females. They share communal latrines. Quoll is solitary creature which gathers with other Quolls only during the mating season.
Mating season of Quolls takes place during the winter. Pregnancy lasts only couple of weeks and ends with up to 30 miniature babies (they weigh less than one gram).
Babies spend first 8 weeks of their life inside the mother’s pouch. After that period, babies are big enough to leave the pouch and ride on the mother’s back. Young Quolls are ready for independent life at the age of 6 months. Female’ pouch is not a true pouch. It forms out of the fold of skin on the stomach after successful mating. Pouch contains only 6 teats, which means that only 6 babies out of 30 will be able to survive and complete their development. Quolls reach sexual maturity at the age of one year. Quolls have short lifespan. They can survive from 2 to 5 years in the wild, depending on the species.
Contrary to popular belief Quolls or as some people refer to this documented species as the ‘Tiger Quoll’ are not rare. The species and entire genera are in fact nocturnal, so while your asleep they’ll most likely be happily wondering through your garden or local parks and nature reserves. However the species is threatened and decreasing with a population size of some 20,000.
Thank you for reading.
Dr Jose Depre.
Don’t forget to check out the upcoming Embassy Day hosted by SAYNOTODOGMEAT.NET please click the link here below further information > http://saynotodogmeatevents.info/2015/07/26/embassy-day-september-17th-2015/
Endangered Species Friday: Ailurops ursinus
Endangered Species Friday: Ailurops ursinus
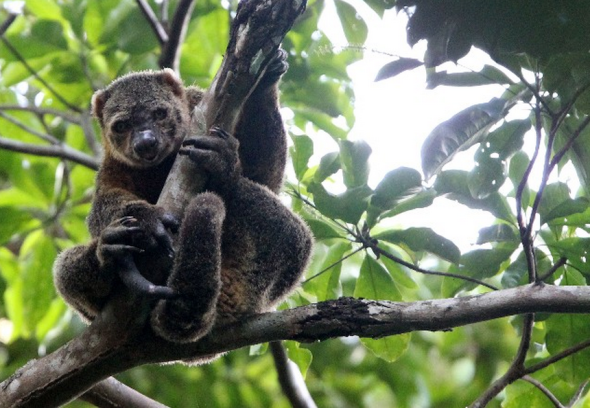
A. ursinis was identified back in 1824 by Dutchman Dr Coenraad Jacob Temminck - (31 March 1778 – 30 January 1858) was a Dutch aristocrat, zoologist, and museum director. Listed as vulnerable the species is endemic to Indonesia on the island of Sulawesi of which there remains limited data on this rather fine specimen of marsupial that resides in the family phalangeridae. (Image: Young Bear cuscus)
Populations of the (Bear cuscus) as its commonly known continue to steadily decline even though there are limited - conservation measures in place protecting the species (There remains as yet no data on population size). The Bear cuscus has practically gone extinct within the Tangkoko-DuaSudara Nature Reserve of which a staggering 95% decline has been recorded within the region alone of which the primary threat within the nature reserve is hunting and trade for pets.
North Sulawesi has also seen a staggering decline identical to the population decreases documented within the Tangkoko-DuaSudara Nature Reserve too. Yet again hunting and the illegal pet trade are very much responsible, and may very well within the next five to ten years lead to a complete extinction occurring.
As much as I myself hate to say it I am pretty certain from viewing statistical data past and present that extinctions are going to occur even sooner than predicted. Should extinctions occur it proves yet again that poaching is having a disastrous effect onto just about every African and Asian species known.
Habitat loss and forest clearance are all playing a pivotal roll at decreasing populations of this beautifully attractive marsupial. As a conservation and botanical scientist sometimes I wonder to oneself why we even bother to help species of animals and flora when some governments show no support, or respect whatsoever in our quest to protect and serve. Then I remember, my children and their children’s heritage is just as important as mine and the teams fight to protect.
Bear cuscus are known as arboreal marsupials meaning, they mostly thrive and spend the majority of their peaceful and playful lives within trees and dense forest. Unfortunately these forests and trees are slowly dwindling in size primarily for land clearance to support local farms and communities and, not forgetting slash and burn activities. I cannot begin to imagine what these creatures think and feel when destructful and greedy humans destroy their homes and pastures. The feeling of not-knowing-when such harm is to be inflicted must be terrorizing for them.
The genus contains the following single species that is known to be related to the Bear cuscus; Ailurops melanotis that inhabits the Salibabu Island listed as (critically endangered) and endemic to Indonesia on the island of Sulawesi. Typically found in undisturbed tropical lowland moist forests, this species does not readily use disturbed habitats, thus it is not usually found in gardens or plantations. It is a largely diurnal and as explained a arboreal species that is often found in pairs. Diet usually consists of a variety of leaves, preferring young leaves, and like many other arboreal folivores it spends much of its day resting in order to digest similar to the Koala bear of Australia.
Image: Bear cuscus relaxing in the canopy of Tangkoko
The only known conservation actions that are taking place are within in few protected areas, that include: Tangkoko-DuaSudara Nature Reserve, Bogani Nani Wartabone National Park, Lore Lindu National Park, Morowali National Park, and a host of forest reserves. This species is nominally protected by Indonesian law. Unfortunately even though the species is protected the illegal pet trade still continues of which I myself have on many occasions located small pet shops in Indonesia selling Bear cuscus from rusty, cramped cages.
Threats
The species is threatened by habitat loss due to clearance of forest for small-scale agriculture and through large-scale logging. It is also heavily hunted by local people for food, and collected for the pet trade. Cuscus hunting forays are often planned before special occasions (e.g., birthday celebrations) in order to provide future guests with the greatly appreciated meat. (These inferences are based on some six months of residence among Alune villagers in 1993–95, which included participation in forest activities and standard ethnographic data collection.)
Thank you reading.
Dr Jose C. Depre
Environmental and Botanical Scientist.
Please donate by clicking the link below and help the board of directors establish their Viet Nam pet and wildlife rescue and rehabilitation clinic today. Without your help we cannot take dogs, cats and small bush meat animals of the streets and into safety. No donation is to small and all donations are greatly and kindly appreciated.
Please donate here:
https://www.facebook.com/SayNoToDogMeat/app_117708921611213
Stay up to date with our SNTDM newsletter:
https://www.facebook.com/SayNoToDogMeat/app_100265896690345
Thank you.
Stay up to date with African and international environmental and animal welfare affairs here:
https://www.facebook.com/pages/International-Animal-Rescue-Foundation-World-Action-South-Africa/199685603444685?fref=ts






