Endangered species Friday: Acinonyx jubatus
Endangered Species Friday: Acinonyx jubatus
This Fridays endangered species I speak up about the now (not co common Cheetah). Endangered Species Watch Post (ESP) tries to limit the amount of commonly known specie on the platform, however due to recent declines we’ve now included the specie within the (ESP).
Listed on the ‘threatened list’ of (endangered species) as vulnerable, the common Cheetah was formally identified by Johann Christian Daniel von Schreber (1739 in Weißensee, Thuringia – 1810 in Erlangen), often styled I.C.D. von Schreber, was a German naturalist. (Image Cheetah, photographer unknown).
Identified back in 1775 there remains a total of some five sub-species known that inhabits north, south, west and east Africa. The sub-species A. j. venaticus is known only to inhabit Iran. Some very contradictory reports state there may or may not be populations living within Central India too.
From 1996 to 2002 A. jubatus populations haven’t increased of which this amazing hunting cat commonly known as the Cheetah or (Hunting Leopard) continues to sit at (vulnerable listing). Further population declines will most certainly see the specie qualifying for the category of (endangered). Should this occur the African Cheetah will become the first specie of big cat within the new millennium to hit endangered level.
Cheetahs have disappeared from some seventy six percent of their known historical range which now overtakes that of the Panthera leo (Lion). African populations are considered ‘widely common’ however still known to be sparsely populated. Meanwhile in Asia the Cheetah has practically vanished which is why we must do more to protect the last known remaining Africans populations before further extinctions occur. Cheetahs were known to be quite common throughout Mediterranean and the Arabian peninsula, north to the northern shores of the Caspian and Aral Seas, and west through Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan, Afghanistan, Pakistan into central India However this is no longer the case.
One reason for for Asiatic Cheetah population declines was due to live captures of the animal which were trained to hunt other fauna. Unfortunately that was not the main reason why the specie spiralled into near extinction. The primary threat was Cheetah prey decline. This same problem has also been noted as effecting other big cats within Africa and Asia too. Agriculture, over-unregulated-hunting, over-culling, urbanization and habitat destruction via humans, has all played a significant role pushing the species furthermore into the realms of near extinction. Within Iran the sub-species A. j. venaticus is known to be (critically endangered)
In Tunisia Cheetahs were known to roam freely, however there are no known populations remaining within the country. The El-Borma region, near the Algerian boundaries, was probably among the areas where Cheetahs have last been seen in 1974 and documented. Reports compiled back in 1980 now tell us the specie is incredibly rare (if not regionally extinct already). Recently hunters yet again stated that (hunting) has never impacted on the species whatsoever. That’s a complete barefaced lie by members of (PHASA) Professional Hunting Association of South Africa and (DSI) Dallas Safari International.
Cheetahs became extinct from most of the Mediterranean coastal region and easily accessible inland habitats of El-Maghra and Siwa oases one decade after being widely distributed in the northern Egyptian Western Desert until the 1970s. The main reasons explaining cheetah extirpation have been attributed to (extensive and uncontrolled hunting and the development of coastal lands). Please view images lower down the article.
“The main reasons explaining cheetah extirpation have been attributed to (extensive and uncontrolled hunting and the development of coastal lands)”…
Current data on Cheetah population within Eritrea, Sudan and Somali is unknown. Populations within these three countries could very well already be extinct. Reports conducted within most “known Chad Cheetah zones” have sadly concluded the species is no longer present within the of much African country either, 2008 surveys did pick up few roaming species within Southern Chad though. Few populations remain within Central Sahara although to what extent is again unknown.
 Image: Hunter, Canada - 7,000 to 10,000 Cheetah remain and this is allowed by Cites.
Image: Hunter, Canada - 7,000 to 10,000 Cheetah remain and this is allowed by Cites.
Within the African countries of Cameroon, Central African Republic, Congo, and Democratic Republic of Congo again population counts are not known. (Its’ quite possible that the species has already gone extinct). Cheetahs are already officially extinct within Burundi and Rwanda. Reports have sadly confirmed the species is also extinct within Nigeria. Poaching and over-hunting have wiped all populations out within the three central African countries. A 1974 study ‘suggested’ that few populations may be occupying both Cameroonian boundaries and Yankari Game Reserve. This report is though mere speculation and not confirmed evidence.
EXTINCTIONS TO DATE
Regional Extinctions
Extinctions have already occurred within; Burundi; Côte d’Ivoire; Eritrea; Gambia; Ghana; Guinea; Guinea-Bissau; India; Iraq; Israel; Jordan; Kazakhstan; Kuwait; Oman; Qatar; Rwanda; Saudi Arabia; Sierra Leone; Syrian Arab Republic; Tajikistan; Tunisia; Turkmenistan; United Arab Emirates; Uzbekistan and Yemen.
Possible Extinctions
Afghanistan; Cameroon; Djibouti; Egypt; Libya; Malawi; Mali; Mauritania; Morocco; Nigeria; Pakistan; Senegal, Uganda and the Western Sahara.
Known Endemic Zones
Algeria; Angola; Benin; Botswana; Burkina Faso; Central African Republic; Chad; Congo; Ethiopia; Iran; Kenya; Mozambique; Namibia; Niger; South Africa; South Sudan; Sudan; Tanzania, United Republic of; Togo; Zambia; Zimbabwe. (Updated 2015)
2015 WILD POPULATION COUNTS
(Please note the following populations below are wild and not captive nor farmed)
Reintroductions of Cheetah populations have taken place within Swaziland however to what extent the populations are within Swaziland is unknown.
What we know to-date is that populations within the “Southern Africa” (not just South Africa) hosts the largest populations at roughly some 5,000+ mature individuals. Botswana and Malawi holds roughly 1,800 mature individuals. Populations are unknown within (Angola) and ‘considered possibly extinct’. Mozambique holds some 50-60 mature individuals, Namibia 2,000. SOUTH AFRICA holds some 550 mature individuals, Zambia some 100 mature individuals, Zimbabwe 400. A large proportion of the estimated population lives outside protected areas, in lands ranched primarily for livestock but also for wild game, and where lions and hyenas have been extirpated. So we do question why trophy hunting and unregulated hunting still persists out of farmed areas.
Ethiopia, southern Sudan, Uganda, Kenya and Tanzania holds an estimated (2,500 mature individuals) however due to intense hunting pressure, poaching and habitat destruction this number could be much lower. (There is NO evidence that hunting within any of the ‘legal zones’ has increased Cheetah populations whatsoever”. Furthermore I challenge all hunting organisations within the legally allowed hunting areas to prove myself wrong? The largest population (Serengeti/Maro/Tsavo in Kenya and Tanzania) is estimated at 710.
Kenya hosts some 790+ mature wild individuals, Tanzania 560+ to 1,100 individuals. Uganda, Gros and Rejmanek (1999) estimated 40-295 with a wider range in the Karamoja region, whereas now Cheetahs have been extirpated and just 12 are estimated to persist in Kidepo National Park and surroundings. North-West Africa the species stands at no fewer that 250 mature individuals (if that).
Within Iran the ‘sub-species’ of Asiatic Cheetah - A. j. venaticus (if still extanct) stands at some 60-100 mature individuals. We do like the fact the conservation trustee is a known hunter allegedly supporting Cheetah conservation. We’ve yet to see an real improvement of Iranian Cheetahs in the country (more money talk)…
The overall “known Cheetah population” for Asia and Africa is by far more threatened that the Lion. To date there are some 7,000 known mature individuals remaining within the wild but no greater than 10,000. This sadly make the Cheetah by far more threatened than Panthera leo. African Lion populations stand at some 15,000 to 13,000 maximum. As the Cheetah population will not likely exceed 10,000 individuals - the species therefore qualifies for (vulnerable status).
Nowell and Jackson stated that Cheetah populations in the past have undergone some alarming declines, now it would seem that history is re-repeating itself (this time the specie may not survive). The Cheetah exhibits remarkable levels of genetic diversity in comparison and compared to other wild felids, so there could be a high chance the species may make it back from the near brink of extinction within the wild.
Problem is poaching and over-hunting then wasn’t as prolific as it is today. Scientists stated that interbreeding among other individuals had saved the species from bottleneck declines in the past. This history dated back some 10,000 years. Sport hunting then wasn’t an issue as it is today, so in all fairness the species could be hunted into extinction illegally or legally (with much thanks to Cites on the ‘legal part’). So in all honesty we may lose the Cheetah before the Lion.
While the causes of the Cheetah’s low levels of genetic variation are unclear [back then], what is clear is that large populations are necessary to conserve it. Since Cheetahs are a low density species, conservation areas need to be quite large, larger than most protected areas. Major areas of the African continent are being overtaken by humans, agriculture to cope with human expansion and deforestation. No longer is it a case of ‘if’ rather than ‘when’….
MAJOR THREATS
Cheetahs are ‘hunted for sport and trophies’, as well as handicrafts products. Live animals are also traded - the global captive Cheetah population is not self-sustaining. Pest animals are also removed.
In Eastern Africa, habitat loss and fragmentation was identified as the primary threat during a conservation strategy workshop (2007). Because Cheetahs occur at low densities, conservation of viable populations requires large scale land management planning; most existing protected areas are not large enough to ensure the long term survival of Cheetahs. A depleted wild ungulate prey base is of serious concern in northern Africa. Cheetahs which turn to livestock are killed as pests. Conflict with farmers and depletion of the wild prey base are also considered significant threats in parts of Eastern Africa.
In Iran, the Asiatic Cheetah A. j. venaticus is threatened indirectly by loss of prey base through human hunting activities. In addition, most protected areas are open to seasonal livestock grazing, which potentially places huge pressure on the resident ungulate populations through disturbance and potential competition. Additionally, domestic dogs accompanying the herds present a likely threat to both Cheetahs and their prey. An emerging threat is the possibility of fragmentation into discontinuous subpopulations as a result of increasing developmental pressures (mining, oil, roads, railways); this is particularly the case in Kavir N.P., currently the north-western limit of the Asiatic Cheetah’s range.
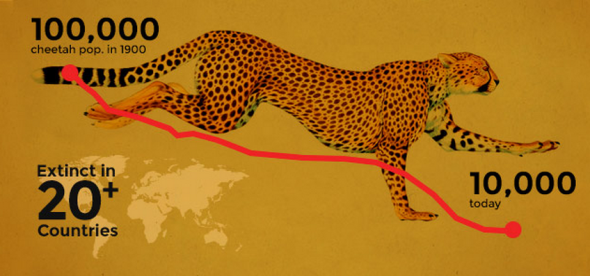 Image: Cheetah populations are more threatened than Lions.
Image: Cheetah populations are more threatened than Lions.
Conflict with farmers and ranchers is the major threat to Cheetahs in southern Africa. Cheetah are often killed or persecuted because they are a perceived threat to livestock, despite the fact that they cause relatively little damage. In Namibia, very large numbers of Cheetahs have been live-trapped and removed by ranchers seeking to protect their livestock (from government permit records, Nowell [1996] calculated that over 9,500 cheetahs were removed from 1978-1995). While removal rates have fallen, in part due to intensified conservation and education efforts, many ranchers still view Cheetahs as a problem animal, despite research showing that Cheetahs were only responsible for [3% of livestock losses] to predators. Although Cheetah in Iran have been killed because of predation on livestock, since 2003, there has been no direct evidence of killing Cheetahs, though it is likely most incidents go unreported.
“Cheetahs are also vulnerable to being caught in snares set for other species”.
Another threat to the Cheetah is interspecific competition with other large predators, especially lions. On the open, short-grass plains of the Serengeti, juvenile mortality can be as high as 95%, largely due to predation by Lions. However, mortality rates are lower in more closed habitats.
CITES [allows legal trade in live animals and hunting trophies under an Appendix I] quota system (annual quotas: Namibia - 150; Zimbabwe - 50; Botswana - 5). This was accepted by CITES as a way to enhance the economic value of Cheetahs on private lands and provide an economic incentive for their conservation. The global captive Cheetah population is not self-sustaining; Cheetahs [breed poorly in captivity] and in 2001 [30% of the captive population] was wild-caught. While analysis of trade records in the CITES database shows that these countries have reported almost no live exports since the late 1990s, Conservation groups are concerned that there is a substantial illegal cross-border trade in live animals.
There is also concern about illegal trade in skins, as well as capture of live cubs for trade to the Middle East. There is an increasing trade in cubs from [north-east Africa into the Middle East], but there is currently little trade in cubs from the Sahel region, where it was previously considered a major problem. Cheetahs are active during the daytime and there is concern that they can be driven off their kills by [tourist cars crowding around, or mothers separated from their cubs]. Burney (1980) conducted a study and concluded that [tourist cars did not seem to harm cheetahs, and in fact sometimes helped, as cheetah chases more often ended in a kill when there were cars around, distracting prey, providing cover from which to stalk, or otherwise waking Cheetahs up to notice prey in the area]. However, [tourist numbers have risen sharply by then, and its potential impact on cheetahs remains a concern].
The Eastern African Cheetah conservation strategy identified four sets of constraints to mitigating these threats across a large spatial scale. Political constraints include lack of land use planning, insecurity and political instability in some ecologically important areas, and lack of political will to foster Cheetah conservation. Economic constraints include lack of financial resources to support conservation, and lack of incentives for local people to conserve wildlife. Social constraints include negative conceptions of Cheetahs, lack of capacity to achieve conservation, lack of environmental awareness, rising human populations, and social changes leading to subdivision of land and subsequent habitat fragmentation. These potentially mutable human constraints contrast with several biological constraints which are characteristic of Cheetahs and cannot be changed, including wide-ranging behaviour, negative interactions with other large carnivores, and potential susceptibility to disease.
Disease is a potential threat to the Cheetah, as its reduced genetic diversity can increase a population’s susceptibility. However, the most serious disease mortality thus far documented in wild Cheetahs was from naturally occurring anthrax in Namibia’s Etosha National Park; Cheetahs, unlike other predators, do not scavenge carcasses of ungulates killed by anthrax, and thus [had no built-up immunity] when they preyed upon springbok sick with the disease. The Cheetah’s low density may offer some measure of protection against infectious disease; for example, Cheetahs were not affected by an outbreak of Canine Distemper Virus in the Serengeti National Park which [killed over 1/3 of the Lion population]. Serological surveys of Cheetahs on Namibian farmland indicate some exposure and survival of the disease.
We are losing the Cheetah faster than the specie of Lion. Although some regulations are in place with the species listed on Appendix I (Cites) its quite likely we’ll lose wild populations should hunting, poaching and unregulated hunting not stop now.
Thank you for reading.
Dr Jose C. Depre
Environmental and Botanical Scientist.
Sources; Cites, Red List, Wiki, Wild Forum, DEA, CCG, DSI, PHASA, Cambridge University, Oxford University.




