FACEBOOK: IVORY TRADE OFF THE SCALE | VIET NAM | PART I
FACEBOOK | IVORY TRADE IN VIET NAM
Written by Dr Jose C. Depre (Chief Environmental Officer).
By the time it takes me to finish this document an estimated 20-50 elephants will have been slaughtered. Once you turn your head and continue to do nothing, come tomorrow 100 elephants would have been killed for their ivory to supply the South East Asian black market. Back in January 2015 I launched yet another online and ground intelligence gathering operation relating to the illegal wildlife trade; We are focusing on China, Viet Nam, Laos, and Thailand of which the team, a twenty four strong experienced male and female unit originate from all backgrounds. Today I’m focusing more on the online trade which has now increased to worrying new levels.
Since January 2015 when [Operation Stop It] was launched Environmental Crimes Officers have found what we believe is a new trend of ivory trade in operation on the United States platform known as Facebook. External Affairs Officers became aware of the huge trade when investigating a Vietnamese national identified as Mr Trang from June 2015 to December 2015. Unfortunately since providing law enforcement agencies with masses of evidence just on this one trader; very little in the way of arrests and/or confiscations has been witnessed.
The ban on international trade in ivory was introduced in 1989 by CITES (Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora) after years of unprecedented poaching. In the 1980’s, an estimated 100,000 elephants were being killed per year and up to 80% of herds were lost in some regions. However despite the ivory trade ban in place, very little in the way of illegal trade reduction is being witnessed within Viet Nam, China, Laos, and Thailand.
Viet Nam is one country of interest that we’ve noted as hosting “unusually large amounts of (raw ivory tusks), most of which seem to be originating from impounded stocks, with other tusks clearly removed from ivory pyres”. While we are aware a large majority of ivory tusks are originating from Africa, there is also a significantly large amount also originating from Asia. Asian ivory tusks are more favored for carving over that of African elephant tusks.
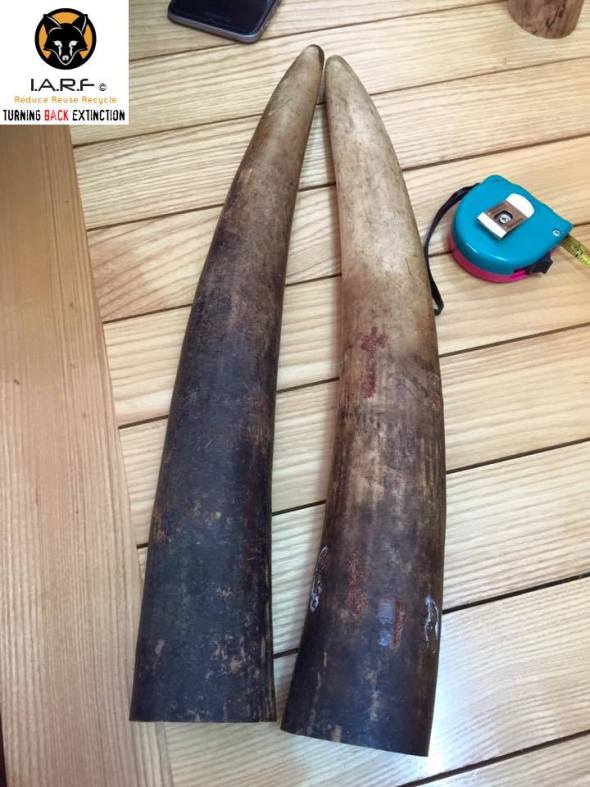
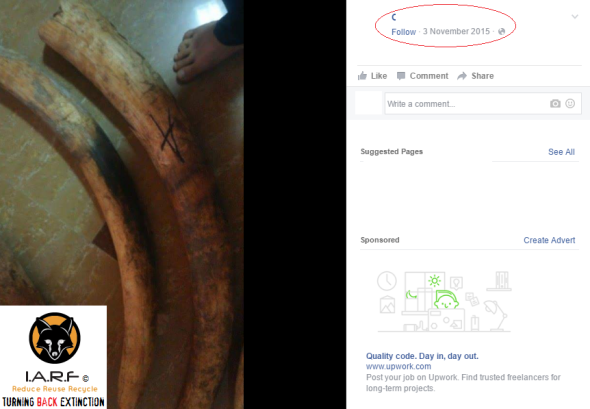
Image: Two tusks located for sale on Facebook 16.05.16 from | impounded or stolen from pyres?
The two elephant ivory tusks (pictured above) were located on Facebook for sale yesterday which we suspect have originated from a recent or past ivory burn. Normally ivory tusks are white, or a dusty creamy color with some dark tinges to them; embers can clearly be seen on the left hand tusk with visible white dehydration and salt marks too.
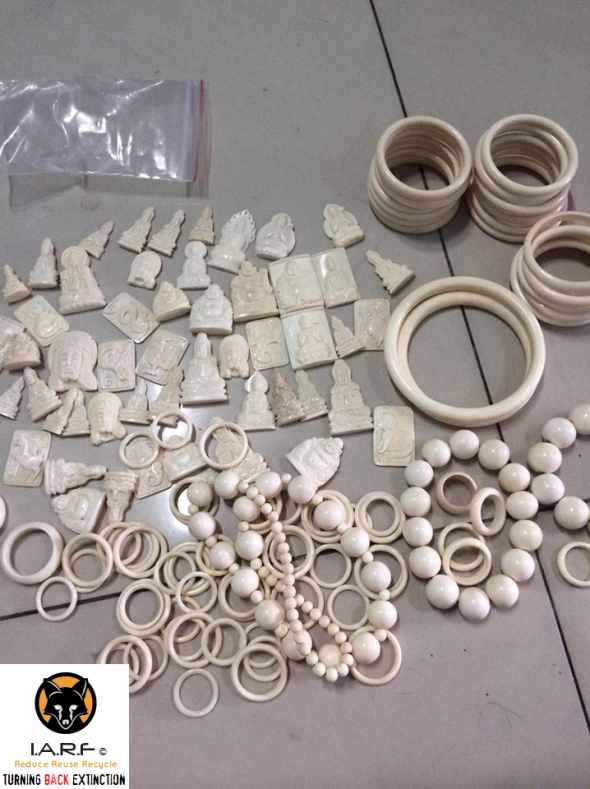
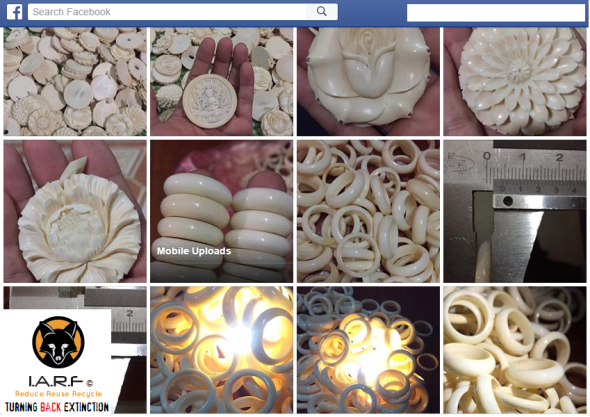
Image: Ivory jewelry smuggled from Africa into South East Asia now on sale on Facebook.
While the online trade is no big secret, the fact is Facebook hosts no terms and conditions in place that bans such illegal trade; the Facebook platform has no systems in place to recognize such imagery (I.e raw tusks) using BOTS that can then report back to a third party Policing team. Finally IARFA Environmental Crimes Officers have found Facebook is being exploited by many South East Asian citizens primarily from Viet Nam, and Thailand peddling ivory from Asia and Africa.
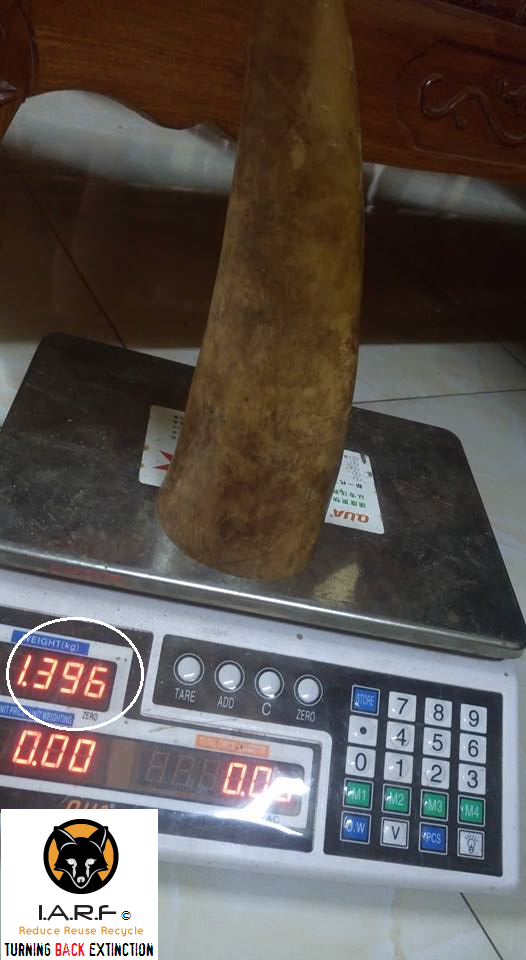
Image: Ivory trader weighs up tusks he is trading online via pseudo Facebook account shops.
The image above clearly demonstrates just has serious the ivory trade has become online and on the Facebook social media platform. Traders will commonly show their products to prove their wealth (I.e as a status symbol), or to prove/demonstrate the legitimacy of their products compared to other traders, that may be selling counterfeit ivory. The trader who we can only be name as Mr Phong then demonstrates just how much he will be making come the end of the month. The total amount of ivory Mr Phong is selling on Facebook (pictured above and below) will fetch him around $15,000-$20,000USD depending on how the ivory is sold and/or manufactured.
Image: My Phong weighs up this illegal haul of ivory, fetching him some $15,000-$20,000USD
Despite international and domestic trade bans nothing is actually working, furthermore we do hold concerning evidence that shows without a doubt many tusks are being removed from compounds in Asia and Africa then sold onto the very people that police took the ivory from. Police have been witnessed trading confiscated ivory at high prices back into the hands of smugglers knowing too well they are going to make a good wage due to the high demand for ivory tusk products.
Back in 1992 Viet Nam officially outlawed the ivory trade, unfortunately since the ban was implemented any ivory that was purchased before “Viet Nam’s ivory ban” can still be sold legally so as long as the tusks host the correct certification; Fortunately CITES did rule that “re-worked ivory or any tusks/ivory products that were purchased before or after the 1992 Viet Nam ivory ban that are then re-worked, would then be classed as new ivory (non-exempt) thus making that product that was legal - now illegal.
Meanwhile back in 1975 international trade in “Asian elephant ivory” was also banned. There has been quite a few tusks examined by experts and third party experts located on the United States Facebook platform as originating from Asian elephants. Asian elephant tusks are much smaller than your average African bush elephant tusks. Come the 1980’s it was then stated no fewer than 50,000 Asian elephants existed which are now listed on CITES Appendix One and known to [endangered].
One out of every six Hanoi citizens are dealing ivory on the United States Facebook platform. Most of this ivory is as explained originating from Africa and Asia, with clear and obvious signs of trafficking, and thefts from impounded ivory and ivory pyres.
Image: One of many thousands of online ivory trading Facebook shops in Viet Nam.
The image above was picked up from one of many thousands of Viet Nam ivory traders. Traders establish a sophisticated network of “pseudo Facebook accounts”. These accounts are rarely in the real name of the trader. Traces of some accounts via the IARF Environmental Cyber Crimes Unit have shown ivory traders using Virtual Proxy Networks [VPNs] to conceal their Internet Protocol Address.
Furthermore when dealing over the phone traders normally use cheap (non-smart throw away phones) so that should enforcement agencies locate them, tracing the traders exact whereabouts, and who they are selling ivory onto is almost impossible. Its not uncommon to witness traders with a number of cell phones. One phone (the throw away one) will be used for trade and can easily be disposed of with all evidence destroyed containing names and numbers of ivory dealers and buyers. Meanwhile smugglers, traders and carvers also host a smart phone for normal everyday conversations and general surfing the web or interacting with friends and family on Facebook, Twitter or Weibo.
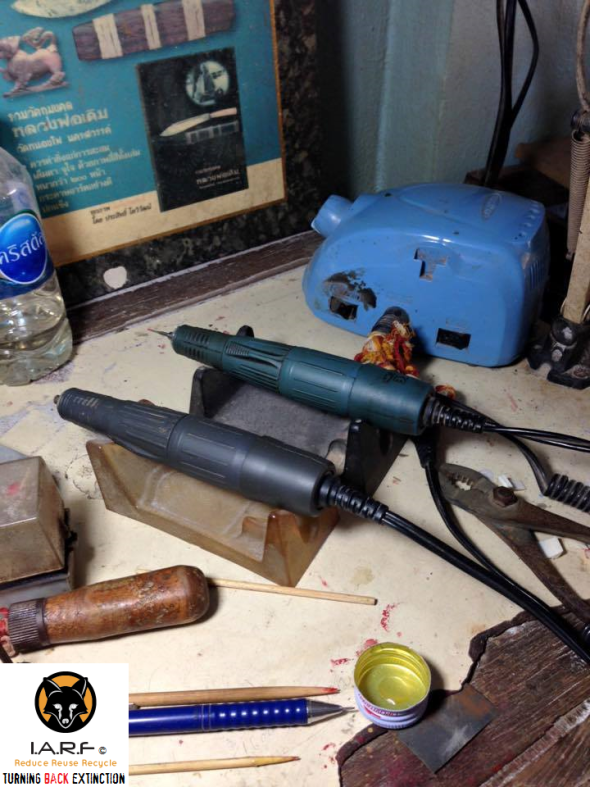
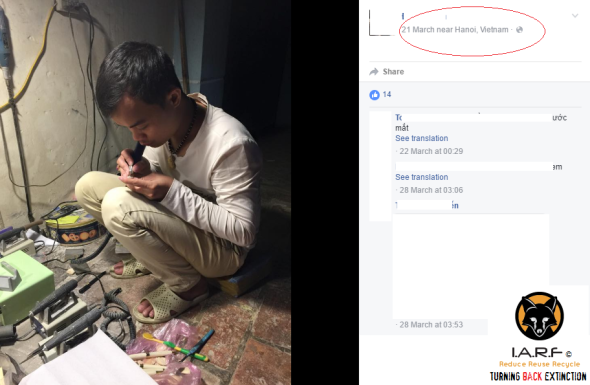
Back in March of 2016 International Animal Rescue Foundation’s- Environmental Crimes Officers located three Viet Nam ivory trading carving factories all advertised on the United States Facebook platform. Moreover it wasn’t just carvers and ivory advertised for sale; we also located evidence of ivory carving tools, measuring and weighing instruments and “DIY ivory carving instructions for beginners”. The carving instruments below were found in one Hanoi carving workshop (on the Facebook social media platform), meanwhile underneath the bottom image is proof of more raw ivory tusk carving.
Image: Ivory carving tools, Viet Nam, Hanoi used to intricately carve ivory.
Image: In the same carving room more raw ivory tusks were located readied for carving on Facebook.
Environmental Crime Officers have located a staggering 80,000 “ivory and wildlife trade shops” all in operation on the United States Facebook platform, yet little if anything is being done to stop this trade or even restrict traders activities. When submitting this evidence with films, images and Facebook accounts and the current laws on ivory trade to Facebook’s Security Head, Alex Stamos we we’re unfortunately ignored.
Yet Facebook’s moderation team are quite willing to remove accounts that have violated their “bullying, harassment or terrorism polices” (all of which are crimes), sadly the social media platform is unwilling to remove highly active wildlife traders breaking domestic and international wildlife laws that are making a ton daily.
On the 3rd March 2016 the BBC reported “Facebook wildlife trade prompts fears among environmentalists”. Traffic - an Environmental Crimes Investigation Organisation located hundreds of online profiles selling endangered and threatened animal species. Facebook stated “It will not hesitate in removing content that is promoting such trade”. Yet when we contacted Facebook submitting more than enough evidence relating to ivory, rhino horn, tiger and pangolin trade all accounts are still in operation.
Facebook did quote though “They are developing practical solutions to combat trade“, unfortunately these solution’s seem to aimed only at “animals rather than animal parts”. For the time being Facebook has no terms or polices in place that would remove illegal wildlife traders dabbling in rhino horn, tiger parts, pangolins, or [non-exempt] ivory. And with some 1.32+ billion Facebook users, Facebook will we believe now have a large job on their hands in combating such trade as from 2014 trade on the Facebook platform has exploded.
“Investigators are concerned that the use of social media and smartphones means that anyone interested in selling wildlife can rapidly access huge numbers of potential buyers”….
Image: More ivory Facebook shops churning out thousands of euro in ivory, all from raw re-worked tusks.
While Facebook has stated they are developing new measures and applications to combat trade, these new measures and whatever applications will be made to combat trade are all too late. Facebook is probably one of very few platforms where you can actually create “private groups”, where only those that are interested in such trade can enter and interact with other users.
Moreover Facebook provides you secrecy in relation to pages; I.e: Traders can censor which countries they don’t want to view their pages then continue trading whatever they like. In relation to pages there are ways and means around that censorship, which will not be published hereto.
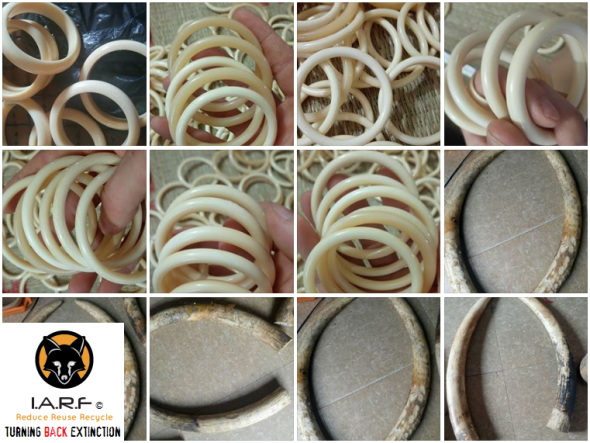
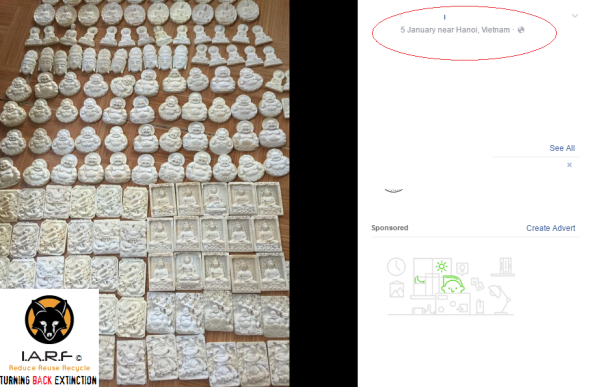
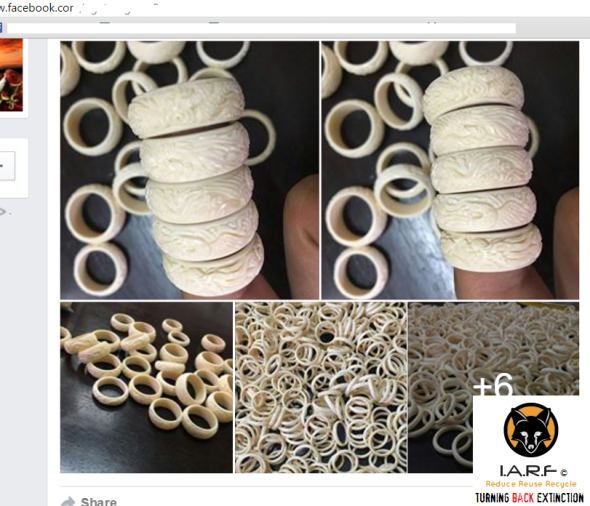
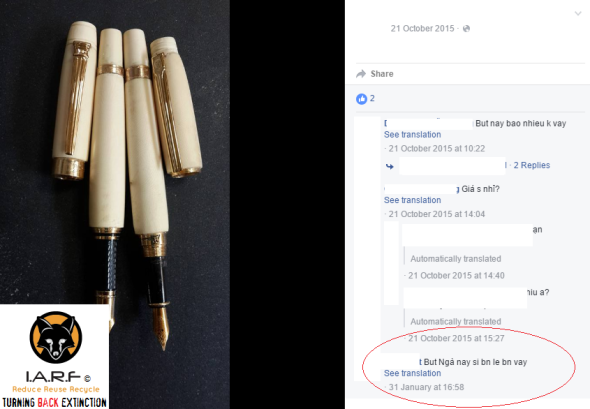
One of the largest items we are seeing traded on Facebook is that of ivory bangles, ivory necklaces, ivory wrist bands, ivory chopsticks, ivory pens, ivory encrusted watches, ivory sex toys and ivory cigarette holders (in the thousands). Overseas tourists that visit Viet Nam are often caught or witnessed buying these small cheap products, and the longer they (the tourist) purchase from ivory carvers and traders, the longer demand will continue to increase and fan out. That is one area of the trade we need all be focusing on (demand) to nip in the bud sooner rather than later.
Ground Sales Survey of Ivory:
Back in 2014, a total of 1614 ground outlets were surveyed in 21 localities throughout Viet Nam. Eighty-five of these outlets (5%) were found to have a total of 2300 ivory items for sale. Buon Me Thuat city was found to have the highest percentage of shops (50%) offering ivory. However since CITES has placed more pressure onto Viet Nam to clamp down on ivory and other wildlife trade, these shops are slowly reducing trade, although we do highly suspect traders are now operating more freely on line from which policing this area of the trade is more difficult.
While it was stated that many shops on the ground had increased somewhat, law enforcement in Viet Nam has allegedly made it more difficult for traders to openly trade ivory that has no exemption. Its is for this reason we now believe Facebook is being used more and more to trade ivory products, and as one can see in the images above - we are talking massive amounts of ivory pieces and products, 90% of which hosts no certification, furthermore the vast majority of traders we’ve located are carving products from “smuggled ivory”.
It is presumed that the currency in which the price is listed or quoted in many ivory surveys may indicate the nationality of the most common buyers in that area. Both observations and questions to particular sellers substantiate the fact that ivory is sold to both “foreign tourists and Vietnamese nationals”. For example in HCMC, the majority of the ivory buyers in the two markets are assumed to be tourists from China as prices were quoted in Chinese Yuan.
Video: Bryan Christy examines the illicit ivory trade. Interesting we have also have located a number of “counterfeit tusks that are being traded online and on the ground”. Please stay tuned for article two that will delve a little deeper into both the counterfeit rhino horn, ivory and tiger part trade.
The HCMC silver and gold shops that also offered ivory (particularly the smaller, religious pendants and figurines) appear to be targeting Vietnamese buyers with prices advertised in VND. In Dak Lak and Ha Tien, the majority of the ivory buyers are assumed to be Vietnamese tourists as prices there were quoted in VND. In Ha Noi, prices were mostly given in USD when enquiries were made, which may indicate that the buyers of ivory pieces are likely to be international tourists.
While the majority of ivory is presumed to be aimed at mostly Asian tourists - there is no real hard hitting evidence that this is in deed true. For example if you was British you’re hardly going to purchase an ivory bangle in GBP, so exchanging that currency into Vietnamese dollars then places that ivory for sale (at just about everyone and anyone) with the correct currency.
It may be somewhat of a shock but the UK is the third biggest source of intercepted illegal ivory entering the United States of America (US), which has been singled out by CITES (the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora) as a ‘problem country’ with a large domestic ivory trade likely to provoke illegal elephant poaching if not regulated and brought under control. London’s Portobello Road – the biggest antiques market in the world – has been identified as the single major source of this illegal ivory.
Furthermore while antique ivory trade is “problematic” so too is non-antique and the longer these trades persist, more and more elephants will be slaughtered for their tusks. We are growing very concerned now at the large number of ivory dealers operating on Facebook. There is clear evidence that much of this ivory is originating from both Africa and Asia, furthermore as explained - the large number of “raw tusks we are locating clearly shows that security is indeed more than questionable at ports, and pounds that hold confiscated ivory.
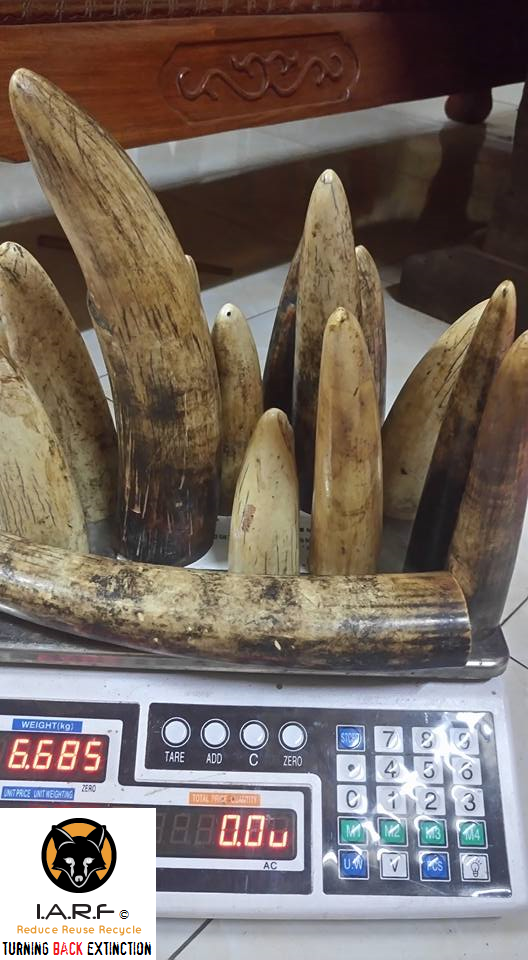
Image: Raw African ivory tusks, cut and sold onto Viet Nam carvers, on sale on Facebook.
Back in 2015 (just before Christmas) External Affairs Environmental Crimes Officers located an “unusual amount of raw tusks from Africa” that we suspect had made their way into Viet Nam from China. IARFEIA Officers located on the Facebook platform some 21 whole raw and non-certified elephant tusks, some of them even had blood around the bases indicating these were freshly poached ivory tusks; all of which is in violation of both domestic and international ivory trade laws.
Image: Vietnamese ivory carver aged 19 from Hanoi, Viet Nam.
The image above doesn’t really show much does it? although the other images below shows exactly what this talented young man has been creating from raw African and Asian elephant tusks (and is still creating today with his freinds - all college students). Ivory traders and dealers make no attempt at concealing their identity anymore neither. However there still remains a hardcore number of dealers that will continue to conceal their faces, names, and never post images onto Facebook that depicts them holding raw non-exempt ivory. This belief that ivory traders, peddlers, and smugglers were all but old, is now a myth. Today we’re witnessing traders and carvers as young as 16 years old, taking over from their parents thus fueling the ivory trade evermore on Facebook.
Image: Young trader named as Mr Manh exhibits his newly carved ivory pieces on Facebook.
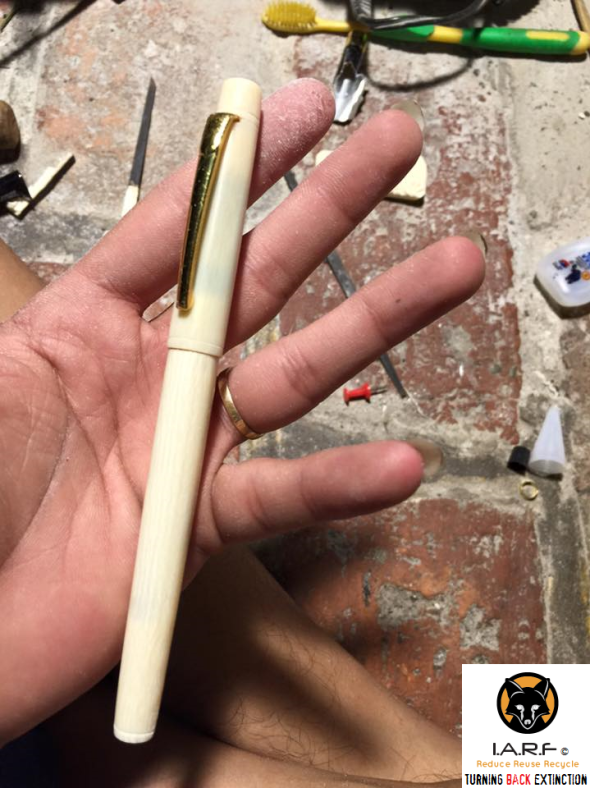
Image:Mr Manh proudly shows one of many hundreds of ivory pens that are in great demand.
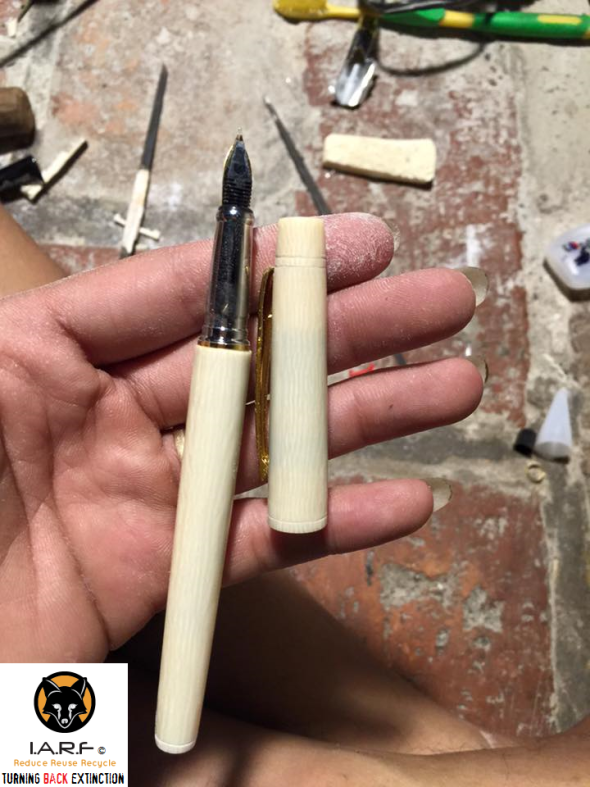
Image: Ivory pen with top off, Viet Nam, Hanoi.
Image: Ivory trader identified as Mr Trang proudly displays carved ivory on Facebook for sale.
Image: More freshly carved ivory cartridge pens on sale in Hanoi, via Facebook.
From 2015 (to date) IARFA Environmental Cyber Crimes Officers and the ground team External Affairs Environmental Crimes Officers have found that Viet Nam is “suspected” of peddling more ivory than China and Thailand. Cyber Crimes Officers are now locating every week on average of 2-3 “raw tusk dealers” operating on Facebook. Meanwhile the database of 80,000 ivory and wildlife trade dealers all operating on Facebook continues to increase by the week.
The whole purpose of this article is to wake people up, and open their eyes. We have a major problem on Facebook, and Alex Stamos Facebook Head Security Officer doesn’t seem to be taking much notice of this ongoing and rather concerning problem relating to just the ivory trade alone. We’ve not got much time left, there is an estimated 50,000 Asian elephants in Asia, and “known - some 600,000 African elephants remaining on the continent of Africa with a probable 1.2 million known but (uncounted).
Facebook has become a hotbed for the lucrative and illicit most illegal wildlife trade. And for the time being not a single thing is being done to control this trade. Please sign the petition hereto: http://www.thepetitionsite.com/645/521/701/facebook-remove-illegal-pet-and-wildlife-traders-from-your-server/
“The Extinction Clock is Ticking”
Thank you for reading.
Chief Environmental Officer, Dr Jose C. Depre.
Environmental Crimes Department.














Thank you for your reply, should it merit a response we will respond in due course. This site is owned by International Animal Rescue Foundation and moderation is used.