Environmentalism chapter 15 - Protea
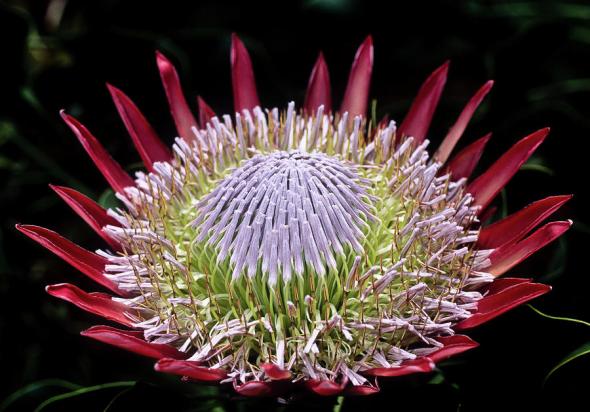

In 2012 I read an article that Sir David Attenbourgh had documented on, followed by a short video that he himself and various botanists had narrated explaining the critical conditions of which our cynaroides where at or better named as the “Protea” family one of the most beautiful sub-tropical plants in the world that’s thrived for on the earth for some three hundred million years and has been left relatively untouched until climate change hit us.
The Protea compromises some eighty genuses with a total of sixteen hundred known species that we are aware of to date, this does not though include species that have been cross breed and haven’t been registered with organisations such as the Royal Horticultural Society, or the Protea Society of South Africa where it thrives and mainly originates from.
A genus “explained” in botanical terminology is a low-level taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms, which is an example of definition by genus and differentia. Genera and higher taxonomic levels such as families are used in biodiversity studies, particularly in fossil studies since species cannot always be confidently identified and genera and families typically have longer stratigraphic ranges than species.
The term derives from “Latin” meaning “descent, family, type, gender”, cognate with Greek: γένος – genos, “race, stock, kin” whereas a “species” a species is often defined as a group of organisms capable of interbreeding and producing fertile offspring.
While in many cases this definition is adequate, the difficulty of defining species is known as the species problem. Differing measures are often used, such as similarity of DNA, morphology or ecological niche. Presence of specific locally adapted traits may further subdivide species into “infraspecific taxa” such as subspecies (and in botany other taxa are used, such as varieties, subvarieties, and formae).
Species hypothesized to have the same ancestors are placed in one genus, based on similarities. The similarity of species is judged based on comparison of physical attributes, especially their DNA sequences, where available.
All species are given a two-part name, a “binomial name”. The first part of a binomial name is the generic name, the genus of the species. The second part is either called the specific name (a term used only in zoology) or the specific epithet (the term used in botany, which can also be used in zoology). For example, Boa constrictor is one of four species of the Boa genus. The first part of the name is capitalized, and the second part has a lower case. The binomial name is written in italics.
The Protea is under great threat and vast awareness of this stunning species of botanical plant now needs to be pushed more aware before we lose one off if not the second oldest living organism on the planet to date. Protea is both the generically and common identification for the plant that is better known to amateur gardener’s as the sugarbushes. They have some of the most spectacular flowers and fleshy cactus like foliage that attract an array of insects from bees, thrips, to butterflies and humming nectar birds.

Professor Carl Linnaeus was the first botanist to locate the Protea family of which he named it after the Greek god Proteus, Professor Linnaeus is the Swedish botanist that invented the botanical bionomical naming system that now helps us to identify many animals and plants to their exact generic make up and species. The genus of Protea was discovered by Professor Linnaeus in 1735 although it had lived on the earth way before Linnaeus had discovered it some millions of years that other botanists and botanical archaeologists had discovered through fossil finds.
The Proteaceae family to which Proteas belong is an ancient one. Its ancestors grew in Gondwana, 300 million years ago. Proteaceae is divided into two subfamilies the Proteoideae, best represented in southern Africa, and the Grevilleoideae, concentrated in Australia and South America and the other smaller segments of Gondwana that are now part of eastern Asia. Africa shares only one genus with Madagascar, whereas South America and Australia share many common genera this indicates they separated from Africa before they separated from each other.
The Protea attracted the eyes of Botanists in the seventh century when exploration teams set out to identify many species of mammalians, aquatic and reptilian species to horticultural species at the Cape of Good Hope where they “thrive” to certain a degree at this geographical location. http://goo.gl/maps/08ott Proteas where then introduced to the European Union in the Eighteenth century of which they were relatively accepted as an expensive decorative plant used in dress making and mainly Milliners which really didn’t catch on to the male “hatters”.
Most Proteas apart from a handful of species are located in South Africa within the Limpopo region, other species although only three in many small numbers are located next to and within the Mount Kenya National Park at this geographical location point, http://goo.gl/maps/Qt4q1
During and after apartheid in South Africa the Springbok and Protea was treated as a national emblem that many people respected both species, keeping to the Protea’s history this plant after apartheid was declared like a weed all over Africa with many people growing the national emblem in their gardens thus keeping lush, green and extravagant species blooming and thriving.
History and climate is changing though and we could now be looking at a massive global wipe-out of the Proteaceae family that are millions of years old, although there some as listed on the International Union for Conservation of Nature only five species of Protea so far of which one is “now extinct” Partula protea, Protea comptonii “near threatened” Protea curvata, “vulnerable” Protea laetans, “vulnerable” Protea lanceolata, “vulnerable” these species compromise many hundreds of now reducing living organisms of the same family that are in grave danger and it seems as each one to two years pass there is another species added to the list raising great concerns with environmentalists and botanists alike.
The Protea cryophila (snow protea) pictured below is also under threat which is listed as near threatened one of a cherished handful of beautiful flowered plants that live in a form of protective captivity out of reach from the earths destructive environment and man and woman that are to blame for this magnificent botanical species now coming under great threat of near extinction.

Protea cryophila is a Near Threatened shrub, which is notoriously hard to find in flower or producing seed. It survives a wide range of weather conditions, from extremely hot and dry in the summer, to freezing cold and covered by snow for weeks in the winter. When flowers do appear, they take a full year to open, and individual plants seldom bear more than three or four flowers, despite reaching up to 70 years of age. The specific epithet cryophila means ‘lover of cold’.
The snow Protea is restricted to the Cederberg Wilderness area of South Africa. It grows mainly in the small snow belt of around 25 km in length, and between 1,750 and 1,900 m above sea level, in the Cederberg Mountains. It is confined to two of the highest peaks, and grows in sandstone soils on rocky ledges and scree slopes.
A prostrate shrub forming dense, tufted clumps, the snow protea grows to 0.5 m tall and 1-3 m wide. It has a single main stem and creeping branches. The leathery leaves are 300-500 mm long, 50-70 mm wide, folded lengthwise and are clustered at the tips of branches. The striking flower head is 130-160 mm in diameter. The basal bracts are pointed and reddish-brown. The involucral bracts (leaf-like structures around the edge of the flower head) are pointed, with a white, woolly-haired outer surface and a carmine inner surface. The centre of the flower head, containing the mass of individual flowers, is creamy white to pink. Flowering occurs from January to April and yet we could see it banished from earth very soon.
Its threat –
Adult plants do not re-sprout, and are killed by fire, which is a major cause of the decline of “this species” not others. Global warming is now also a serious threat, as the Snow Belt is receding rapidly every year and the snow Protea cannot keep pace. The snow Protea rarely flowers in the late autumn and winter, as it depends on the snow as a cue and in recent years the snowfall has been minimal and sadly that is in just a short paragraph what all species of the Proteaceae family now face.
Cultivation of this species at lower altitudes have proven unsuccessful as it is a winter flowering shrub, by moving it to lower but more or less the same environmental living conditions regrettably all attempts to now try and save the species are failing. We all need your help to keep this species alive.
Although much funding and support is being flooded into preserve these stunning species we are sadly losing them at an alarming rate. The International Protea Foundation has achieved some very positive results in the last thirty years that has created more budding species however as each one is created the problem is “keeping them alive and spreading the seeds” then of course retaining the million year old species which is proving very difficult to many botanists and environmentalists of which Sir David Attenbourgh I do remember quoted “man is a parasite to the earth” and “unless the earth’s population doesn’t start decreasing then we will lose many species of plant and animal life”.
Protea destruction and threats;
- Climate change that is creating drought, flooding, sudden high and low’s
- Increased warmer winters that are effecting the near threatened “winter Protea”
- Pollution both acidic rain and debris
- Habitual destruction, Cape of good hope has seen many species lost due to urbanization
- Land fires that would normally generate fresh seed have come to soon thus wiping out habituated areas to whole plant species.
- Flooding
- European species are facing decline now from as pollinators are in danger mainly bees from CCD (Colony Collapse Disorder)
- Smuggling – although unheard of the flowers can sell for approximately $100 “each” on the market and many people are now taking the flowers to even digging the entire plant up and then profiteering for these species which unfortunately sees a massive decline in their species.
- Lack of reproductive plants means that the seed banks are also extinct in the four populations where plants have not been recorded.
- Over cattle grazing
- Brush cutting
- Chemical pesticides, insecticides, herbicides and general pollution
- Shoddy road side maintenance/lack of environmental supervision that has seen whole species wiped out
- Invasion of a fungal pathogen plus pests and diseases
- Fire to increase germination has been systematically started to soon either accidently to intentionally
- Human misunderstanding for instance this example that almost saw the P.oderata listed on the CITES appendix as of a misunderstanding of what CITES actually is and (undertakes) by the South African Management Authorities SAMA. The listed the plant which is “threatened” failing to provide to CITES the real reasons as to WHY it should have been listed that almost saw the plant wiped out die to human negligence and lack of education to understating. CITES quotes “that the species is dependent on the conservation of its habitat, and if anything (active trade should be encouraged) and not banned that would have been most certainly this plants death fall. Had CITES not of remove the species despite it being near threatened then we would of lost another.
Recent highlighted documentaries stated;
Proteas were chosen as the species to be studied for several reasons, according to Tony Rebelo, a researcher with the NBI who initiated and coordinated the PAP project. The flowers are charismatic and fairly easy to identify. More important, the distribution of Protea species is strongly correlated with that of other major plant groups in the region, which makes them good indicators of diversity patterns.
Of the roughly 370 Protea species found in South Africa, 350 occur in the Cape floristic kingdom. More than 120 species are currently listed as endangered or threatened by the Red Data Book, an internationally sponsored list of endangered and threatened species.
Fire plays a vital part in the fynbos ecosystem and is essential in the distribution and germination of the plants’ seeds. The king Protea (Protea cynaroides) releases its seed only when the heat of a fire opens the plant. The seeds fall to the ground and germinate when it rains. The seeds of the pincushion Protea (Leucospermum tottum) are buried in the ground by ants, and germinate only when mature plants have been killed by fire.
Spreading the Conservation Ethic
Researchers at NBI, the University of Cape Town, and the University of Connecticut in the U.S. collaborated to use the PAP data to develop a “climate envelope” for each species. They identified necessary factors like soil moisture content and temperature parameters in which each thrives. The data enabled the researchers to project what the impact of a variety of climate-change scenarios might be.
Under the most extreme climate-change scenario, one-third of all fynbos protea species could lose their range completely by the year 2050. Only 5 per cent would be likely to retain more than two-thirds of their range. These findings are now being extrapolated to other fynbos species.
The information has also proved helpful in devising conservation strategies. The findings contributed to the Cape Action Plan for the Environment, a systematic conservation plan for the entire Cape floristic region. They are also benefitting efforts to identify and protect species on local mountain ranges as well as remaining fragments of natural vegetation on the Cape Flats, a sprawling, built-up area consisting mainly of low-cost housing.
The PAP data have also proved exceedingly helpful in compiling a new fynbos map. The approximately 250,000 records on about 60,000 localities provided far more detail than has been possible to draw from satellite data, which tends to be distorted by alien vegetation.
The information will also be used to update the World Conservation Union’s Red Data List, Rebelo says. The list is called the world’s most comprehensive inventory of the global conservation status of plants and animals.
But perhaps the most important impact of the study was the community involvement. A follow-up survey of volunteers shows that the participants, their immediate families, and their friends gained a better understanding of the fynbos and became more aware of the conservation ethic.
In 2005 it was stated;
A recent study of hundreds of species of Proteas that live only near Cape Town, South Africa, estimates that the plants’ abundance will decrease by more than 60 per cent by 2050. Some Proteas will become extinct. Some already have.
When summer comes to Cape Town, Proteas bloom in riotous colour. On steep, rocky slopes strewn with lichen-covered chunks of granite, the flame-red and magenta-pink flowers dot the hillsides. They attract hordes of tourists and provide jobs for thousands of South Africans who gather Proteas for the worldwide cut-flower industry.
With their vase-shaped bracts surrounding pencil-thin flowers, “proteas look like sea anemones,” said Cheryl Andrews of Orlando, who uses Proteas in the floral displays she designs for large hotels such as the Ritz-Carlton and JW Marriott. “Proteas are named for the Greek sea god Proteus, who could change his form at will. Indeed, there’s a Protea in any unusual shape you can imagine.”
In the Washington area, “buyers attracted to exotic or tropical arrangements love South African Proteas,” said Neil Bassin, owner of Buckingham Florist in Arlington. “But these beautiful flowers might not be around much longer.”
Proteas such as the king Protea, which measures 12 inches across and is the national flower of South Africa, are under enemy fire. In a region where average temperatures have significantly warmed over the past 30 years and suburbs are sprawling up hillsides, Cape Town’s most unusual flowers are besieged, said scientist Lee Hannah of Conservation International.
“In response, Proteas are moving uphill themselves, to cooler spots with less development,” said Hannah, who published results of a study of the effects of climate and land-use change on South Africa’s Proteas in the March issue of the journal BioScience. Some Proteas are already extinct, said Hannah and Guy Midgley, a scientist at the South African National Biodiversity Institute in Cape Town.
Many species have such a tiny range that plowing a field or building a single house can wipe out the world population.
Hannah recently testified before the U.S. Senate Committee on Commerce, Science and Transportation on the impacts of climate change and land use on biodiversity. “I brought cut Proteas with me to the hearing,” he said. “It might have been one of the last glimpses of these flowers.”
More than half of the world’s several hundred Protea species are threatened, Hannah said. Most live in South Africa, but there are several in Australia, and some have been transplanted to Hawaii’s steep-sided volcanic slopes. South Africa has designated 35 Proteas as “endangered with extinction” and 46 as “vulnerable to extinction.” Another 76 are listed as “rare.”
Proteas are the keystone species of South Africa’s Cape Floral Kingdom, the smallest but, biologists say, richest of Earth’s six plant kingdoms. The Cape Floral Kingdom, Hannah said, “is the size of a postage stamp, comparatively speaking. But it has the highest plant biodiversity anywhere on the planet Earth. About 8,000 plant species, three-quarters of which live nowhere else in the world, are found there, in what’s called the fynbos ecosystem.”
The report then explained;
Leathery-leaved fynbos plants cover the mountains, valleys and coastal plains near South Africa’s Cape of Good Hope. “Amazingly, Proteas thrive in the nutrient-poor soils and high winds there,” Hannah said.
In the continental United States, the sole place similar to the Cape Town fynbos ecosystem is near Fallbrook, Calif., north of San Diego. There, several Protea growers are coaxing South African Protea species into bloom. “It’s much cooler here than elsewhere in the region,” said Danielle Kendall, co-owner of Kendall Farms, which grows Proteas on treeless hills resembling those of South Africa. “We have a similar soil type to that of the Proteas’ homeland and constant stiff ocean breezes.”
One farmer in Fallbrook shuttles back and forth from California to Cape Town, tending Proteas in both hemispheres.
For a short summer season, large evergreen Protea shrubs are laden with flowers that, many visitors to South Africa say, might have come from a faraway galaxy. In fact, Proteas came not from another place, but another time. They are remnants of the distant past, when Africa, Australia, India, South America and Antarctica existed as one landmass, called Gondwana.
Through the process of plate tectonics, Gondwana began to break apart about 130 million years ago. By 65 million years ago, about the time dinosaurs became extinct, the continents had divided into positions resembling their present-day configuration. Proteas once thrived on Gondwana; today members of the Protea family live oceans apart.
The last of Earth’s Proteas grow in places known as hot spots, Hannah said. “Hot spots are regions with high numbers of plants and animals found nowhere else in the world, and that have had more than 70 per cent of their natural habitat destroyed. The last thing this species-rich, high-habitat-loss areas need is another threat, but that’s what climate change presents.”
As Earth’s climate warms, species will try to keep pace, moving to their preferred temperature ranges. Protea seeds are carried on the wind to new locations. Those that become rooted in cooler areas will survive.
“Climate change affects plants and animals,” Hannah said, “when they can’t move far enough to escape global warming.” Of 300 species of Proteas near Cape Town, the ranges of nearly all will have to shift by 2050, he said.
Conservation plans that allow species to relocate are an answer, Hannah believes. “It’s something of a new idea, as most of our conservation efforts currently focus on parks, which are fixed in place. However, when a species starts to move, we need a ‘park’ not only where the species is today, but where it will be in the future. We also need protected ‘connectors’ that will allow it to get from point A to point B.”
South African biologists involved in the Protea Atlas Project, an effort to collect information on Cape Town’s Proteas, are providing insights into how climate and land-use change will affect fynbos species, Midgley said.
Tony Rebelo, a biologist at the South African National Biodiversity Institute, said Proteas were chosen as the best species for the project because they are easy to recognize and their distribution is similar to that of other major plant groups in the fynbos.
According to Rebelo, the Greek god Proteus could predict the future. However, Proteus did not willingly part with the information.
“He simply changed his shape and escaped,” Rebelo said. “So we must grasp Proteus tightly this time and make sure that no more of our Proteas become extinct.”
Sherry Moretti, a floral designer at Bellagio, a hotel-casino in Las Vegas, agrees. “I wanted something breathtakingly gorgeous for Bellagio’s opening a few years ago,” she said. “On that special evening, Proteas lined the entrance, bedecked the foyer, and graced every table.
“I can’t imagine an earth without Proteas. They welcome you through the portal, and into another world.”
If you would like to learn more on how you can help the preserve your countries botanical species to even getting your children involved with simple 1-2-3 step horticulture please email myself
Dr J C Dimetri or Dr J Willimson or you can join our online botanical group which you would need to email our administrators a request asking to be added to the group on Facebook of which anyone can join.
For more information please email us at;
Phone our main office at +004401603613367
Or Skype me the CEO at Joseph.Dimetri for an informal chat;
If you would like our team to visit your school, college, or university please contact us at the above address.
Thank you
Environmentalism - Chapter 14 Plastic pollution

Environmental pollution will be the future war to come - Who’s the enemy? Ourselves!.
Plastic is taking its toll on our wildlife which is killing many species of marine life and harming smaller new born aquatic species crating a life of misery and pain which effects not just costal animals but land and avian to.
Pollution is not just responsible for flora and fauna death, please don’t just take me on that word, YOUR the one that’s (going to responsible) for the birth mutations, breathing defects, cancerous cells to form, to land invasion of our own waste. It’s OK though as most of you will just flick through this and not give a damn. The quote I am rapidly become pissed of with (we only live once) is starting to grind on me, WE MAY but what about our generation of children’s children and theirs to come?.
The average family of four mother and father and two children will consume in one week bathroom/toiletry/cleaning containers/packaging, non-essential food containers (e.g. takeout food containers), drink bottles/milk jugs, essential food containers/packaging and other miscellaneous plastic trash (e.g. candy wrappers, snack bars) and this is still in a recent survey form 2012 that sees no reduction in the amount. People this is serious and needs addressing urgently. These items do not include “outside the family too” of which in the commercial working world one is using by far more from water bottles, to food packaging or plastic carrier bags.
The worst offenders are the family and the hypermarkets which still are not being eco-friendly to our environment in cutting the usage of bags or at least offering some form of “bag drop of point” that the member of the public can walk freely in to the hypermarket and purchase or freely obtain a carrier bag thus reducing “production + carbon emissions + usage = (recyclability)
On average the American “individual” not (family) uses between 300 and 700 plastic bags per year we have picked America as they are in the top three polluting nations of the planet with China coming first and India third, and regrettably the (family) will use to the nearest figure based on governmental and consumer data twenty thousand carrier bags per year per that’s a lot and still much of this is not being reused, recycled or placed in the “recycling bin” that ends up in waste dumps or within the oceans.
Shoppers worldwide are using approximately 500 billion single-use plastic bags per year. This translates to about a million bags every minute across the globe used. (Think that’s shocking?).
- If you joined them end on end they would circumnavigate the globe 4,200 times.
- 100,000 marine creatures a year die from plastic entanglement and these are the ones found.
- Approximately 1 million sea birds also die from plastic.
- A plastic bag can kill numerous animals because they take so long to disintegrate. An animal that dies from the bag will decompose and the bag will be released, another animal could harmlessly fall victim and once again eat the same bag.
- The floods in Bangladesh in 1988 & 1998 were made more severe because plastic bags clogged drains. The government has now banned plastic bags.
- In Ireland they introduced a 15c plastic bag tax and reduced their usage by 90% in one year. It is now 22 cents. (Yet this method is not really being put to practice across the globe)
- There are believed to be 46,000 pieces of plastic in every square mile of ocean.
- There are 5 ocean gyres in the world where plastic gathers due to current circulation. These gyres contain millions of pieces of plastic and our wildlife feed in these grounds.
- Every year, 6.4 million tonnes are dumped into the ocean. This is the same as 3,200 kilometres of trucks each loaded with garbage.
- At least two thirds of the world’s fish stocks are suffering from plastic ingestion. (You still eating fish?)
The upsetting fact is this more than a billion people around the world do not have access to safe drinking water. Most countries that buy bottled water have the luxury of quality tap water, yet despite this YET! And here is the point that I really would like you all “pay attention to”.
Americans consume 8.6 billion gallons of bottled watered a year. Yet there are very few water holes in third world nations of which they are families “dying for water” and children “dying from lack of (clean) water” you have the choice to reuse your water bottle and obtain the water from a tap yet you simply throw it away as (it’s dirty?) or you listen to the likes of Alex Jones (non-educated) and other non-qualified environmentalists and geologists quoting water is unsafe as it contains (fluoride) – You seriously are kidding yes?
The Bottle TRUTH;
- FACT – every year Americans use 91,733,000,000 (BOTTLE’S of water a year)
- FACT – every year the entire globe use 563,829,000,000 (BOTTLES of water a year)
- FACT – for every 12 ounces of water bottled 36 ounces are consumed
- FACT – 40% of bottled water comes from the tap and 0% has to adhered to governmental standards
- FACT – every year 17 million barrels of water are used to produce bottled water, that’s 340 million gallons of gasoline
- FACT – only 1-5 bottles are recycled
- FACT – the other 4 contribute to the three billion pounds of plastic water bottles added to land fills
The plastic TRUTH;
- 12 million barrels of oil are used to make the plastic bags consumed in the U.S. annually.
- Plastic creates 4 times the solid waste vs. paper bags; enough to fill the Empire State Building 2 1/2 times a year.
- 88.5 billion Plastic bags were consumed in the U.S. last year.
- It takes up to 1000 years for plastic bags to biodegrade in our landfills.
- The average family of four uses 1460 plastic bags a year.
- An estimated 500 billion plastic bags are sold worldwide each year.
- Less than 1% of all plastic bags are recycled in the U.S.
- Over 100,000 birds and marine life die each year due to an encounter with plastic debris, much of it plastic bags.
- Plastic is getting into the food chain. Even the finest particles of plastic represent a threat to creatures at the lowest level of the food chain in the marine environment, the filter feeders. Then, toxins in filter feeders are passed up the food chain to fish and other marine animals, which humans then consume.
- Plastic is over-running our planet. Estimates run as high as one million pieces of plastic per square kilometre (0.6 mile) floating in specific areas of the Pacific Ocean.
- When one ton of plastic bags are reused or recycled, the energy saved is equal to 11 barrels of oil.
Paper Bag Facts
- 14 million trees are cut down to make the paper bags used in a year.
- Only 20% of paper bags get recycled.
- When one ton of paper bags is reused or recycled, three cubic meters of landfill space is saved and 13-17 trees are spared! In 1997, 955,000 tons of paper bags were used in the United States.
- Paper cannot be recycled indefinitely. It can only be recycled 4-6 times. Some virgin pulp must be introduced into the process to maintain the strength and quality of the fibre, so no matter how much we recycle we will never eradicate the need for virgin fibre.
- Paper is the number one material that we throw away. For every 100 pounds of trash we throw away, 35 pounds is paper. Newspapers take up about 14 per cent of landfill space, and paper in packaging accounts for another 15 to 20 per cent.
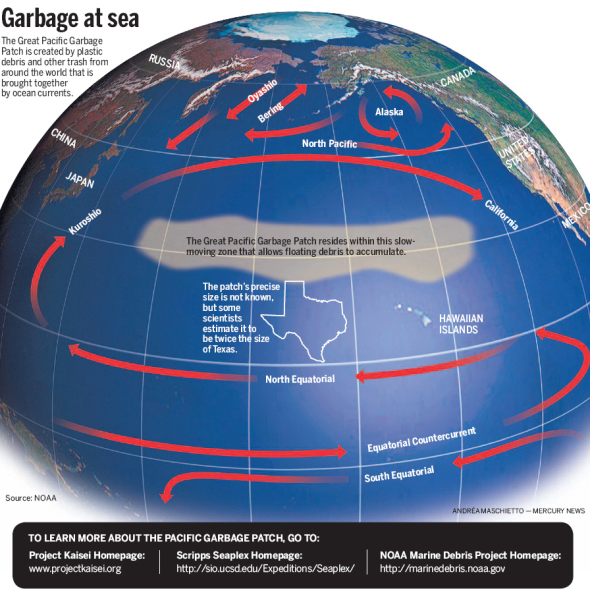
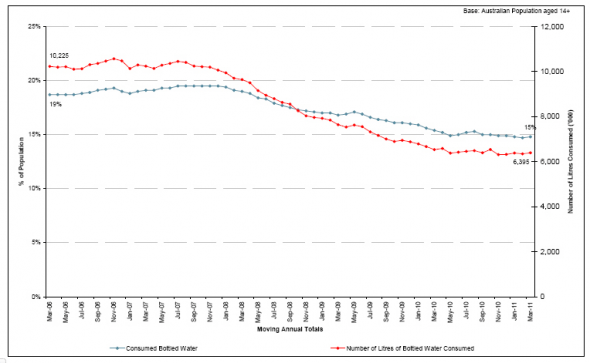
The graph below explains the number of liters of bottled water consumed to the number to “consumed bottled water” up to 2011 and this is one of the largest plastic environmental threats to our oceans to date.
Recent research reveals that even remote areas of the oceans are affected by increasing levels of plastic waste on the seafloor. The study found that quantities of litter from human activities, mostly plastic, on the seabed of an isolated Arctic site, doubled from 2002 to 2011 which is very serious considering that there are many still (unsolved mysteries of the Arctic and few species too. We simply cannot afford to loose these specimens.
Researchers suggest that the problem requires immediate policy attention if we are to prevent levels of deep-sea litter increasing”
Around 60% of the Earth’s surface is covered by the seafloor, yet very little is known about how pollution has affected the deep ocean, in particular, remote areas such as the Arctic.
Despite a ban on solid waste disposal at sea in 1988, under Annex V of the MARPOL Convention1, research has revealed that even the most isolated environments are no longer free from litter.
Most sea litter is made up of plastic waste and more than 10% of the global production of plastics (over 265 million tonnes every year) ends up in the oceans, where it may remain for centuries and can cause potential danger to marine life through entanglement and suffocation. ‘Microplastics’, tiny particles of broken-down plastics, can also release a range of chemicals known to be harmful in high concentrations. These chemicals can be ingested by marine animals, including commercially-harvested prawns, mussels and fish, and enter the human food chain.
Researchers studied over 2,000 photos of the deep seafloor taken at the HAUSGARTEN observatory in the Fram Straight, off the west coast of Svalbard, a Norwegian island within the Arctic Circle. A camera took the pictures of the seabed whilst being pulled along a track at a depth of 2,500 metres in the years 2002, 2004, 2007, 2008 and 2011.
From the photos, the researchers could see that the amount of litter on the seabed doubled in the study period, from 3,635 to 7,710 items per square kilometre, with the majority made of plastic. To put this into some perspective, the density of litter had become greater than that reported in deep-sea canyons near Lisbon (6,600 items per square kilometre), the heavily populated and industrialised capital of Portugal.
67% of the litter affected sea life in some way, for example, through entanglement or by providing a base for organisms to grow on; with sponges and sea anemones particularly affected.
The origins of the litter are not clear, but climate change and the associated shrinking of ice levels may play a role. For example, increased access for fishing and tourist boats in the area may increase litter levels. In addition, a reduction in protective sea ice may also mean that litter drifts into the area more easily on sea currents and strong winds are able to blow waste from the land into the water. Litter levels are likely to increase in the future as global plastic production rises by 5% every year.
Although litter can provide shelter for a few species, it can also smother other species and release toxic chemicals. Litter on the ocean floor may also change the chemistry of the seafloor on a local level, for example, oxygen levels under plastic bags may fall. Furthermore, the ability of plastic litter to move long distances in the sea provides a perfect opportunity for alien species to invade remote areas, such as the Arctic, especially climate change.
The problem does not lie in the arctic though, the main problem is at home and now need to deal with this before we kill our ocean’s before even understanding them and the remaining deep sea mounts that contain an abundance of aquatic biodiversity.
http://ec.europa.eu/environment/integration/research/newsalert/pdf/313na2rss.pdf
“Plastic debris in the area popularly known as the “Great Pacific Garbage Patch” has increased by 100 times in the past 40 years”

Here’s a look at some of the issues that add to the environmental impact of paper and plastic bags taken from several studies and sources listed at the bottom of this article:
Issue 1: Energy and natural resources
According to a 2007 study by Boustead Consulting & Associates, It takes almost four times as much energy to manufacture a paper bag as it does to manufacture a polyethylene bag.
Not only do both paper and compostable resin bags use far more fossil fuel in production and manufacturing, but they also use twenty times as much fresh water vs plastic bags.
Additionally, most paper comes from tree pulp, so the impact of paper bag production on forests is enormous. A 2008 article from the National Cooperative Grocers Association states that each year the United States consumes 10 billion paper grocery bags, requiring 14 million trees. Paper bag production delivers a global warming double-whammy; forests (major absorbers of greenhouse gases) have to be cut down, and then the subsequent manufacturing of bags produces greenhouse gases. However, plastic bags are not the more sustainable solution as they use more fossil fuels and raw materials energy, and consume larger amounts of crude oil and natural gas than paper bags.
Issue 2: Pollution
The majority of kraft paper is made by heating wood chips under pressure at high temperatures in a chemical solution. As evidenced by the unmistakable stench commonly associated with paper mills, the use of these toxic chemicals contributes to both air pollution, such as acid rain, and water pollution. The same goes for compostable plastic bags.
Issue 3: Recycling
Studies indicate it takes 91% less energy to recycle a pound of plastic than it takes to recycle a pound of paper. But recycling rates of either type of disposable bag are extremely low. In fact, 85-90% of paper bags are not recycled according to the Wall Street Journal, and 94.8% of plastic bags are not recycled according to a study conducted by Boustead Associates. The bottom line is recycling disposable bags still takes energy and resources - resources that could be conserved if more people simply switched to reusables.
Issue 4: Degradability
Many people choose paper over plastic because they believe it will biodegrade faster than plastic will break down in a landfill. However, there are a number of factors that determine how quickly, if at all, paper degrades – this includes temperature, pH, the type of bacteria present and the form of paper (shredded paper degrades faster.) That being said, it makes more sense to opt for a reusable bag that will last for thousands of uses over a disposable that will end up in the landfill.
FACT - In 2010 about 690,000 tons of waste HDPE plastic “bags, sacks and wraps” were generated in the United States, but only 4.3% of this total was recycled
FACT - Plastics do not biodegrade, but instead break down into small particles that persist in the ocean, absorb toxins, and enter our food chain through fish, sea birds and other marine life. (But then you knew that hence why pollution is shooting out of the roof)
FACT - Recent studies estimate that fish off the West Coast ingest over 12,000 tons of plastic a year.
FACT - The U.S. has the most pounds of trash per person per day (4.6 lbs of trash per person, 1.5 lbs of recycled materials per person)
FACT - Aluminum can be recycled forever with NO loss of quality (good thing since we use over 80,000,000,000 aluminum cans each year)
FACT - On a good point point - The greenest states are Vermont, Maine, New Hampshire, Nevada, Hawaii, South Dakota, Montana, Idaho, Oregon, and Colorado
PLEASE KEEP OUR PLANET AND OCEANS CLEAN AND GREEN
Dr J C Dimetri V.M.D, B.E.S, Ma, PhD , MEnvSc
Environmentalism chapter 13 - The Amami Jay under threat.
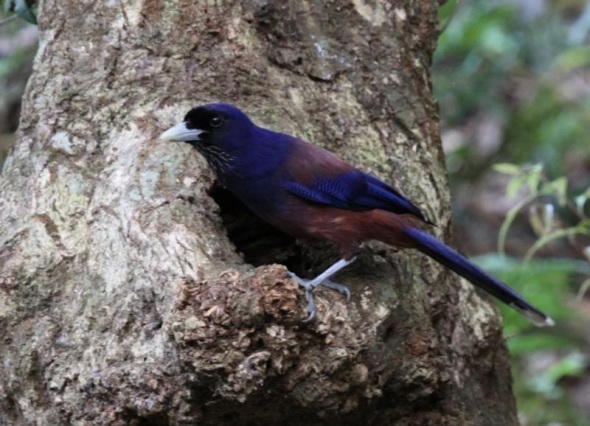

This week I posted a photograph of the most stunning and beauteous bonny Raven I have seen which I asked our supporters to try and guess the name off, I would of thought that that identifying this beautiful ballet bird would have been fairly straight forward considering its part of the Raven family and has resided on earth now for some thousands of years.
Regrettably no one managed to identify it, and who can blame them really when there is little to hardly any awareness of our smaller agile species which in this case are the avian species of bird and the bird I am speaking about is Amami Jay (Garrulus lidthi) a stunning raven species that’s unfortunately now under grave threat of extinction.
The Amami Jay was classified as “vulnerable” on the International Union for Conservation of Nature however it is now near now threatened with a total number of only five thousand left living in the wild if that.
Garrulus lidthi is not really your average jay in terms of colour and distribution, native primarily to Japan its colours vary with a deep purpled breast, throat and head with wings that have such splendid silky deep rustic brown with red belly and breast.
Its beak has a slight yellowy tint mixed with silk white whereas its wattle appears to be speckled which I can only explain to be similar to certain species of the Dollarbird although a completely different in species and diffraction. The Ravens primaries rear has the most abundant mixture of white and deep purpled tail end feathers to making it such a splendid bird standing out from many other avian species, exquisite, natural and pulchritudinous it truly is an avian species that one now needs to focus on to preserve and conserve its natural habitat and species alike.
One would believe that this bird’s natural habitat is being destroyed by deforestation and trafficking hence why numbers are now dramatically decreasing rapidly however it’s not quite that simple. You see the Garrulus lidthi is dicing with death every time it tries to feed on its normal diet of acorns, insects, small reptilians, plants and arachnids as the Indian Mongoose that was introduced to the island of Amami is now seriously threatening this native species of bird of which hunting that’s now ceased didn’t exactly help neither.
Amami Island is located between Kyushu and Okinawa. Its subtropical environment is different from the climate of mainland of Japan making it a paradise haven for many species of mammal, reptilian and aquatics. Amami is very unique in its cultural appearance and biodiversity.
The Amami Jay was named by Bonaparte in 1851 and although the IUCN (International Union for the Conservation of Nature) has quoted there to be 5,000 individuals left native to the island the real figure now stands at a depressing three thousand nine hundred mature individuals that are being rampantly slaughtered by the Indian mongoose that previously hunters used to catch the Jay other species specimens for food and decoration.
International Union for the Conservation of Nature named the Indian Mongoose as the world’s most invasive species of mammal scientifically identified as Herpestes edwardsii and better known as the Grey Mongoose, the Herpestes edwardsii is of the very least concern on the (IUCN) listings of vulnerable to critically endangered mammalians. Mainly located in India, Sri Lanka, Pakistan, Nepal, and it’s native Japan the Amami Jay that resides in sub-tropical evergreen broadleaf dense forest and woodland around human cultivation and habitation the Jay is facing nearing extinction

Indian Mongoose - Herpestes edwardsii
The Amami Jay like “some similar” birds is a ground base floor eater and with their being very large numbers of the Indian Mongoose, and the food of the Amami Jay located at ground level then the Amami Jay stands no chance of continuous survival due to the mass over growing populations of Mongoose in the area.
Being carnivorous the Mongoose feeds on many species ranging from rat to snake, eggs and avian species. The mongoose is a skilful hunter that actively searches for prey by using its strong senses of smell and sight and eats near enough anything it can catch. The Indian grey mongoose commonly eats small mammals such as rats, as well as eggs and a variety of arthropods, including the scorpion. The mongoose sniffs the ground and turns over rocks and stones in its search for prey. If the animal tries to flee, the mongoose chases it. It kills its prey while they are both running by delivering a bite to the neck or head. Although the mongoose eats snakes, including the venomous cobra, the main part of its diet consists of small animals that live or forages on or under the ground. The mongoose is a fast and agile hunter that is always watchful for prey hence why the Jay is being pushed further to extinction.
The Amami Jay being so beautiful in colour was also hunted on the island by man for its feathers to make into hats, garments and skirts to sell at the local markets of which the Mongoose was used as a primary hunting weapon to hunt the Amami Jay, however since agriculture has taken over from “hunting” the Mongoose was no longer wanted as a primary hunting tool and then released into the wild once the agricultural period took off creating a biodiversity nightmare on such a small island. “Agriculture came to the islands around the 12th century, as agriculture caused a divide between the rich and poor, those with power eventually became the ruling class”.

Although the IUCN has stated the Indian Mongoose has been controlled to a “certain degree” we ourselves don’t call a number standing at 3,900 mature individuals as a very safe population and methods to now increase the numbers of the Jay need to be steeped up with rampant humane control methods brought in to control the Indian Mongoose levels as well as measures to secure possible reserves or other grounds of biodiversity interest stepped up and brought in to secure the life species of the Jay before extinction hits and we lose another rather undocumented species of tropical Jay bird.
Some surveys have stated that that if levels of predatory control can be brought in then the Amami Jay can be down-listed which we just think at this moment is absolutely absurd and ridiculous. A recent report suggested (quote) “It has been suggested that the population is now stable (K. Ishida in litt. 2012), but until new data is available the trend is precautionary assumed to be very negative. Although forest loss is unlikely to be having a significant impact upon this species, reduced reproductive success owing to nest predation by mammals is perhaps still leading to a moderate to large decline overall in Jay numbers (un-quote).
Snakes have been reported to prey on young birds and eggs too that have been introduced on the island after the Indian Mongoose. However, it is not known whether this apparently increased predation pressure will have a long-term effect on the population of Jay’s and other avian species. The numbers of Large-billed Crow Corvus macrorhynchos on Amami-ooshima have recently increased, probably because of increased garbage disposal on the island. The effect of logging on its population is probably relatively small and fairy non-documented as of strict pollution and deforestation laws, with heavy fines and the island being relatively clean.
The Amami Jay is legally protected in Japan. Yuwandake on Amami-ooshima was established as a National Wildlife Protection Area, mainly for the conservation of this species and Amami Thrush Zoothera major. Several surveys and ecological studies have been completed. It has been quoted that the Introduced small Indian mongoose has been controlled within its range in recent years and as a result the species may now be stable or increasing however there is still no known “proven data to back this claim up with the Jay remaining at critical levels”. Distribution of Large-billed Crows Corvus macrorhynchos on Amami-ooshima have also added to biodiversity control and natural habitual action
Proposed conservation ecologists conduct regular surveys to ascertain whether the population is in fact stable or recovering and to take action where and when needed immediately. Conserve and restore remaining areas of mature forest on Amami-ooshima. Provide nest-boxes in areas where there is a shortage of suitable natural nesting sites. Control alien predators on Amami-ooshima, although these conservation efforts are proving “fair” not enough is being done and we could lose the Amami Jay for good.
Dr J C Dimetri V.M.D, B.E.S, Ma, PhD , MEnvSc
As one can see below the Indian Mongoose is a powerful hunter, hence why it has caused so many problems on the Amami islands.
Environmentalism chapter 12 - Shark Fin

Sharks are one of a kind of Chondrichthyes that have swam the planets oceans for millions of years dating back to the prehistoric realms of the dinosaurs, living through the ice ages, colossal seismic activity that saw many millions of oceanic species wiped out. The shark though a silent stalker and predator remained unscathed.
They were not in any real danger to of traditional Chinese medicine demand or pollution and swam within the oceans with little if any predators, sadly this is hastily no longer factual and the entire species of sharks are being wiped out for a “soup” or medicine used frequently within the Asian medicine market just for tongue and texture.
The species of Shark are not mammalians they are classed as Chordates which is the only unique species of their type separating them from mammals, Chordate are deuterostome animals possessing a notochord, a hollow dorsal nerve cord, pharyngeal slits, an endostyle, and a post-anal tail for at least some period of their life cycles that then develop into the species of which the Deoxyribonucleic acid is programmed to make them into.
Being relatively blind they are agile swimmers yet superb deep sea divers that can smell through an array of senses a drop of blood in the ocean from half way around the world which scientifically is factual although they cannot exactly home in on this being some thousands of miles away there smell is unique from any other form of fish, human or other mammal predator.
The shark noses use ‘smell stereo’ to detect tiny delays no more than half a second long in the time that odours take’s to reach one nostril compared to the other one and that truly is amazing. All species including the deep sea sharks use a combination of directional cues based on scent and the flow of water - to keep them orientated and find what they are searching for.
So the theory that they are human eating man eaters which coincidentally is what the Asians believe hence why they like to consume as well parts the Panthera tigris as in their fake book of counterfeit medicine it states the shark “is a beast and man eater with much energy” that should they consume the shark it will make them a fiery hunter in bed. Its utter nonsense, scientifically untrue, and fairy land tails.
If the delay between the scent reaching one nostril and the other is between a tenth and half a second, the sharks turn their heads to the side where they first smelled the bleeding or anxiously suffering prey such as the squid one of the sharks favorite foods.
If a shark experiences no delay in scent detection or a delay that lasts too long a full second or more they are just as likely to make a left-hand turn as they are to make a right, which makes them rather interesting and a species we must all PROTECT”.
The popular notion that sharks and other animals follow scent trails based on differences in the concentration of odour molecules hitting one nostril versus the other are based on 2010 scientific analyses. It seems that theory doesn’t hold water when one considers the physics of the problem.
Most creatures come equipped with two odour sensors - nostrils or antennae, for example - and it has long been believed that they compare the concentration at each sensor and then turn towards the side receiving the strongest signal.
‘But when odours are dispersed by flowing air or water, this dispersal is incredibly chaotic.’
This recent research on sharks predatory hunting behaviour living has led to findings that has also lead to underwater robots that are better equipped to find the source of chemical leaks, like the oil spill that plagued the Gulf Coast in 2010, 2012 has already seen this research placed to use in many “deep-sea” submersibles now actually using this research to develop state of the technological maritime breakthroughs that have seen many documentaries recorded and sea bed chemical leaks from pipes that are not that easily traceable by other older technologies that can break down at the blink of an eye lid.

Previous robotic submersibles were programmed to track odours by comparing odour concentrations, and they failed to function as well or as quickly as live animals.
The oil spill in the Gulf of Mexico, and main oil slick was easily visible and the primary sources were easy to locate, smaller sources of Odour-guided robots are an asset for these types of situations with great thanks to the sharks.
The smell organs in the noses of some sharks are able to detect one droplet of blood in one million drops of sea water. They are often attracted to chemicals found in the guts of animals and loiter near sewage outlets so this great research has helped many in the maritime industrial.
Sharks have swam the oceans as far back as we can tell for about 400-500 million years of which there was an estimated 480 species that belong to the subclass of Elasmobranchii, which is in non-scientific jargon cartilaginous fish such as rays which makes them quite different from normal species of fish such are whales that are a sub class of Eutheria distinguished from noneutherians by various features of the feet, ankles, jaws and teeth.
One of the major differences between placental and nonplacental eutherians is that placentals lack epipubic bones although fish don’t have feet, some species that moved from land to waters thousands of years ago have then later evolved in to this “subclass” which the shark species are a subclass of their own from what we know of million year old fossil investigations through archaeology.
Most sharks such as the Carcharodon carcharias, Galeocerdo cuvier, to the Sphyrna lewini are classed as “apex hunters” which basically means they are at the top of the human food chain, they are feared by ourselves even though attacks are rare and just to give you an example of shark attacks verse the bathroom toilet.
Shark attacks for 2011 where 75 global shark attacks, a number closely matching the decade average and the number for 2012 was from what I located to be 62 although that is still to be confirmed surfers and others involved in board sports took the brunt of the attacks, accounting for 60 per cent of unprovoked shark attacks, swimmers 35 percent and divers about 5 per cent.
However the bathroom toilet is quite amusingly odd in 1945, the German submarine U-1206 was sunk after the toilet malfunctioned, and a crewman’s botched repair forced them to the surface killing all on board. King Wenceslaus III of Bohemia was murdered with a spear while sitting in the garderobe (toilet) on August 4, 1306. George II of Great Britain died on the toilet on October 25, 1760 from an aortic dissection. According to Horace Walpole’s memoirs, King George “rose as usual at six, and drank his chocolate for all his actions were invariably methodic. A quarter after seven he went into a little closet. His German valet de chambre in waiting heard a noise, and running in, found the King dead on the floor.” In falling he had cut his face.
Bathing and showering appear to be particularly dangerous. Overall, about two-thirds of accidental injuries happen in the bathtub or shower — which makes sense, because each can become slippery. But many injuries involve the toilet: standing up, sitting down, or using it. (Yes, about 9% of the total injuries were from overexertion.)
Still believe that shark attacks are common and they are “aggressive out of control people eaters” ridiculously untrue please read on. Overall, mishaps near the bathtub, shower, toilet and sink caused an estimated 234,094 nonfatal injuries in the U.S. in 2008 among people at least 15 years old, the Centres for Disease Control and Prevention reported online in its weekly Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. And the injury rate rises with age.
Researchers used emergency room data on accidental, nonfatal injuries and some statistical number crunching to reach their conclusions. Their report is full of statistics (which makes it good bathroom reading, if you have 15 minutes and an Internet connection) on the slips, sprains, contusions, fractures and concussions that can happen in the bathroom, to even death.
- About 81% of the injuries were caused by falls (from the bathroom toilet)
- Women were more likely to be hurt than men
- Two-thirds of all injuries occurred in the tub or shower, though only 2.2% occurred while getting into the shower or tub
- Overall, only 1% of accidental nonfatal injuries occurred in the bathroom, but for those 65 and older, 2.5% occurred in the bathroom.
The report can be located here http://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/mm6022a1.htm?s_cid=mm6022a1_w how prevailing and odd but very true, so the next time someone states to you that sharks are people eaters and aggressive please remember when you go to the bathroom that your actually “risking your life” Shark attacks though are very unheard of however the reason why they are classed as man eating killing machines is because the press adore to give them a rather bad name.
Such as “GREAT WHITE TORE MAN’S LEG OF” I suppose the headlines “MAN FELL FROM TOILET SEAT AND DIED” just don’t make GREAT reading which is why the press love to make such a mountain out of a molehill over something that could actually be a probing nip which is what a shark will do before “any such attack” takes place. http://mauinow.com/2011/06/07/study-details-hunting-behavior-of-tiger-sharks/
http://www.livescience.com/12783-shark-attacks-hit-10-year-high.html shark attacks on humans only hit a ten year high from recent accident and emergency reports gained from”2011” from all global hospitals. Extraction from the report states;
“Scientists investigated 115 alleged incidents of struggles between humans and sharks worldwide in 2010. They confirmed that 79 of these were unprovoked shark attacks on live humans”.
“Unprovoked attacks are ones that occurred with the predators in their natural habitats without human instigation. The other 36 incidents included 22 provoked attacks — such as assaults after divers grabbed sharks — including three cases of sharks biting boats, four incidents dismissed as non-shark attacks, five scavenging incidents of human corpses and two cases where there was not enough information to determine if an unprovoked shark attack had occurred”. Please read the report as it gives scientific reasoning as to why they have attacked more within the 365 day period. http://dsc.discovery.com/sharks/why-do-sharks-attack.html
What does all this have to do with sharks and the species under threat though? Good question as most of this does as of lack of awareness, the fright factor, and then of course traditional Chinese medicine the NUMBER ONE REASON.
There are MORE attacks on sharks than there are on any other species of fish, and now we need to start taking note of this as we are losing these amazing species rapidly due to counterfeit Asian pharmaceuticals and the disgustingly tasting shark fin soup.
I have always been a firm lover of wild and “predatory dangerous” animals such as mammals from the big lion to Tiger’s, reptilians from Python to Crocodile, and marine aquatic species mainly the shark. In 2010 I traveled to Shenzhena bustling rather smog filled sky scraped city that had many restaurants and street quick food fixes mainly selling animal parts to eat of which shark fin was on the menu.

Thousands of Sharks lay dead in a Singapore fishmongers. Within central China it is said by many, and even activists that the sharks are only craved for, for their fins. This is untrue and this picture was taken three days ago in Singapore’s market. The market sells the shark meat and the fins for major profit making Singapore one of the richest Asian islands in the world.
Being a firm lover of sharks and great studier of the species I wanted to see what all the fuss was about and why sharks where being wrenched out of the water like candy from a baby then de-finned and thrown back to the seabed from which they died a slow agonising death from asphyxiation. Being a vegan for thirty years I really couldn’t care at that point as the main objectives was to try this dish to see if this was indeed a great reason why it is used in Asian medicine, to try and ascertain why one of my favorite species of animals was being slaughtered,
The soup smelt repulsively strong and acidic, and when tasting it without almost vomiting, one can only explain that even with a sprinkle of chive that entire first spoon and that being the last, tasted revolting, and more like hot water with the odd lump of shredded fish cuisine within. Oh yes I forgot the tender informed me that it would make me fit and strong even though I already was in 2010 being a healthy vegan for over 30 years.
https://www.facebook.com/SingaporeFoodRecipes
DISGUSTING AND BLOODY CRUEL - THIS IS ONE RESTAURANT THAT NEEDS BOYCOTTING
The soup did nothing, and there was no magical dragon like hallucinogenic that gave me the power of a thousand men. “Shark fin soup does not under any circumstances improve erectile dysfunction (not that I tried), enhance muscle power, to even warding of any diseases/illness that I actually picked up from visiting the shite hole city of smog and environmental pollution, it does nothing and has no proven health qualities at all. The one spoon fall of fowl tasting crap was enough to show to me that one of the most majestic creatures on earth was being slain for “monetary gain” and not any magical belief. Utterly unbelievable.
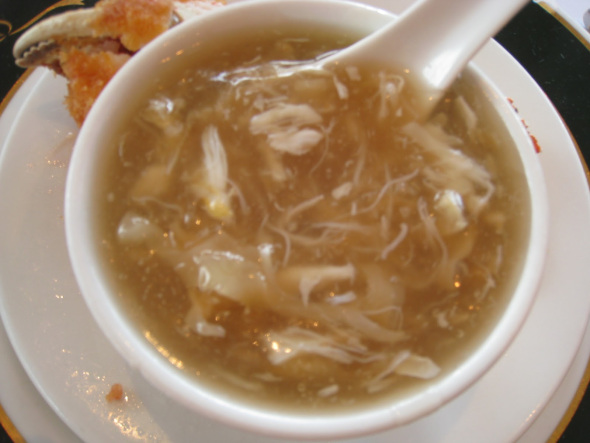
Chinese Shark Fin soup is a “luxury” food served (mainly) at banquets, weddings, parties and cultural masses, however it’s killing the species of and rapidly. The Chinese claim “The shark fins provide texture while the taste comes from the other soup ingredients. The soup originated centuries ago during the Ming Dynasty.
However demand for the soup has increased as income levels of Chinese communities worldwide have risen. International concerns over the sustainability and welfare of sharks have impacted consumption and availability of the soup. So because the Asian consumers require “texture” to their soup then sharks have to be slaughtered in their thousands. There is such thing as we croutons or (toasted bread) that add more texture to this pile of watered down crap which contains one of my favorite animals.
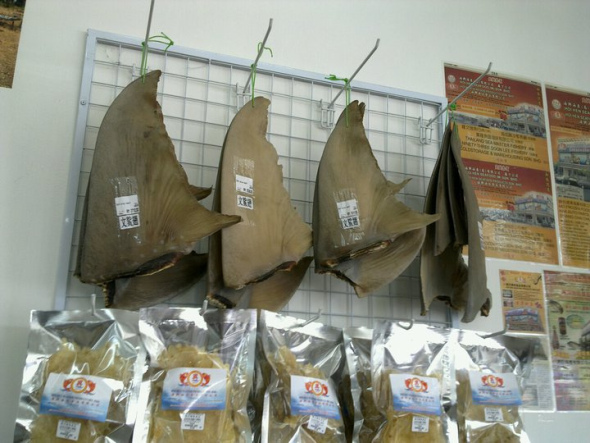
It is estimated that 100 to 200 million sharks annually are killed for their fins alone that’s seen many species now pushed to the brink of extinction and just to give an insight of how bad a problem this is please view the link http://www.foxnews.com/world/2013/01/04/hong-kong-traders-dry-thousands-shark-fins-on-roofs-to-avoid-scrutiny/
Sharks that are caught and their fins cut off are not always dead when their bodies are thrown back into the sea. Without its fins the shark simply sinks to the bottom of the ocean where it dies. Such a horrible death for such a magnificent creature and diet, the whole entire practice is unethical, environmentally damaging and will cause havoc in the biodiversity predatory hunting circle if we lose our species of sharks.
Shark fins, once they are harvested, are then dried to be sold in markets to individuals and restaurants to be made into shark fin soup and sold to the public (especially tourists) for as much as $350 per bowl! The shark fins don’t even add any flavor to the soup. Chicken or pork are used to flavor, the fins are for texture only.
The shark fin soup industry uses a wide variety of relatively large sharks. The majority of these sharks are now under threat. They are slow to mature and breed sharks give birth to a few live young or lay a small number of large eggs depending on species, rather than produce thousands of eggs at a time in the manner of many bony fish. Large sharks also do not mature until they are several years old. These characteristics mean that shark populations cannot support high levels of exploitation = nearing extinction to species vaporisation for a bowl of lousy fowl tasting soup.
Mackerel Sharks
The order Lamniformes includes some of the best-known and biggest sharks. Among them are the great white shark, the basking shark and the thresher sharks. All these species are targeted for their fins, and all are either endangered or vulnerable. The great white shark, for example, might be the most feared species of shark, especially after starring in the ’70s thriller “Jaws.” However, they are more threatened by humans than humans are by them.
Ground Sharks
Carcharhiniformes is another order boasting well-known sharks, such as the bizarre looking hammerheads, whose fins command high prices. The order also includes the family of requiem sharks. These are sharks are your typical sharks, with streamlined bodies and sharp teeth. Tiger sharks, bull sharks and the spinner sharks, which jump out of the water, are all requiem sharks, and they are all taken for their fins.
Dogfish
The order Squaliformes includes all the sharks known as dogfish, the bramble sharks and the rough sharks. They are generally small, benthic, seabed-dwelling sharks that lay eggs and reproduce relatively quickly. Their fins are not of much value, although these animals are often targeted for their meat. The tails of some species of dogfish are used for cheap versions of shark fin soup.
Of the five remaining orders of sharks, carpet sharks, bullhead sharks, angel sharks, frilled sharks and saw sharks, few species are used for shark fin soup. They are mostly small sharks, with small or undesirable fins, and they are not valuable in the shark fin market. Some species, notably the critically endangered angel sharks and the whale shark — a species of carpet shark and the largest fish in the world — are targeted for their meat or oil, but not the fins.
If we don’t take urgent notice now and demand that CITES Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora take more action and demand that law enforcement cease this repulsive and degrading trade then we will see an ocean without any sharks that will unfortunately create a massive aquatic biodiversity nightmare in the aquatic hunting food chain.
Sharks eat many prey, these prey need to be naturally controlled to preserve OTHER species of smaller aquatic marine fish, and should the shark numbers carry on dwindling at massive proportions then we are heading for a global catastrophe.

THE SLAUGHTER HAS TO END NOW - PLEASE TAKE IMMEDIATE ACTION AND NEVER GIVE UP HOPE
http://www.hongkong-companies.com/wo-loong-ho-sharksfin-company-limited-b1v6/
https://www.facebook.com/pages/Shark-Fin-Chinese-Bistro-Pensacola-FL/269850188099?fref=ts
PLEASE DEMAND CITES TAKES MORE ACTION NOW BEFORE MARCH OF THE FOLLOWING SPECIES LISTED ABOVE AND BELOW.
Mackerel Shark
Ground Shark
Dog fish
Bullhead shark
Angel Sharks
Frilled Sharks
Lemon Sharks
Saw Sharks
Hammer Head Shark
Reef Shark
PLEASE CONTACT / DEMONSTRATE / PETITION / - 33 DAYS LEFT BEFORE COP 16TH MEETING
CONVENTION ON INTERNATIONAL TRADE IN ENDANGERED SPECIES OF WILD FAUNA AND FLORA;
CITES Secretariat
International Environment House
11 Chemin des Anémones
CH-1219 Châtelaine, Geneva
Switzerland
Tel: +41-(0)22-917-81-39/40
Fax: +41-(0)22-797-34-17
Email: [email protected] (email them hard to get a response)
CONTACT IUCN (International Union for Conservation Nature)
IUCN Conservation Centre
Rue Mauverney 28
1196, Gland, Switzerland
Opening hours: 8:00 to 17:30 Monday to Friday (except Swiss public holidays).
Phone: +41 (22) 999-0000
Fax: +41 (22) 999-0002
Dr J C Dimetri V.M.D, B.E.S, Ma, PhD , MEnvSc
Please support our fundraiser for Benue http://fnd.us/c/3PFe2
Kami ingin mengingatkan orang-orang yang mengirimkan pesan yang tidak diinginkan bahwa situs Anda akan menutup jika Anda tidak berhenti.
We wish to remind all that visit that should you spam “your sites and the server sending to individual registering shall be reported with IP shut down regardless of whom you are” we take spamming seriously and we advise you to cease now.
CHINA STATED IN 2010 AND 2011 THAT THEY WHERE GOING TO BAN CIRCUSES AND THE DOG AND CAT MEAT TRADE (LIES)
ANOTHER ASIAN GOVERNMENTAL LIE - MEDIA FALL FOR THEIR LIES - CHINA CANNOT EVEN REMOVE THE RHINOCEROS HORN OR IVORY THIS VIDEO BELOW IS JUST A PRIME EXAMPLE TO SHUT ACTIVISTS UP - THEY WILL CARRY ON AND STILL IMPORT..
11 months ago CNN stated that China was going to ban SHARK FINS - What China meant was (they where going to hide them from activists which is a common lie from Asia) video taken over three ago.. How coincidental.
Environmentalism - chapter 11 - Blood Fur

I don’t normally speak much on the fur trade however I have noticed in the last ten years that the trade has taken of massively again and it’s now a major international business once again with companies taking millions of dollars per year.
The trade never really did die off to a full extent however with much awareness and celebrity support and vast protests the trade was hit with a substantial loss in profit margin seeing some fur traders eventually putting down tools and moving on.
Climate change cannot be blamed on the sudden increase and influx in the marketing levels here nor can a drop in sales as of wide spread economic recession that’s seen hundreds of thousands made redundant to small high street stores pushed in to liquidation at a rate of 6 a day in the European Union, not to mention large chains this year in 2013 hitting the headlines of the press and media closing resulting in thousands of people made jobless.
We believe the massive upsurge in the fur trade has been caused by a lack of awareness and high profile figure’s that once went against the fur trade now going back to the trade which is seeing more younger people purchase fur thus more animals placed through a life of misery then extreme torturous death just for a fur coat.
I really cannot compare the fur trade to factory and cattle land farming or abattoir abuse as they are both as bad as one another and within the abattoirs the animals hide from cows mainly is used as a bi product to make leather chairs and upholstery, shoes and automobile furnishings.
The fur trade rose from the exploration era mainly of polar of arctic travel which furred animals were used to keep explorers warm, massive urbanization saw many families from these cold areas of mainly indigenous people then move closer inland of which they sold their furs and skins on the street markets to non-indigenous people thus passing on the trade to others creating a horrifying new trend without them really knowing what the future lay ahead for these animals from mink, rabbit, canine, feline, and bear to more.
Exploration teams from Russia, Canada the Americas and Antarctic also brought back with them forms of fur from Polar bear to Artic fox fur that was passed on to others thus seeing more people craving the “luxury” of a real warming fur coat, trim, to gloves, hats boots and more.
The fur trade can be roughly located back as far as 500/600 AD however the trade didn’t really pick of until the 1500’s when exchanges where made between Indians and Europeans. The Europeans are more to blame for the trade hence why there is by far more fur trade and capture in Europe than any other part of the world with China being to date the largest exporter mainly of imported “near finished products” from the European Union and America.
The label at the end of the coat or other material that’s last trade route was for example China will show produced or (made in) in China, however it doesn’t mean that it was mostly manufactured there. It’s much cheaper nowadays to export a luxury product to another nation where other added products and labour is much cheaper which companies practice now regularly. Once the item is finished for example a simple inner lining sown within with, a label will be placed on the finished product stating its final destination as “made in” but not “caught in or 80% produced in”.
The trade took off when the Europeans started their first polar explorations which then unfortunately saw fur “farms” established in North America back in the 1860’s then further on in Canada roughly from the 1890’s of mainly mink and wild fox.
Europe now accounts for some 60-70% of all fur farming with Denmark leading in the mink production of some 28% with China actually being the smallest producer along with the Baltic States, Netherlands and America. The Netherlands is now phasing out fur farming which we will see in the near 2020’s all fur farms banished from the Netherlands. There are 5 licensed mink farms in the Republic of Ireland and, between them, it is estimated that 200,000 to 225,000 mink are farmed a year in appalling conditions.
The United Kingdom banned all fur farming in 2002 along with Croatia then following along with Austria too. There is also wide spread condemnation of fur farming, trapping and trade of which is seeing many organisations and conservationists to animal welfare charities now fighting to end this sick repulsive and bloody barbaric trade.
In the early and mid-1970’s wearing a real fur coat was seen as an extravagance with many rich and famous people purchasing fur not really understanding the cruel and immoral practices that animals are put through when slaughtering is carried out. Nor do they see that trapping and holding in such solitary confined enclosures animals suffering from sores, rotten flesh wounds due to poor farm husbandry, species fighting as of overcrowding to psychological trauma, and death is some cases. The standards by “some” ethical animal welfare groups regarding farms around Europe, and internationally confirms the farms to only be in “fair to moderate standard with neglect and abuse rampant” which conditions are not even fit for a canine or feline.

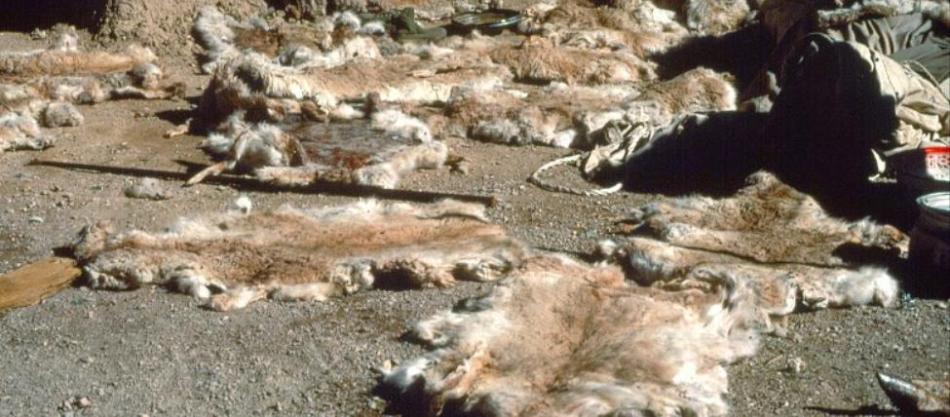
Emotionally not a pretty site - Picture taken by Sergey Maximishin of a Russian fur farm’s waste pile.
It would be politically incorrect for me to state that fur farming, production and trapping reduced in size as of “animal rights extremism” as this was on a low scale in proportion. And no matter how many (extremist) activities took place copious fur farming and production progressed as the insurance firms were willing to pay out for the damage caused by animal “rightists” and not necessarily the A.L.F/A.R.M as these “non- ALF/ARM combatants” were seen to be opportunists hell bent on causing criminal damage without a real motive or plan that saw many animals once the “rightists” had released them placed back into poorly maintained huts. Insurance companies where paying out to the big farmers as of the “demand” for their top quality skins even though it was disgusting.
However some smaller farms both internationally and within Europe where shut down via arson or harassment to damaging the farmers hard finically which insurance companies couldn’t keep up with continued pay-outs simply because they were new to the market or lacked financial gain to experience.
Demand decreased primarily due to high priced identical line products and lack of design lines from the designers and marketers that where still seen back in the 1970’s-1980’s as vastly uneducated in this area. Campaigns from groups such as PETA (people for the Ethical Treatment of Animals) did play a decent role in this area that aided more trade to decrease however it didn’t and never has halted it even with celebrity pressure and television advertisements to covert militant surveillance uncovering some shocking footage of fur farm cruelty.
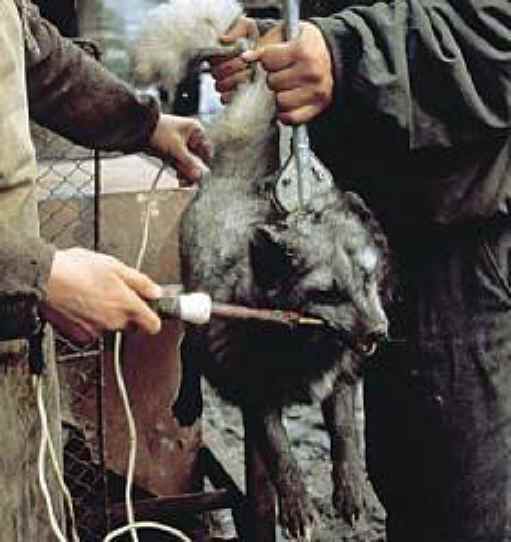

Fox - Electrocuted to produce less damaged garments via the traditional method of slaughtering.
Sales have regrettably though soared since the 1990’s mostly in China via imports and Europe with new technologies, news designers and more “youth” to the younger rich generation evolving wanting the latest design. Although the trade did take a pounding from PETA with many celebrities explaining the cruel and repulsive barbaric methods used to capture wild animals for fur via trapping, including “fur farming and breeding” and slaughter, some of these celebrities have gone back to their old ways and are again wearing fur.
Was it money and prospects of more sponsors that made them switch back to fur? We believe so hence why we are not a big affluent supporter of PETA as they aren’t a rescue as explained to ourselves by the United Kingdom PETA support in an email regarding Sunder the Elephant plus they use high profile dignitaries and celebrities to carry out their work whilst talking donations for this form of awareness which is more than bribing it’s dirty awareness that we despise.
The suffering;
I have outlined in bullet points the extreme suffering that many animals are put through below to gain fur;
- Animals such as foxes, mink, ferrets, and sables (an animal in the weasel family) spend their entire lives stacked on top of one other in barren cages with nothing beneath their feet but wire mesh.
- Animals at the top of the cages are a little more fortunate as they do not have urine and faeces falling on to them like the animals below as of the opened top cages.
- Animals that are caught in traps desperately try to free themselves thus causing immense pain, suffering to even eating their little legs of to save themselves that sadly then succumb to death.
- 9/10 many animals are forced to spend their lives in cramped confinements with other animals that have no shelter from the wind, rain, freezing cold or snowy temperatures, lack of water, feed and are left with the same bedding for days on end that they sit rotting in.
- Nearly all the animals suffer from psychological trauma from head bobbing, pacing, cage bashing, eating their own faeces, self-mutilation, and cannibalization, to species conflict.
- Minks that normally roam the wild spend most of their days frantically pacing up and down the cages scared witless trying to escape biting their own tail out of anxiety and cognitive stress.
- Fur farms inflict such terrible psychological trauma on animals that in one study of vixen (female foxes), half of the kit loss that occurred prior to weaning was attributed to infanticide behaviours, primarily mothers eating their young.
- Many animals suffer skin sores that are similar to bed pressure sores in humans however these sore aren’t caused by resting in the same position for many hours, they are regrettably caused by the animals sitting in their own urine and faeces.
- Many diseases form in farmed pens of fur farmed animals that don’t in wildly captured animals, the animals suffer tremendous pain, suffering, to prolonged death as of poor farm husbandry.
- After suffering through years of confinement, animals are killed and skinned for their pelts. Killing methods are typically cheap, crude, and performed in such a way so as not to damage the animal’s fur; there is no such thing as humane “euthanasia” on a fur farm.
- Caught, caged then farmed for the rest of their life the capturer either keeps the animals to breed on, or slaughterers them by breaking their neck, farmed animals suffer at the hand of their slaughterer from gassing in chambers of which the animals take up to 10 minutes to die or from strangulation, electrocuting via the anus and mouth, or just skinned alive as the fur is less damaged. (Can you imagine being skinned for life)?
- As quoted above on U.S. fur farms, one of the most frequently used methods of killing animals is electrocution: the “farmer” puts a metal clamp in an animal’s mouth, a metal rod in the anus, and sends a high-voltage current surging through the body.
- Then there is lethal injection of various chemicals that kill through paralysis, which can result in immobilized animals being skinned alive and neck breaking.
- More than 36 million animals die on fur farms around the world each year. Thirty-one million (or about 90 per cent) of these animals are mink. Foxes account for another 4.5 million, while chinchillas, sable, ferret (usually marketed as “fitch”), coypus (an aquatic mammal also known as “nutria”), and raccoon dogs (not to be confused with the North American raccoon), account for most of the remaining half-million animals. Due to the recent drop in pelt prices for mink and fox, some of U.S. fur farms have attempted to “diversify” by raising bobcat, coyote, raccoon, and beavers, along with coypus and rabbits — all in equally abhorrent conditions.
- When the United Kingdom, Scotland, and Wales stated this “Fur farming is not consistent with the proper value and respect for animal life. This is a moral issue that goes beyond welfare considerations. In the 21st century, animals should not be killed just for the business of stripping their skins off their backs … In a modern society there should be room for Government to make ethical decisions and it is right and proper for the Government to have introduced this ban”.
- The United States then stated this “the U.S. government seems not to agree with this assessment. In fact, no federal laws regulate how the animals on the nearly 400 fur farms in operation in the U.S. are to be housed, cared for, or killed, fur farming shall continue”.
Animals used for farming;
- Beavers
- Chinchillas
- Dogs and cats
- Foxes
- Minks
- Rabbits
- Raccoons
- Seals
- Bears
- Arctic fox
Animals that are used for the “illegal skin/pelt trade that often becomes mixed in with these brands are;
- Tiger (critically endangered)
- Cheetah
- Leopard (critically endangered)
- Snow Leopard (critically endangered)
Celebrities that wear fur that should be setting a good example on the younger generation;
These are simply a handful.
- Lady Gaga
- Lindsay Lohan
- Paris Hilton
- Nicole Richie
- Jennifer Lopez
- Beyonce
- Jay-z
- Katie Eary (Designer)
- Hardy Amies (Designer)
- Ulyana Sergeenko (Modelled for the Time’s)
- Kim Kardashian
- Ciara
- Jessica Alba
- GIORGIO ARMANI (Designer)
- Rihanna
- Kourtney Kardashian, Scott Disick and their son
- Chloe Green
- Rapper Big Boi
- Anna Karenina
- Poppy Delevingne
This is just twenty and there are by far many more such as David Beckham and Victoria Beckham, Kate Moss to Naomi Cambel all of these celebrities are still wearing and still flaunting the repulsive disgust without a care in the world of how that dead animal around their waist, neck or head suffered on the fur farm, or whether it spent days in a field trapped in a leg jaw trap suffering agonising pain and discomfort before having its neck broken in two.

Sores on his feet, dehydrated, as well as psychologically disturbed this poor fox still suffered, in pain, eating his own feet out of pure anxiety and cage stress. This is no way to treat an animal, this is disgusting..
Conditions on fur farms throughout Europe are fair to standard with neglect common practice. An undercover investigation by Compassion in World Farming - Ireland and Respect for Animals in 2003 found that mink were kept in cages about 3 foot long and 1 foot wide, plus a small nest box at one end. Fox cages had a floor area of about 4 foot by 4 foot and were about 28 inches high.
A Council of Europe Recommendation Concerning Fur Animals (1999) lays down new cage sizes for fur animals, which came into place in 2010. The new cage sizes are slightly bigger than the cages that were filmed in a 2003 investigation. Fox and mink cages are usually in rows inside buildings that have open sides. The animals’ droppings fall through the wire mesh floor of the cages.
Farmed mink and foxes are fed on a porridge-like food made from chicken, meat and fish offal. This is placed on the top of each cage and the animals eat it through the wire mesh. Mink and foxes are confined in cages throughout their lives until they are taken out to be killed.
In a recent press article read here http://www.huffingtonpost.com/christina-anderson/wearing-fur_b_2239881.html?utm_hp_ref=fb&src=sp&comm_ref=false some celebrities give their reasoning as to wearing fur, if only they were taken to a fur farm or wild trapper to view how cruel the conditions are to what these animals go through it “could” change their ways to even supporting the no fur industry.. What annoys ourselves the most is some animal rights groups believe that “trapped animals” are treated (humanely) there is NO humane treatment of any animal that’s to be murdered for human gain.
Fur trade is cruel, barbaric and primitive and although it dates back to the cave man era does it give us the moral rights to then wear it as we believe the animals have been treated fairly? Although PETA claim to have scored victory over the some retailers as stated here “PETA has scored victories by getting major retailers like TOPSHOP, Forever 21 and J. Crew to stop selling fur items - and scored messes by pelting flour bombs at Paris Hilton when she was in London”. Its hasn’t made any difference to the TOPSHOP industry as seen here https://www.facebook.com/photo.php?fbid=593287620698148&set=a.188186667874914.55931.176078879085693&type=1&theater “Chloe Green, television personality, shoe designer and daughter of Top shop owner, paired her gorgeous Barbados holiday tan with a leather jacket with fur trim”
There are many fur retailers in the world from London Canada and Asia
http://www.thelondonfurcompany.com/about.htm
http://sitebuilder.yell.com/sb/show.do?id=SB0001741542000020
http://www.mayfair-london.co.uk/ladies_fashion-FursofMayfairLtd.htm
http://www.furinsider.com/ (Sweet fur stories)
http://www.yellowpages.ca/bus/Quebec/Montreal/Nicholas-Turgeon-Fourrures/1807739.html
The top listed retailers sell mainly animal fur with little faux fur “fake mixed” nylon material fur within their premises. Prices start from $2,000 to $70,000 for a mixture of animal skin pelts.
In a 2010 investigation in 2010 the investigations showed the following;
In their own words;
For the past year-and-a-half, the Animal Rights Alliance investigation unit has been mapping out the Swedish fur industry. We have combed through environmental inspection protocols, court documents and research reports and what’s more - we have visited one-fifth of the 75 mink farms in Sweden to see them for ourselves. We have discovered major environmental violations by an industry that is already highly-criticized. Above all we have discovered the mink. Clever, beautiful wild mink imprisoned in shed after shed, housing row after row of small dirty cages.
Mink that will never see any water beyond what comes out of a water nipple even though they are hunters that naturally spend half of their life in water. Mink that express so-called stereotypical behavior, endless repetitive motion without purpose, a feeble attempt at dealing with stress and frustration.
We already knew that this would be the case. We were prepared for meeting curious eyes behind bars from animals that are so psychologically-broken that they incessantly circle their cages. We knew that it would be bad, but reality on the farms was worse than we could have ever imagined.
Scandinavian Fur Farm - Please click the link to view the horror
We understood that the mortality rate would be high. Several reports show that one out of every four or five animals die before they reach 6 months of age. But we didn’t know how they die – and how they suffer. Now we know. We have seen pups chewing on their dead littermates, entire litters where every animals has had its ear bitten off; young animals with gaping wounds on their heads; and fully-grown mink that twist and turn in agony, screaming in panic from pain and illness that minutes later ceases but only with their death.
It has been terrible to see all of this without being able to do anything about it. On our worst days, we felt completely powerless. But we’ve been driven to continue toward our goal – to make public the horrific animal cruelty that occurs on the farms. This animal cruelty cannot continue in silence.
The fourth paragraph of the Animal Welfare Act clearly states that all animals must be allowed to express their natural behaviours and that they must be protected from unnecessary suffering. But Sweden continues to allow mink to be bred and kept in mesh cages that are no bigger than 30 x 90 centimeters before being killed to produce an unnecessary luxury product that nobody needs. In 2003, the Swedish Commission of Inquiry into the Fur Industry gave Swedish fur farms until 2010 to comply with the Animal Welfare Act. Seven years later we can conclude that the Swedish fur industry has done nothing to improve conditions for mink on fur farms. It is high-time that the fur industry is made history.
The Animal Rights Alliance
The Animal Rights Alliance is a not-for-profit campaigning group that speaks for the animals. Founded in 2005, we have since then brought about the criminalization of bestiality, organized five veggie food conventions and exposed the Swedish pork industry through undercover investigation. Our work for the animals is completely dependent on donations, supporting members and active volunteers.
STEREOTYPICAL BEHAVIOR
“Animals shall be kept and maintained in an environment that furthers their good health and allows them to behave naturally”. – Animal Welfare Act (1988:534), 4 §
We have filmed evidence of stereotypical behaviour on thirteen of the fifteen farms that we visited. The stereotype, by which we mean incessant repetitive motion that serves no purpose, is a feeble attempt by the mink to deal with stress and frustration. It is a common symptom of an animal’s natural needs not being met “The majority of mink show typical signs of derangement that animals express when confined to areas that are too constrictive” – Sverre Sjölander, Professor in Zoology.
SICK AND INJURED ANIMALS
“A sick or injured animal shall be given necessary medical attention, if the illness or injury isn’t severe enough to justify the animal being put down immediately”.
Animal Welfare Act (1988:534) § 9.
We have found sick animals with infected eyes and ear; unconscious, convulsive and dead animals were found on two-thirds of the farms. Maimed, bleeding animals with torn-off ears, large gaping head wounds and missing limps were found on eleven of the fifteen visited farms. The horrific injuries are the result of fights caused by crowding, in shockingly small cages in the wild mink interact only to mate – but the injuries are also oftentimes caused by self-mutilation. According to 2 § of the Animal Welfare Act, animals are to be “treated well and are to be protected from unnecessary suffering and illness”.
“If a cow becomes sick, then we’re called immediately. But the mink are so many that if one animal becomes sick, then we’re not called – the animal has too little economic value for the farmer. We only get called if there is an epidemic. But every animal has an intrinsic value and the Animal Welfare Act clearly states that if an animal becomes sick, then it must be treated or euthanized. Large farms like mink farms have so many animals that it can take time before illness is discovered”
– My Leffler, District Veterinarian who used to work on mink farms.
DEAD ANIMALS IN THE CAGES
On 80% of the farms, we found dead animals in the cages – in most cases, the carcasses were left among other living animals. In many cases, the carcasses had been half-eaten by their mother and siblings.
“In the natural world, it isn’t normal for a mink to be forced to be around another dead mink. When it happens on a farm, it can lead to cannibalism because they are so under stimulated and don’t know how to react to the situation” – Mark Collins, Veterinarian
DIRTY CAGES
On 67% of the farms, we found cages where large amounts of faeces had piled up, oftentimes in thick layers. Mink avoid their own feces so when the cage fills up with waste, an already small space becomes even smaller.
ILLEGAL SEWAGE RUNOFF
Manure runoff could be documented at 80% of the farms. Mink manure contains high levels of nitrogen and phosphorus and causes contamination of water and soil if leaked out into the environment. Mink farms are therefore classified as environmentally-hazardous operations. By law, manure must be stored in such a way that it is sheltered from rain while preventing soil seepage.
ILLEGAL HANDLING OF CARCASSES
“Carcasses awaiting transport shall be stored in such a way that disease cannot be spread through contact with wild animals. The waste shall be stored separate from living animals” – Board of Agriculture Regulations 2009:6, section K 14.
Dead mink that had been left to rot throughout and around the farm property, or were otherwise disposed of improperly, were found on 73% of the farms, even though all carcasses must be immediately removed and stored, preferably frozen. Many carcasses had been left to rot for at least 6 months, since the pelting season last November.
CANNIBALISM
We have documented cannibalism on half of the farms. Mink females that kill their young and littermates that kill and eat one another is more the rule than the exception. Cannibalism is caused by stress and lack of stimulation. The mink have no release for their hunting instincts and those mink that fall victim to attack have no possibility to take flight or cover in their tiny cages.“Animals on fur farms have high levels of stress and this can cause cannibalism” - My Leffler, Veterinarian.
In a 2012 investigation the designer Giorgio Armani;
In PETAs own words;
A disturbing new undercover exposé of rabbit fur farms on two different continents shows that rabbit slaughter, no matter why or where it occurs, is always cruel. The video, narrated by actor Gillian Anderson, shows rabbits kicking and screaming during slaughter. After the skin is ripped from the rabbits’ bodies, it is sold to designers such as Giorgio Armani—who uses rabbit fur in his new designs.
The undercover investigations of rabbit fur farms in China and France—two countries from which Armani buys rabbit fur—revealed pitiful living conditions for rabbits, who are confined to tiny wire cages before they are slaughtered.
In the video footage from the investigation, workers at the Chinese farm pull rabbits out of cages by their ears and shock the screaming animals in the head with a handheld electrical device, often multiple times. Rabbits with slit throats can be seen twitching and shaking, with their eyes wide open, before they die.
Armani now sells fur, including rabbit-fur coats for babies and children. The new designs mean he has broken the promise he made just last year when he said, “I spoke with the people from PETA, and they showed me some materials that convinced me not to use fur.”
Please contact Giorgio Armani and urge him to keep the promise that he made by permanently removing all fur from his collections.
Please also send polite comments to:
Giorgio Armani Corporation
114 Fifth Ave., 17th Fl.
New York, NY 10011
212-366-9720
Still believe fur is ethically correct? We don’t and we are fighting this blood soaked war silently but surely and will cease this repulsive disgust.
Email us for more information at
Donate for a Zoologist in Benue http://fnd.us/c/3PFe2 read more in the link..
Together we can stop abuse – Together we can make change happen
Dr J C Dimetri V.M.D, B.E.S, Ma, PhD , MEnvSc
Apparantly the video below is “ecological mink farming the exact same as “Europe and Canada” so the narrator quotes..
Environmentalism chapter 10 - The Abyss
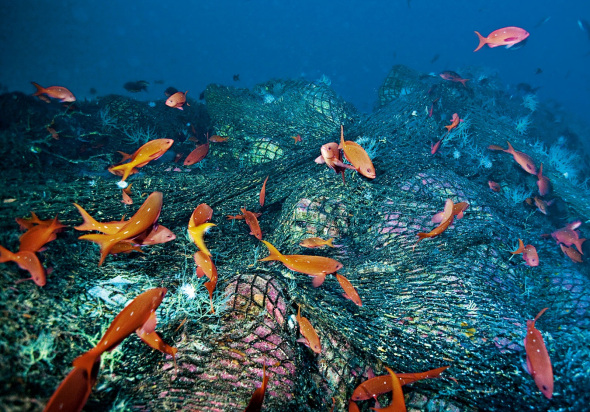

What lurks beneath the deep blue sea? Well in the way of sustainable fishing and poaching of Sharks, Seals and Whales in the Arctic, Pacific and Indian ocean that I shall explain more on in the next in depth document there is indeed a whole garden of aquatic life from botanical marine species, plankton, Octopus, to sea Snakes and the deep blue monsters of the oceans as some refer too which has gotten many scientists, marine biologists, botanists and conservationists excited.
On a recent article that we reported on within our South African site that is the information and awareness centre for our work within Africa https://www.facebook.com/pages/International-Animal-Rescue-Foundation-World-Action-South-Africa/199685603444685?fref=ts I recently reported in brief some of the most fantastic aquatic and oceanographic finds made by explorers using the DeepSee submersible that that explored the rocky ridges and mountainous terrain of the “Las Gemelas” which Author Mr Greg Stone reported on the rough terrains of the sea mounts deep below the surface of the water in 2012 of which a ten person team spent ten days studying the area then releasing all conclusive data which was absolutely intriguing to read and view.
The Submersible descended over six hundred feet below the surface of the ocean of which there are located worldwide hundreds of thousands of “seamounts” that rise from the earths floor, only three hundred have ever been explored and still to this very day we have not discovered even 50% of what lies beneath at such amazing depths that the normal diver would not be able to survive sue to the crushing ocean pressure that would kill him/her instantly.
Just to give you a glimpse of the size of these seamounts of which these scientists descended to over 600+ feet below the surface of the water, the Empire State Building stands at 1,454ft tall that’s including the lightning rod too, the height start of “Las Gemelas” is 1,115ft at the summit “ whereas the entire size from top to surface of the Gemelas is a staggering 14,000ft that see’s deep ocean currents rushing up then spiralling around the mount of “Las Gemelas” with a vortex type cyclone whooshing around the summit of the mount at 1,115ft as quoted.
You could almost be fooled into thinking that nothing lives at such insane depths however that’s where most people are wrong and it’s at these depths that scientists believe some form of “how our universe” evolved lies deep below. Before I briefly go in to what species of aquatic marine life lives at such depths let’s take a sheer look at “Las Gemelas” that’s truly one haven of breaming marine and botanical life untouchable by any poacher to hunter.
Las Gemelas is located at Cocos Island territory coastline, located in the Indian Ocean, southwest of Christmas Island and approximately midway between Australia and Sri Lanka. The territory consists of two atolls and 27 coral islands, of which two, West Island and Home Island, are inhabited with a total population of approximately 600 individuals mostly if not all, are native and indigenous.
The Cocos (Keeling) Islands consist of two flat, low-lying coral atolls with an area of 14.2 square kilometres (5.5 sq mi), 26 kilometres (16 miles) of coastline, a highest elevation of 5 metres (16 ft) and thickly covered with coconut palms and other vegetation. The climate is pleasant, moderated by the southeast trade winds for about nine months of the year and with moderate rainfall. Cyclones may occur in the early months of the year.
There are a total of 24 individual islets forming an incomplete atoll ring, with a total land area of 13.1 square kilometres (5.1 sq mi). Only Home Island and West Island are populated. The Cocos Malays maintain weekend shacks, referred to as pondoks, on most of the larger islands. The islands belonged to the British Empire from 1857 then were placed within the hands of the Australian government in 1955 which still flies the British flag within its now Australian flag.
On the morning of 9 November 1914, the islands became the site of the Battle of Cocos, one of the first naval battles of World War I, During World War II, the cable station was once again a vital link. Allied planners noted that the islands might be seized as an airfield for German raider cruisers operating in the Indian Ocean.
The islands or islets as they are better referred to have no rivers or lakes of which fresh water is extremely limited, the islet inhabitants either make do or rely on supplies from the main lands.
The Tour of Seamount is located deep out to sea from the islands and not as close as some may believe, and being within such mineral rich and warm waters an abundance of life forms from the summit to the entire depth of the ocean floor.
When scientists went on to explore Las Gemelas in 2012 they located a rich biodiversity of corals, sponges, crabs, sea urchins, star fish, to sea cucumbers, deep sea fish and exciting views of a complex underwater mountain system similar to the other three hundred other “explored” ridges and sea mounts throughout the oceans underworld internationally.
Although the exploration team found teems of deep sea fish and rich biodiversity that still to this day cannot be identified correctly or even named the facts are there, however in the numbers there are more fishers than protectors, and as with many MPAs the world over, it was witnessed that current efforts need further support within this region to protect this swarming ecological system or we could “loose it”. However let’s not jump one hundred paces forward and keep it at one step at a time. These areas are remote, they cannot be accessed easily, and other species of life can be introduced to sustain biodiversity and even the odds out for all thus leaving an area rich in natural habitat.
What lies at such gargantuan depths though, well this is the truly amazing part and that’s why I have only kept the write up short on this particular page and will go in to some detail on amazing biodiversity finds old and new in the “later”.. It truly is a wonderful ecosystem down there though. One that has to be explored more..
Explanation of a sea hydro-thermal vent ?
Well firstly lets view the hydro thermal sea mount more or less the same but they are a little smaller and are more commonly refereed to as smoking chimneys I have included the video for you to understand more on this as I think it’s a lot easier for you to “view and hear” in real time the difference between the two. To view more on this particular sea “chimney” please click the picture, alternatively please view the video below.
A hydrothermal vent is a fissure in a planet’s surface from which geothermally heated water issues. Hydrothermal vents are commonly found near volcanically active places, areas where tectonic plates are moving apart, ocean basins, and hotspots. Hydrothermal vents exist because the earth is both geologically active and has large amounts of water on its surface and within its crust.
Common land types include hot springs, fumaroles and geysers. Under the sea, hydrothermal vents may form features called black smokers. Relative to the majority of the deep sea, the areas around submarine hydrothermal vents are biologically more productive, often hosting complex communities fueled by the chemicals dissolved in the vent fluids. Chemosynthetic archaea form the base of the food chain, supporting diverse organisms, including giant tube worms, clams, limpets and shrimp. Active hydrothermal vents are believed to exist on Jupiter’s moon Europa, and ancient hydrothermal vents have been speculated to exist on Mars.
Explanation of a sea-mount?

A seamount is a mountain rising from the ocean seafloor that does not reach to the water’s surface (sea level), and thus is not an island. These are typically formed from extinct volcanoes that rise abruptly and are usually found rising from the seafloor to 1,000-4,000 meters (3,000-13,000 ft) in height. They are defined byoceanographers as independent features that rise to at least 1,000 metres (3,281 ft) above the seafloor.
The peaks are often found hundreds to thousands of meters below the surface, and are therefore considered to be within the deep sea. There are an estimated 100,000 seamounts across the globe, with only a few having been studied. Seamounts come in all shapes and sizes, and follow a distinctive pattern of growth, activity, and death. In recent years, several active seamounts have been observed, for example Loihi in the Hawaiian Islands.
What lies beneath this particular Sea Mount that exploration teams located in 2012?
There is an abundance of aquatic sea, molluscs, plankton to sharks, squids and corals that live in this particular area of the Americas coast line, the further that one descends into the deep blue sea the warmer then colder the ocean layer becomes
One cannot travel any further below than this and what you are witnessing in the videos below is the surface of the earth miles below or to be precise over 22,000 feet below the surface level exactly four and half miles down to the earths layer excluding the crust which scientists, marine biologists, and geologists study as a way of knowing what “may of lived or still resides other planets to understanding evolution and geology land mass geography, and the planetary systems.
The five largest sea mounts that hold an abundance of biodiversity are located in between the Atlantic Ocean and just across the Pacific which are named as Cortes Bank standing and El Bajo sea mount at two points, Las Gemelas sea mount, Cross sea mount, with a sprawling sized mounts at Raja Amoat Islands.
Las Gemelas biodiversity in brief;

Sea Lilly - Crinoids are marine animals that make up the class Crinoidea (And to think they where a “plant”)

Pseudotriakis microdon - False Cat Shark, the behaviour of this shark is by far a lot different to that of the typical species of sharks, however they are endangered due to over fishing, hunting, and pollution
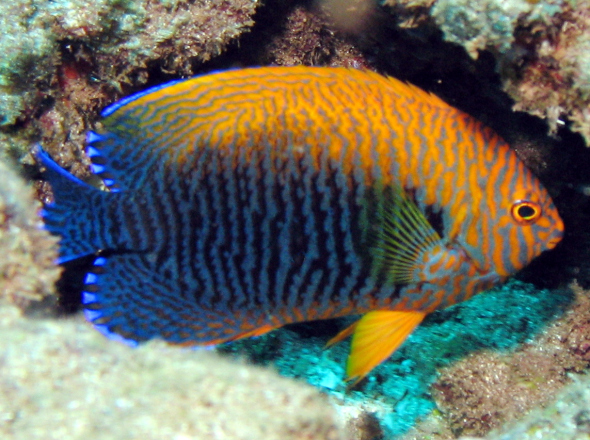

Centropyge potteri - Potters Angel Fish can be located near enough sea level, the Centropyge potteri swims just below that of the Humpback Whale at just above 1,300 feet
Enypniastes eximia - Swimming Cucumber located at depth of just under 13,000 feet in ice cold waters

Ophidiidae - Cusk Eal (This species of fish live deeper than any other known fish on the planet to date)

Isididae - Bamboo coral, this living species thrives along the 47 mile Puna Ridge (Quite fantastic to know that botanical species such as this thrive in such harsh conditions without photosynthesis)

A little further on the corral lay Surgeonfish amid a school of yellow snappers

Culcita Novaguineae - Cushion Star (12,000 ft this has to be the lowest species of Star Fish to survive) as such low depths
I will continue on with this document in three parts as there truly is some fantastic species of life both above the sea level and below it spanning globally on the sea mounts that are rarely explored.. Who know’s what else is down there.
Please view the video’s below and please stay tuned for our Fox documentary that will be focusing on the European living fox.
Environmentalism Chapter 9 - Animal parts trade - Probing the problem part II
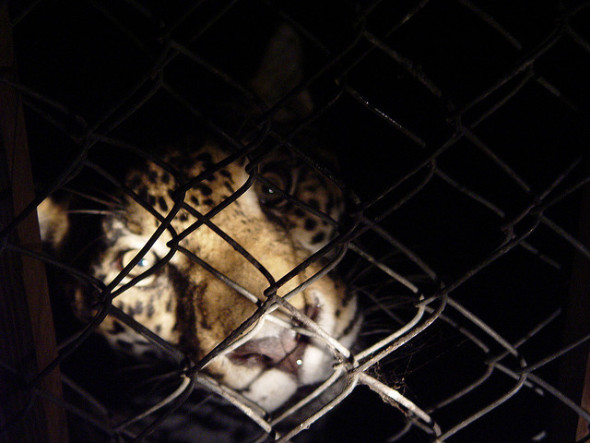

At the start of the month January we had the pleasure of screening a young wildlife photographers work by Pooja Gupta regarding the trade in Parrots and whether it is an ethical choice or not on purchasing them to just place within solitary confinements of a cage.
The pet trade is mirroring that of the illegal tropical pet trade of which many animals from around the world are stolen from their natural habitat then bred time again that provides an array of animals both for the “legal pet trade in tropical domestic tropical animals” to the illegal trade of which 90% of all funds now go to illegal arms sales and deals to fund terrorists.
These terrorists are mainly groups such as Al-Qaida, Abu Nidal Organization, Army of Islam, to the communist party of India and China, and internet terrorists such as Anonymous that claim to be “animal lovers” when in reality their battle is nothing more than fighting politics alongside all other domestic and non-domestic terror cells that cause havoc and disruption on an international scale without understanding the basic fundamental views of what they are fighting for, to even battling in the wrong perspective causing more harm than good.
One cannot preserve life by fighting on the computer, nor can one cannot save an animal online hence why we stand by our word and will not nor ever “support terrorists” that lack support of millions hence why they attack in certain ways and “areas” to gain support of weak minds” that fight with “emotions and love instead of education and hands on experience.
One of the main mission statements of the International Animal Rescue Foundation © is to create awareness of the key animal and environmental international issues that are effecting our way of living and Mother Nature that surrounds us. The illegal pet trade and animal parts trade is one of them and it’s now time to attack this head on and pin point the main spots that we now must focus on before the situation grows more out of hand.
As I stated yesterday 23 January 2013 the illegal animal parts trade and pet trade is now the number one easy money maker plus is now finically supporting terrorism in many nations online and on the ground. How bad though is the problem? I have outlined this below in brief;
- The global illegal trade in live species and animal parts — used for luxury accessories, Asian medicine or folk remedies like aphrodisiacs — is estimated to be worth up to $20 billion a year, Interpol quoted in 2011 this has now risen to a eye watering 34.6 billion a year “just for illegal pet trade”.
- Dealers will specialise in mainly big profit animals such as arachnids, reptilians, big cats, to birds and fish making on average for each species a whopping $30,000 to $90,000 (each) the more the sell of one species the quicker that species becomes critically endangered.
- It’s now a well-known fact that law enforcement and customs are poorly trained on recognising endangered species to taking action with the offenders getting of scot free or with just a slap on the wrist.
- Links between the animal tropical pet trade and narcotic smuggling are now identical with animal trafficking now seen as best opportunity to make money easily and quick without the authorities being alerted as narcotic smuggling would be.
- According to a series of U.N. studies on the illicit traffic of wildlife, wildlife experts claim that Chinese, Japanese, Italian, and Russian organized crime syndicates are “heavily involved in illegal wildlife trade.” While such claims do not suggest that organized crime syndicates are involved in all forms of wildlife trafficking, the United Nations reports that syndicates are “strongly present” in some sectors. Further, even when criminal syndicates are not controlling the trade, much of the trafficking is commonly described as “highly organized…” Anecdotal accounts also indicate that some organized groups are involved in both illegal wildlife and human trafficking.
- Although evidence has been reported as “slim” to link the pet trade to terrorism the evidence that’s been located so far by Interpol states that Asia and Africa are the two number one key groups that are profiteering, trafficking and involved in illegal arms deals to terrorism of which “animals are the number one sufferer”.
Two incidents from the last few years show;
In a major 2007 sting operation by the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, the largest of its kind, undercover agents spent three years infiltrating a ring smuggling endangered sea turtle skins from the shores of southern Mexico to as far north as Chicago. Illegal drugs turned up on both sides of the border over the course of the investigation, U.S. Fish and Wildlife agent quoted.
In the same investigations another incident showed;
In the United States, marijuana was seized at one of the raided warehouses filled with animal skin boots. On the Mexican side, smugglers offered to ship cocaine along with the hides of turtles whose numbers are rapidly dwindling in the wild. “It was just thrown out there like ‘Hey, we can also move this stuff if you want.’… They are pretty much moving anything from pets to animal parts.
The pet trade and illegal animal parts trade we all know is big but does it ever enter into the “professional business’s” and then people’s homes? I mean you would expect that professional pet stores that are selling freely handing out advice to advertising on television would know the difference between an “endangered species” and a pet yes?
“Since the World Trade Center Attacks the illegal animal parts trade and exotic pet trade has driven terrorism vastly funding organised crime from narcotics to the military arms deals in Asia and Africa”..
Location Beirut;
Grey parrots and vervet monkeys mingle with cats, dogs and hamsters in many of Lebanon’s pet shops, but if you want the really exciting animals, you have to ask behind the counter.
Lions, panthers and bears—in fact many of the mascots from the American sports franchises—are just a few of the animals you can buy here. One pet store in Beirut—whose owner requested anonymity for fear of protests from animal rights groups—offers a chance at owning your own piece of the wild. The owner received a degree in veterinarian studies in Russia and, unlike many pet stores here, the six dogs strategically placed in the window are clean, healthy and vaccinated.
But these aren’t the only animals he sells. He can get you lion and bear cubs, leopards, even a baby crocodile. Sitting behind a tidy desk surrounded by bags of pet food, he describes the process of how a wild animal is ordered and smuggled into Lebanon.
It starts with a deposit (lions, for example, require a down payment of $1,000-$1,500). The pet store owner then puts in an order to a Lebanese middleman who contacts a farm in neighboring Syria, where lions are raised for sale. The animals are placed in boxes and loaded into taxis that head for the Lebanese-Syrian border. At the border the taxi driver will often bribe a guard around $10, usually saying there are dogs in the crates.
According to Jason Mier of Animals Lebanon, chimpanzees in central Africa can go for as little as $20. This means buying and reselling the animals abroad can bring in a huge profit. (Photo courtesy of Animals Lebanon)
The pet store owner offers a video on his iPhone as proof of the process. In it a lion cub is jammed into a metal kennel most likely meant for domesticated dogs or cats. A man whose face is out of the frame kicks the cage.
“[The animals] have a better life here [in Lebanon] than on the farms in Syria,” says the pet store owner, adding that carnivores like lions and leopards are often underfed because farm owners can’t afford to feed them meat. But despite his concern for the animals, his motives are economic. He says orders are sporadic and so exact figures are hard to pin down, but one lion cub tends to go for $3,000-$5,000. In the right market, with the right client, the cost can go as high as $10,000.
Current Lebanese animal welfare legislation consists of just three sentences and calls for a maximum penalty of less than $15. In addition, it is rarely enforced—Animals Lebanon states “extensive research has not shown this law used even once in the past twenty years.”
And though Lebanese parliament voted in July to become the 176th member of the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species, few here seem convinced that the trade of exotic animals will stop. Because the trafficking of exotic pets is illegal in Lebanon, it’s hard to know exactly how many wild animals are smuggled into the country every year. The pet store owner estimates there are around 40 locations in the country that keep exotic pets on private or public display—from zoos to pet stores and even family homes.
“The phenomenon of keeping large ‘dangerous’ animals as pets appears to be gaining popularity in the Middle East,” writes Richard Thomas, communications coordinator for the wildlife trade monitoring organization TRAFFIC International, by email. “We receive regular report[s] of … Cheetah, Lions, Tigers, etc. in that region.” A lion is rescued by Animals Lebanon from an Egyptian circus. (Photo courtesy Animals Lebanon)
Lebanon and Syria are not the only countries implicated in this trend. Jason Mier, executive director of Animals Lebanon, says that in addition to “at least four zoos in Damascus,” Central and West Africa are hotbeds for wild animal smuggling.
Mier, who worked on animal welfare issues in a number of African countries before coming to Lebanon, says poverty drives the exotic animal trade in many countries. He says he saw vendors in the Congo selling baby chimpanzees for $20, an amount that represents a “huge profit when people on average earn 23 cents a day.”
According to Mier, other countries that supply Lebanon include South Africa, Ukraine and Bulgaria (where Mier says you can rent a lion cub for a day). According to the pet store owner, crocodiles are often smuggled through the airport from Malaysia labeled as “fish.”
So who is buying and raising these animals? Especially at time when the Lebanese middle class is struggling with electricity and water shortages? “The keeping of exotic animals as pets is centuries old,” explains Thomas. “Cleopatra is believed to have owned a pet leopard named Arrow and possibly even a pet tiger too.” But history aside, Thomas says prestige among Lebanon’s upper crust is the real reason people want to have exotic pets.
“The impression I have is that it has become something of a fashion/status symbol to own a dangerous pet,” he writes, “which is why it’s growing in popularity.” According to the pet store owner, the secluded villas of the Lebanese elite outside Beirut are the destination for many of these animals. They are kept in cages or allowed to roam in fenced gardens.
Souraya Mouawad grew up in such a villa, one that was briefly home to a doomed leopard named Moulou in the 1970s. Speaking on the phone, Mouawad, who was born and lived in Africa as a child but moved to Lebanon as a teenager, fondly remembers the adored childhood pet.
http://animal.discovery.com/tv-shows/fatal-attractions/lists/facts-exotic-pet-trade.htm
“My father bought a big house in Tripoli with lots of space and he went back to Africa. We settled there—my sister, my mother and my aunt. When my father came back he brought us a 3-month-old leopard.
Foxes are one of the few wild animals native to Lebanon that are kept as exotic pets. (Photo by Carine Mechref) “We named him Moulou. When we first got him … we stayed at the Carlton, a five-star hotel. The valet parking man who was wearing white gloves brought steak for Moulou to eat. Moulou slept in the Carlton hotel garden that night and when we woke up he had broken all the small plants and trees.”
As infants, wild animals are often cute and manageable. But Mounir Abi-Said, founder of a wildlife preservation in Aley (a town northwest of the capitol), says wild animals are often locked in small cages and left in poor conditions once they become older, more dangerous and more expensive to care for. “Moulou was an adult at one year,” says Mouawad of the leopard’s transition from a cuddly playmate to a wild animal. “He ate 10 pounds of fresh meat a day and drank 5 liters of milk.”
Despite the family buying a large parking area so Moulou could get his necessary exercise, Moulou suffered from back paralysis and couldn’t run. “We didn’t know he should be in Africa and not with us,” says Mouawad, who is now founder of Animals Pride and Freedom (APAF), an animal rescue organization.
As danger from Lebanon’s civil war rose in early 1975, Mouawad and her family decided to return to Africa, but Moulou couldn’t travel in his condition. After numerous attempts at finding a new home for the leopard, Mouawad’s father had the animal secretly euthanized just as the family left for the airport.
When Mouawad learned the truth years later, it caused a deep rift between her and her father. “I didn’t eat at the same table with my father for four years and I didn’t talk to him for four years,” she says. The vervet monkey is commonly found in Lebanese pet stores. (Photo courtesy of Carine Mechref)
Exotic pets often meet tragic ends. Owners are faced with the reality of a full-grown wild animal in their house and among their family. For some, like Mouawad, there is an emotional attachment; in other cases the animal is simply an accessory that has grown inconvenient.
Mier remembers one recent case when a chimpanzee was left on the side of the road next to a private villa. Despite the poor conditions, Mier was unable to do much legally and it took months to convince the owner to hand over the chimp to Animals Lebanon so they could relocate it to a sanctuary.
Lebanon’s lack of laws—and the government’s inability to enforce them—pose challenges to animal rights supporters. While it doesn’t replace national laws, Mier maintains that CITES’s framework will help Lebanon develop proper laws as well as educate officials to take appropriate actions toward the wild animal trade.
“[In other countries, CITES] slowed smuggling and saved some animals from going extinct,” said Mier.
Mier contends that it will take more to slow the “multibillion-dollar industry” that is the exotic animal trade here.
Location Japan; 2012
Animal charities have condemned NOAH: The Inner City Zoo for selling penguins, meerkats, alligators and monkeys. The creatures are caged in one squashed room — on the second floor of an office building.
Set up in 1999, NOAH (Nature Orientated Animal House) also sells otters, megabats, sloths, foxes and a crane — alongside several other exotic animals. Some of the animals cost thousands of pounds to buy and customers even have to pay a £4 entry fee to look around the shop.
One onlooker said: “Most animals were quiet, as if they’d come to terms with their enforced captivity. Many are in tiny cages, and the owls are tightly fixed down so they can’t fly.
Josey Sharrad from the International Fund for Animal Welfare, said: “IFAW absolutely condemn the treatment of these animals. “These conditions cause severe stress for the animals which can weaken immune systems and leas to risk of disease. “When these creatures are available for purchase, it confuses people as to whether an animal is really at risk of extinction or not.”
According to their website, NOAH has just recently taken stock of marmosets, fennecs and squirrels — all as babies. Prices are often on request, and a prairie dog — a type of rodent — was priced at £1,500. Alan Knight, Chief Executive of International Animal Rescue said: “We would urge people to stay away from this pet shop and others like it. “Exotic animals should live in the wild as nature intended, not in captivity as a source of entertainment and prestige, and to line the pockets of greedy pet shop owners.
“Breeding and selling wild animals as exotic pets is cruel and irresponsible. “Undoubtedly many of them are eventually abandoned when they become ill or grow too large and too strong for their owners to manage.” Owner, Kenji Takahashi, 59, insists that he obeys all the rules of Japan.
He said: “I may not agree with all the laws of Japan, but I must obey them. “My premises may not be perfect and the space we have for each animal is not as big as we would sometimes like. “But the same could be said for any zoo across the world. “What I am trying to do is increase the love that humans have for exotic animals.”
In the United Kingdom one of the last continents that one would least expect to find or even know of anyone selling or profiteering from the exotic pet trade of which you would think that this is simply a taboo and that the United Kingdom is known for its love of animals and nature wouldn’t be involved in such crimes.
Regrettably that there are many illegally exotic pets entering England and leaving the England every day that customs are still “not trained” in identifying to going through every single item in the crates.
In the UK, wild animals deemed ‘hazardous’ are licensed under the Dangerous Wild Animals Act of 1976. However, this legislation was created mainly to protect the public rather than ensure high standards of animal welfare.
In the UK there are known to be at least 154 big cats held in private hands (including 12 lions and 14 tigers), almost 500 assorted monkeys, over 250 venomous snakes and 50 members of the crocodile family. (Big cats in Britain, 2006)
Between 1994-2004, the European Union was one of the largest importers of wild-caught birds, importing a massive 9.5 million birds of species listed in the Appendices of the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES) – equivalent 87% of world trade. However, as a result of the avian influenza outbreak and campaigning by the RSPB¹, APA² and others, July 2007 brought permanent ban on the import of wild birds into Britain and the rest of the European Union.
Location; United Kingdom Leeds 2010
A couple who ran a pet shop turned their hand to illegal trading in the skins and bones of some of the most endangered species in the world.
Graham and Norah Pitchforth sold on eBay, among others, a stuffed lion cub and birds of prey, monkey skulls, flying fox skulls, butterflies, snake skulls and the skin and skull of a penguin.
Other species included baboons, macaques, otters, macaws, rhinoceros, kestrels and a porcupine. The Pitchforths ran a legitimate business, called Get The Bug, on the internet auction site, selling specimens of animals they had imported or acquired – but some transactions were outlawed. They each pleaded guilty earlier this year to multiple charges relating to the importing, exporting, selling and possession of endangered species after failing to get necessary documentation.
Leeds Crown Court heard that the couple sometimes labelled packages as other items, such as “table decorations”, to avoid suspicion, and on one occasion agreed with a seller to claim that a stuffed snowy owl was a gift when he had paid £150 for the item. The pair, from West Yorkshire, were yesterday sentenced to 44 weeks’ imprisonment, suspended for 18 months. They were also ordered to carry out 200 hours of unpaid work.
The court was told that the couple, of Wrenthorpe, Wakefield, had run a pet shop for 20 years and were “extremely well-thought-of” in the local community. Graham Pitchforth, 61, had an interest in collecting specimens and taxidermy and had a part-time job lecturing students at Wakefield College about endangered animals. The pair set up the eBay shop and sold 3,637 animal specimens – of which 22 were found to have been traded illegally between October 2005 and December 2006, making a profit of £2,329.16.
The court heard that the couple failed to get the relevant permits for the importation, exportation or sale of these 22 transactions, despite knowing they were needed. Sentencing, Judge Christopher Batty told them: “You fall to be sentenced for 22 transactions made in the full knowledge you were not entitled to make them. You did and knew you did not have the necessary authorisation so to do. Much of your business was legitimate, and as such it is clear that you had the relevant knowledge and expertise to deal legitimately in the trade of endangered species.”
Judge Batty said Norah Pitchforth, 65, received a police caution in July 2005 for offering a barn owl for sale without the appropriate permit. On other occasions, the couple were told that some skulls required certificates but continued without and a consignment of hornbill casks exported to the United States was seized for not having proper documentation. Some transactions were arranged by email, which the couple sometimes asked to be destroyed following the sale.
The couple held hands and Norah Pitchforth repeatedly wiped her eyes as Judge Batty told them he would suspend their sentences, despite the serious nature of the crimes.
He said: “I have thought long and hard today about what to do with you. This was a deliberate flouting of the regulations for commercial gain.” The pair admitted 12 counts of illegally exporting, three of illegally importing, seven of illegally selling and two of illegally possessing specimens under the Customs and Excise Management Act.
3,637 Animal specimens sold – 22 of which were found to have been traded illegally.
No continent is immune from the illegal wildlife trade or the exotic pet trade and although this et store was not you “average Joe Blogs” it still accounts for a pet store that kept no records of which somewhere in the United Kingdom people have in their possession “critically endangered species” and this is why International Animal Rescue Foundation © never fuels, or supports such activities that are wiping out our species every year.
The Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES) has brought together 175 nations to combat the illegal and unsustainable wildlife trade through a uniform regulatory regime and increased coordination on a global scale. The U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service’s (Service) Division of Management Authority and Division of Scientific Authority, as well as the Office of Law Enforcement, are primarily responsible for implementing and enforcing CITES in the United States.
Recently, CITES founded the International Consortium on Combatting Wildlife Crime (ICCWC), a collaborative effort between the CITES Secretariat, INTERPOL, the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC), the World Bank and the World Customs Organization (WCO). ICCWC was formed to increase prosecution and punishment for caught smugglers and poachers as well as increase law enforcement in developing nations. Visit the CITES website to learn more about ICCWC.
Yesterday we focused on two fundamental and known factors of which we are fully investigating, Climatological destruction we are 100% certain is fuelling the skyrocketing demand for more wildlife/pet products, because the normal TCM/TIM markets are running short of medicinal plants that the TCM/TIM markets are mostly made up of.
As quoted we have to look at all sides of the problem and not just focus on the poacher and “demand for fake medicine to the individual consumer purchasing for entertainment and consumption purposes” because this is NOT the key element that is funding the trade of illegal animal parts and the exotic animal trade of illegally imported animals.
The trade is also being funded by “ourselves without knowing” which we are investigating and and now producing an international survey as well as asking other a-like wildlife organisations for their help to now pinpoint even the smallest of problem areas, highlight them, and then deal with them. You can answer the survey anonymously below and please be truthful. We will not know whom has answered to what location in the world your based. The survey is a simple yes and no answer poll with multiple questions.
We will only accept one answer per question and one cannot re-answer the poll of which gives us accurate results. We thank you for your honesty and feed back and would be most kind if you would share this survey to your friends, family and Social Media friends.
The other main factors are;
- Pet trade (lack of awareness and education) Purchasing exotic pets that have been illegally imported which the customer purchases “unwittingly” not knowing the damage they are causing to vulnerable, endangered, and critically endangered species.
- Tourism (Tourists purchasing trinkets or souvenir’s from beach sellers, to flea markets, again the buyer unwittingly knowing they are funding the illegal wildlife trade/pet trade) from purchasing products.
- EBay and other Internet sales sites (International Animal Rescue Foundation © has two operation’s in progress so far, one running from 2011 and the other from 2012 Operation Trojan horse – OTH) is focusing on the illegal pet and animal parts trade in seven locations internationally and Operation Swift Cover OSC – is primarily focusing on international online, market and black market sellers to tourism and two other areas that are not named for security reasons.
We must look at the poacher as the harvester as that is all he or she is they are not the seller, producer, courier, or trafficker they simply harvest the goods via an order from the “top of the pyramid” above which in reality is the “least of our worries” and/or the live animals of which they then pass the item/animals on to the courier that then reach the producer/buyer of which the item/animal is then sold on to the “distributor” = a purchaser being the last “action” trade that makes the sale. The profits are then fed In to terrorism/narcotics and the vicious circle goes round again.
Opportunistic poacher/trafficker
The opportunist mostly derives from a poor family with very low income or an individual that needs financial support, and this we all need to tackle and nip in the bud as it is contributing to barbaric slaughter and the exotic pet trade. The Opportunist mainly derives from a poor background and is only seeking profits for their family or themselves of which the government have let them down. So “Community relations /education and AWARENESS” is needed vastly to help in this area.
Within first world nations opportunistic theft is similar to poaching/smuggling although it doesn’t include animals but rather stealing money from the government’s via benefit fraud, illegally working with no permits to basic shop lifting as the opportunist is looking for “a better life or way of living”. So in reality the the poacher/smuggler is no different to that to the modernized thief hence why community relations need to be built to tackle this area.
This area we must address and with Africa and Asia being the number two nations involved here within trafficking/poaching/ and exotic pet trade we must deal with this sensitively and with love and consideration too that will in turn cease the trade of the “opportunists” therefore killing part of the “the problem”.
E-bay and other international buy and sell online sites must be tackled too as there simply is not enough online trade and customs monitoring to cease the sales of inland and international sales of pet/animal parts sales.
January 23rd 2013 we located an Eastern Russian buy and sell site that had within it’s hunting listings Tiger and Leopard skin’s for sale with the opportunity of satisfying the customer with “exotic skins and endangered animal parts”. This has since been reported to law enforcement of which the surveillance team working within Operation Trojan Horse’s Unit have deployed more people to this particular area to probe.
You are breaking the law if you commit an act of poaching/purchasing/distributing/or dealing in endangered species to exotic pets.
Please don’t be a statistic or you could end up in prison.
Please click on the link below to stay up to date with news, view and media on animal and environmental affairs.
Dr J C Dimetri V.M.D, B.E.S, Ma, PhD , MEnvSc
WARNING IF WE/LAW ENFORCEMENT SUSPECT THAT YOU ARE POACHING/TRAFFICKING/LAUNDERING/DISTRIBUTING/AND OR DEALING IN WILDLIFE PRODUCTS YOU WILL BE LOCATED AND PROSECUTED, ANTI POACHING TEAMS ARE NOW SHOOTING POACHERS ON SITE DON’T BE A STATISTIC ARE A FEW $$ REALLY WORTH YOUR LIFE?
Many people ask why we don’t support reserve’s and zoo’s to captivity - Please watch the video all the way through below.
Environmentalism Chapter 8 Animal parts trade - Probing the problem part I

Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) dates as far back as the Shang dynasty (14th–11th centuries BCE) although Shang didn’t actually understand the whole concept of Chinese traditional medicine it then later took of exactly over two thousand years ago that’s seen Asia’s economy benefit.
Mainly used in China, Vietnam, Taiwan, Cambodia to even Africa it’s seen as an alternative to synthetic medicines (manmade) that can have acute side effects to even seriously harming ones health if not administered correctly to overdosed on.
Herbal medicine, acupuncture, reflexology, and massage was the main concept of traditional Chinese medicine at which point really only plant based tinctures where prepared then administered, the same type of medicine was used back in the American years of President Abraham Lincoln to even Europe although little is really known of this very crude western type of practice.
Traditional Chinese medicine has taught many thousands of “registered” practitioners in Asia from the books of the Emperor’s Inner Cannon http://www.unesco.org/new/en/communication-and-information/flagship-project-activities/memory-of-the-world/register/full-list-of-registered-heritage/registered-heritage-page-4/huang-di-nei-jing-yellow-emperors-inner-canon/ and the other ancient old book Treatise on Cold Damage http://history.cultural-china.com/en/60H11290H14411.html
It is unclear to this day when animals where used in the traditional Chinese medicine market however what we do know is that the market is now thriving on animal parts more today than it ever did back in the early 1940s of which we can locate some “form” of evidence which we believe originated from Tibet from reading the Traditional Medicine Handbook that one can view more no here http://www.vitcm.org/?page_id=125
From this point Korea then started to become more involved within the alternative medicine market of which again very “few” animals where used, and to be precise the classic traditional book of alternative Asian pharmaceuticals states from the Tibetan era that 442 were plant parts, 45 were animal parts, and 30 were minerals. Moving forward to present 2013 we now see very more plants are used with many more “species” of animals mainly from the Asian zodiac chart of 12 animals that include Rat, Ox, Tiger, Rabbit, Dragon (lizards are used in TCM) Snake, Horse Sheep, Monkey, Rooster, Dog and finally the Pig.
Traditional Chinese “herbal” medicine then became more used in the 1970’s within America within forty states of which fifty oriental medicine colleges where introduced for students of all backgrounds to train on.
In Korea, more than 5000 herbs and 7000 herbal formulas are used in Traditional Korean Medicine for the prevention and treatment of ailments all deriving from traditional Chinese medicine, Japan followed on from which they refer to (TCM) as Kampo meaning Han Chinese Medical Formulas http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC538517/
However cultures have changed and the world has evolved into a self-destructive planet that now see’s many animals slaughtered internationally to tortured in medieval practices to sustain this ancient form of medicine from which China is the main player and trade route from which animal parts are shipped to, then processed to transported to their final destination.
Taking the million year old Rhinoceros for instance once poached the Rhinoceros horn[s] are then transported over the border once the slaughter has taken place and can be in Asian medicine markets within a three to four days.
The World Health Organization (W.H.O) quoted that nearly 80 per cent of the world’s population depends for its primary health care needs on medicines derived from plants and animals and with disease and illness being rife in third world nations especially Asia then Asia makes up most of this eighty per cent mainly due to poverty.
What’s changed though? Why are we seeing now so many animals slaughtered for medicines that the Asians and we know don’t work as traditional medicines, when you have the other alternative called “Homeopathy” that was first really put into practice in 1700’s by the German physician and chemist Samuel Hahnemann whom lived from 1755-1843. We simply don’t know the complete answer to this however we are searching for the truth and below I have placed some interesting points that we are working on.
- Climate change
- Usage of pesticides, herbicides, insecticide’s, fungicides,
- Over urbanization
- Air pollution and land pollution
- Season weather disruption
These five points are fine indicators of what we have noticed now for some years to be contributing to lesser agricultural plants and herbal stock used which regrettably is equaling to more animals destroyed. I have explained below in brief detail below of our findings to date.
- Climate change – Contributing to fewer herbal crops via extreme unpredictable weather
- Usage of pesticides – Contributing to the destruction of insect and bud pollinators
- Over urbanization – Contributing to land destruction thus reducing land mass to plant reproduction
- Air and Land pollution – Contributing to poorer air quality equaling decreased photosynthesis whilst land pollution being a major factor that leaches toxins in to the ground plus debris pollution
- Seasonal weather disruption – Contributing to moister winters and dryer summers = disruption in agricultural and herbal crops growing and budding at the correct time of season = lower yield
Civil war and international conflicts I shall go in to detail further on as this does require a lot of attention and awareness.
As conservationists and animal welfare professionals we cannot say that demand is just the number one factor here that is driving the illegal animal parts trade, there has to be some form of reason for us to view further beyond demand and it was not until recently going through some 4,000 documents that we started to view a pattern that “may” or may not be the reason why “demand” is high.
Yes there are poor families in Asia just like there is in any other continent, but within these continents that are non-Asian there are very few if any traditional medicine markets like there are within the borders of Asia which has lead us back to “climate change”.
I may sound like a broken record however International Animal Rescue Foundation looks at the (facts) and being a very large organisation on ground and on line we are also educated to.
So let’s look at the facts here first and see if one can start to break the web of destruction open of which we are only going to concentrate on two points here and that is climatological disruption and change and civil war to conflict.
Climatological disruption and change within Asia.
Setting the facts down;
Climate change has moved on from “global warming” and there is no way of stopping the destruction that is being caused now, of which we the human can only “slow the destruction down”. I have contacted the University of Virginia’s traditional Chinese Medicine University as I wish for their secondary advice on whether they think the increase in “animal parts usage” in Asian medicine is due to a decrease in the number of “plants” used in Asian medicine as of botanical climate disruption blamed on climate change.
At present there is no documentation that we have managed to locate on a decrease in “Traditional Chinese medicine botanical use in fact it’s increased alarmingly” or TIM (Traditional Indian Medicine) however this doesn’t mean for one minute that the evidence is not there, it simply could/can mean that people are just not fundamentally aware of this issue. So let’s look at some facts.
Firstly any botanical medicines from herbs to trees such as Aconitum carmichaelii, Flueggea suffruticosa, to Magnolia and Lavandula angustifolia can be grown in just about any nation, leaves, seed’s to bark and roots are all used in TCM and TIM for alternative practices more or less the same as homoeopathic treatments.
The traditional Chinese medicine market is though massive both economically with demand being a main factor which I have highlighted below the average prices of botanical medicine that “does not” include the use of mammals, reptilians, to aquatics species and invertebrates within the arthropod phylum family.
- The herbal industry shares about $62 billion United States dollars (all continents included)
- he World Bank reports trade in medicinal plants, botanical drug products and raw materials is growing at an annual growth rate between 5 and 15%
- Within the European community, botanical medicine represents an important share of the pharmaceutical market the nutraceutical sector is also growing rapidly
- In India the value of botanicals related trade is about US $10 billion per annum with annual export of US $1.1 billion
- China’s annual herbal drug production is worth US $48 billion with export of US $3.6 billion
- Presently, the United States is the largest market for Indian and Chinese botanical products accounting for about 50% of the total exports. (interesting fact) (Fig W.H.O)
- Japan, Hong Kong, Korea and Singapore are the major importer of TCM taking 66% share of China’s botanical drugs export
So these are just some of the main market facts of “botanical medicine” and from what we are now aware of America is by far the largest number one exporter into both China and India with Japan Hong Kong, Korea and Singapore the largest “exporter” to mainly America “oddly” and 80% of European nations.
Other material sourced was what we more or less knew anyway which was China was the main user of Traditional Chinese Medicine however what was more startling and is now making us more nervous is the fact westerners are the second largest user of traditional Chinese medicine. Please view below.
- TCM was popular among the Chinese population in Taiwan during the period studied. More than 60% of all subjects had used TCM during the 6-year interval this figure has since risen again to another 6.8%
- Recent studies have demonstrated dramatic increases in the use of, and expenditure on, CAM in the United States, Canada, Australia and European countries
- Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) is an important category of CAM in Western opinion
- In Europe, North America and other industrialized regions, over 50% of the population have used complementary or alternative medicine at least once.
- In San Francisco, London and South Africa, 75% of people living with HIV/AIDS use TM/CAM.
- 70% of the population in Canada have/do use complementary medicine at least once.
- In Germany, 90% of the population have/do use a natural remedy at some point in their life.
- In the United States, 158 million of the adult population use complementary medicines and according to the USA Commission for Alternative and Complementary medicines, US $17 billion was spent on traditional remedies in 2000.
- In the United Kingdom, annual expenditure on alternative medicine is US$ 230 million.
- The global market for herbal medicines currently stands at over US $ 60 billion annually and is growing steadily every year.
- The most common user of TCM/CAM is the female and not the male as suggested by some
Leaving out acupuncture, reflexology and manipulation and Bianshi and illegal animal parts trade we can clearly see that botanical alternative medicine is vast in size and is widely used from the ages of 25-40. This then creates a massive market for demand which we are more than aware of thus increasing more usage of agricultural land which from looking at the points raised “Asia” is the largest exporter to date therefor meaning a massive usage of agricultural land.
We know that in total there are roughly 13,000 medicinal’s used in China and over 100,000 medicinal recipes recorded in the ancient literature. Plant elements and extracts are by far the most common elements used.
In the classic Handbook of Traditional Drugs from 1941, 517 drugs were listed – out of these, “only 45 were animal parts”, and 30 were minerals. Many plants are used mostly as medicinals, with detailed instructions that have been handed down not only regarding the locations and areas where they grow best, but also regarding the best timing of planting and harvesting them.
So it doesn’t come then as a large shock that in order to keep up with such vast demand then one has to use more land which in China and now America problems are now becoming evident that not all environmentalists have viewed yet but those that are botanically experienced such as myself and others have noticed.
This is where climate change has now been notified but not yet fully recorded and we are hoping that we can start the ball rolling. Climate change effects plants in many ways and in Asian alternative medicine the most common part of the plant used are the leaves, flowers, seeds, and shaving’s and root’s.
Those plants that require mass insect, wind and animal pollination are now being affected greatly in Asia and America of which both nations are vast users and exporters by climate destruction. The two largest users of TCM/CAM, animal land invasion, droughts, moister winters, and floods, as well as decrease in pollinators such as flies, thrips, butterflies, moths, bees but most importantly though bee’s that have decreased in size dramatically from 2007 since CCD was noted that have been decreasing more every year as of CCD better known as Colony Collapse Disorder which has cause untold loss of agricultural crops in Asia and America to Europe with the United Kingdom being rarely unaffected.
Please read more here http://npic.orst.edu/envir/ccd.html and here http://www.epa.gov/opp00001/about/intheworks/honeybee.htm CCD is serious and it has now hit Asia hard with many arable farmers having to pollinate their crops by “hand” thus decreasing yield which in turn equals less money or flying in honey bee hives from thousands of miles away just to pollinate crops.
The phenomenon is now killing more bees leaving hives empty which reduces pollination of crops. So this is one theory that we are aware of and have known about since 2006-07 from which we have started working on in Asia with regards to TCM, for now all investigations on this are not “concluded”.
More noticeable issues that are causing a shortage of arable agricultural land are over urbanization/over population, pollution, raging/orflash floods that have destroyed homes, villages and TCM crops in remote Asia, followed by massive unpredictable weather surges followed by economic failure.
With the TCM/CAM market being vast in size and now taking on average near enough the same amount of monetary gain as illegal arms sales could this be the “number one factor” for increased poaching to feed the demand for TCM/CAM products that is making in China to date an average of $50 billion United States dollars? or are we going to keep believing that the demand is due to Asians wanting to get rich quick?.
Leaving Elephant Ivory out of the entire equation as this is not used as a an “animal bi-product medicine” as such we now focus on the worrying factor and that’s civil war and conflicts.
January 22nd 2013 we contacted an [un-named] American Zoo of which details we always keep back of our contacts and investigations for privacy and confidentiality.
The point of contact was the illegal animal parts trade and the American armed forces. The email that we sent can be viewed below.
21st January 2013 - 07:02 GMT
Re Snow Leopard
Dear *******************
I am not sure if you can help me however I am hoping that one can, my name is *********** and I am conducting a study on endangered species and wildlife trafficking which mainly focuses on South Africa with regards to the Rhinoceros horn, Elephant ivory, Pangolin, to parrots, bones, claws and more within the Traditional Chinese Medicine Market within the whole of Asia.
One of the animals that I am currently just looking at now is the Snow Leopard of which I located your article online that stated a “report” had been carried out with regards to the US Army and endangered species I was wondering if you had in you possession this report or survey that I could read and then right up on exactly what the United States military forces are purchasing with regards to endangered and critically endangered animal parts.
The news report within the link doesn’t really explain “all parts that are/have been purchased”, if you have this “survey or document and would be willing to share to myself for the purpose of creating awareness, education, to tackling this repulsive and barbaric trade that we have been fighting since 2009 which we are now moving to great depths I would be very grateful.
The survey/report that you or the ******* **** did carry out I would be most appreciative if you would share this or give further information on “what animal parts where found” to what areas of Asia as I have investigators in ****** and ****** along with ************ that are locating more information for myself and photographic evidence plus one investigation team within India ******. I don’t require any other information, and your help would be greatly accepted.
Many thanks
Kind regards
Director
The information that we received back was shocking yet not surprising and although the information only focuses on the “purchasing of illegal wildlife products” and not killing them it still amounts to an area that now needs to be focused on dearly and completely banished.
By cleaning this area up through education and awareness and ensuring that no military solider from the USA the largest forces in the world purchases or brings back with them illegal contraband that is not always checked then we will be hitting the demand hard here in the bases thus decreasing slaughter of vulnerable, endangered, and critically endangered.
I didn’t expect that I would actually receive a positive reply back however this has now opened our eyes more and I do hope it now opens yours and you share this document to all military personal so they are aware that it is “illegal” to purchase CITES contraband products.
The results can be seen below and please be aware that only;
From 2007-2009 a survey was undertaken in to military airbases that had been within Asian borders mainly Iraq, Afghanistan to observe which species of animals were being purchased by United States armed forces and the results although not “that alarming” are shocking enough to know that this is on-going and now needs massive awareness to educate and cease all animal parts sales.
The report goes on to state;

ALL ARMED UNITED STATES SOILDERS ARE AND MUST BE MADE AWARE OF THE FOLLOWING
Military personnel who buy wildlife products overseas and import them back to the U.S. risk violating three levels of laws and regulations: U.S. laws (The Endangered Species Act 1531, 2008; Lacey Act of 1900; Lacey Act Amendments of 1981), local laws of the country in which military are serving (Islamic Republic of Afghanistan Environment Law of 2007; Executive Order 2, 1388, 2009 NEPA), and military regulations (United States Central Command 2006; United States Defense Transportation Regulation 2009; USCENTCOM REG 600-10). They also risk violating international conventions, in particular the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora
Soldiers reported skins of wild felids and gray wolf Canis lupus as most commonly observed wildlife products available for sale in Afghanistan. Forty per cent of respondents said they had either purchased or seen other members of the military purchase or use wildlife products. The U.S. military was willing to assist in curtailing supply and demand for wildlife products in order to protect soldiers from unknowingly breaking the law and to conserve wildlife in the countries where they serve.
War can have multiple effects on natural resources, including wildlife (Homer-Dixon et al. 1993; Dudley et al. 2002; McNeeley 2003). In isolated cases, neutral or demilitarized zones with limited human activity may provide a safe haven for wildlife to proliferate (Martin and Szuter 1999; McNeeley 2003. However, modern warfare practices and civil strife associated with war have made recent conflicts highly detrimental to wildlife populations, primarily because effective enforcement of regulations protecting wildlife becomes limited without rule of law (Dudley et al. 2002).
Conflict can also lead to increased direct pressure on wildlife through higher wild meat consumption, increased use of wildlife products to barter for food, arms, ammunition and other goods or services, direct sales of wildlife products, and shooting at animals as target practice.
During civil wars in Rwanda and the Democratic Republic of Congo, hunting of wildlife for meat increased dramatically due to war refugees hunting for their own food and to obtain income by selling the meat in local markets (Plumptre et al. 1997; Renner 2002). The more than 30 years of conflict in Afghanistan has resulted in severe declines in wildlife populations due to the combination of increased availability of firearms, food shortages, and lack of effective law enforcement (Formoli 1995; Zahler 2005). The negative effects of war on natural resources are particularly true in countries, including Afghanistan, where most of the population subsists on locally available resources for their livelihoods (Formoli 1995; Renner 2002; Dudley et al. 2002; Zahler 2010).
More of a concern;
Demand for potentially illicit wildlife products by U.S. military and other personnel in Iraq and Afghanistan is a particular concern, given the strong military presence and important wildlife populations in each country. In June 2009, approximately 135,000 U.S. troops and 120,000 U.S. contractors were in Iraq, and 55,000 U.S. troops and 72,000 U.S. contractors in Afghanistan (Schwartz 2009). Iraq and Afghanistan are at the nexus of the Indomalayan and Paleoarctic biotic realms (Udvardy 1975) with additional influence from the Afrotropical realm (Johnson and Wingard (2010; Zahler 2010).
In combat zones, soldiers may have limited access to areas outside of their assigned base, so they often purchase items at military bazaars, also known as post exchanges, which operate inside their bases. Goods purchased at on-base bazaars in Iraq and Afghanistan are generally less expensive than similar items found in the U.S. (e.g., carpets, hand-crafted-jewelry, antique guns, and fur coats), and can provide a significant income to local people.
Among the local items offered for sale at on-base bazaars are wildlife products. In this paper, ‘‘wildlife products’’ refers to items comprising or made from wild terrestrial vertebrate species including, but not limited to, pelts, coats, hats, other clothing, blankets or rugs made from furs or skins, preserved mammals or birds, antlers, shells, horns, teeth, claws, or other animal trophies, meat from local mammals, birds or reptiles, wildlife pets including wild mammals, birds, and reptiles, ivory or products containing ivory, and medicines derived from wildlife.
The survey then went on that was conducted in 2008 in Fort Drum, New York, USA questioning n average of 2,500 to 3,500 army personal the survey answers are below;
Three of the questions asked out of seven are the most concerning regarding the results that where then obtained by the researchers;
1) Had they whilst on duty in Middle Eastern nations seen wildlife products on display?
2) Had they purchased “any wildlife products”
3) Had they heard of CITES (Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species)
Number three out of the other four questions that are irrelevant we would of thought that the typical American solider had heard of CITES considering America is a large hunting nation with many American and Canadian’s hunting and also traveling overseas to hunt in Africa, and Canada. The results though where somewhat alarming and no many hadn’t heard of CITES hence the reason why there was such vast numbers of them purchasing illegal wildlife skins, rugs/carpets/ meat, ivory, horn and medicine.
The “organisation” asked about CITES because it is the broadest, legally-binding international agreement addressing wildlife trade and many of the countries in which U.S. soldiers serve are signatories to CITES. Respondents were also given the opportunity to provide written comments. The survey took less than 10 min to complete. Soldiers placed completed surveys in a box and then received a small non-monetary thank-you gift. Data from the survey were entered and analyzed in SPSS 16.0.
The aims of the survey where;
“The aims were twofold: to obtain information on the type of wildlife products available to soldiers serving overseas; and to teach military police how to identify items listed under CITES or as protected species in Afghanistan”
The number of respondents can be seen below that took part in the survey;
Part ONE
The survey starts with the “nation they were based in at time of survey” then “the number of respondents” that = the % ALL OF THE RESPONDANTS WERE FROM FORT DRUM U.S.A
1) Afghanistan 209 56.3 %
2) Iraq 160 43.1 %
3) Korea 95 25.6 %
4) Germany 86 23.2 %
5) Kuwait 58 15.6 %
6) Bosnia 27 7.3 %
7) Kosovo 19 5.1 %
8) Japan 16 4.3 %
9) Saudi Arabia 12 3.2 %
10) Honduras 10 2.7 %
11) Other 157 42.3 %
In total for the other many soldiers were based or deployed in more than one country during their service “and” 63 countries in which less than 10 respondents indicated they had been based or deployed
The survey then went on to part TWO
Table 2 the types of items, listed by country, reported being seen for sale in on-base or off-base markets by Fort Drum soldiers = 1,304
The countries they reported seeing for sale in on base or of base markets by Fort Drum Soldiers are named below
Afghanistan, Iraq, Korea, United States, Germany, Kuwait, Kosovo, Thailand, Japan, Bosnia, Australia, countries with less than ten items reported totalled 133 seen for sale in on-base or off-base markets by Fort Drum soldiers.
The total Items “seen” for sale in Part TWO of the survey where, fur and skins, taxidermy, meats and pets, trophies ivory and medicines. Fur was totalled at 307, taxidermy 168, meat 231, pets 222, trophies 224, ivory 112, medicines 40 seen “for sale”
The survey then went on to part THREE
Wildlife items, listed by country, which Fort Drum soldiers reported purchasing while stationed or deployed overseas = 143 purchased – purchased in the following nations below;
Afghanistan, Iraq , Korea Germany, Africa, Japan, United States, Kuwait, Bosnia, Kosovo, Norway, Australia, United Kingdom.
The total items purchased where;
1) Afghanistan – 27 furs/skins, 3 taxidermy, 28 meat, 11 pets, 5 trophies, 6 ivory, 2 medicines
2) Iraq – 5 furs/skins, 10 meat, 1 ivory
3) Korea – 10 furs/skins, 8 meat, 3 pets, 2 ivory
4) Germany – 2 furs/skins, 7 meat
5) Africa – 1 fur/skin, 1 meat
6) Japan – 1 fur/skin, 1 meat
7) United States – 1 fur/skin, 1 meat
8) Kuwait – 1 meat
9) Bosnia – 1 meat
10) Kosovo – 1 ivory
11) Norway – 1 meat
12) Australia – 1 meat
13) England – 1 meat
The MOST CONCERNING WAS - more than 40% of respondents had either themselves purchased or seen other soldiers purchase wildlife products less than 12% had heard of CITES. Of the 220 soldiers surveyed who had served in Afghanistan 12% reported that they had purchased items such as clothing, rugs, comforters, or blankets made from wildlife fur.

The most popular items purchased where fur and skins and meat – illegally or legally is not known, however what we do know is that many trader where given warnings to cease selling illegal CITES contraband that MP’s and seniors knew was illegal to purchase, many traders on the base had their licences revoked and then removed.
Only 10% of the soldiers at Fort Drum had heard of CITES, with over 40% that had seen other mates purchase and over 44% seen other soldiers seen others purchase wildlife items with just under 29% purchasing themselves.
Cited in 13 Oct 2009), soldiers suggested that APO by-passed the tougher military customs screenings. These soldiers gave descriptions of the products being posted, such as ‘‘lots of sand fox pelts with heads,’’ ‘‘dried lizards and snakes,’’ and others noted that items with ivory were particularly common in Iraq. While recounting these experiences, soldiers noted that they were unaware of laws or regulations prohibiting the sale or transport of certain wildlife items or of the possible detrimental impacts of their actions.
Hundreds of wildlife items were noted in Eggers, Bagram, ISAF and Phoenix military installations in Afghanistan during on-base market surveys. For example, in April 2008, U.S. surveyor’s identified 230 items potentially containing CITES species in one on-base bazaar at Camp Eggers.
The most common species identified by surveyors in the military bazaars included Eurasian wolf Canis lupus, Eurasian lynx Lynx lynx, jackal Canis aureus, red fox Vulpes vulpes, Corsac fox Vulpes corsac, and small felid species including leopard cat Prionailurus bengalensis and wild cat Felis silvestris.
At ISAF Airport, snow leopard pelts, leopard pelts, and Marco Polo sheep Ovis ammon pollii skulls and horns were also identified. Of these, only red fox is neither protected by CITES nor by Afghanistan laws. WCS staff also observed international aid workers and contractors purchasing wildlife products at a popular bazaar in Kabul known as ‘Chicken Street.’ results from these market surveys confirmed similar findings by Mishra and Fitzherbert (2004) in the same bazaar.
However - In 2008, after a series of market surveys and wildlife trade training seminars conducted by ***** staff, the number of prohibited wildlife products witnessed for sale in military bazaars in Afghanistan declined however this is JUST for the USA and no other military units from broader nations which is now of a huge concern to ourselves International Animal Rescue Foundation ©
Once trained by WCS staff, military police began con-fiscating prohibited wildlife items from soldiers departing from Afghanistan. A total of 350 confiscated items was reported from Bagram Air Field and Camp Eggers at the end of August 2008 with at least 50 additional items being confiscated between July and December 2009.
Confiscated items appeared to include parts of leopard cats, Pallas cats Otocolobus manul, black-and-white colobus monkey Colobus guereza (a species not found in Afghanistan), and Blandford’s fox Vulpes cana, all of which are listed under CITES. Military police also confiscated items apparently containing jackal, which is listed as a protected species in Afghanistan.
INTERNATIONAL AWARENESS AND EDUCATION TO ALL MILITRY BASES
Surveys found that unless training sessions and surveys continued on a regular basis or were institutionalized in induction trainings for new military police, vendors would reintroduce items when new military rotations came in and the previous group rotated out. In Afghanistan, ISAF military police rotate every 6 months, while U.S. troops rotate every 9 months.
However, demand still abounds in the military and many products are available off-base in Kabul and other cities around Afghanistan (Manati 2009). WCS staff saw 13 snow leopard pelts and one cheetah pelt (among other potentially illegal items) for sale on Chicken Street, Kabul, in November 2011. In August and September 2009, Bagram Air Field Military Customs seized what was thought to be a wolf pelt, a wolf hat, and a Himalayan lynx coat from soldiers who were leaving for the U.S. Demand for wildlife apparently continues, as reflected in comments from military personnel who attended a Fort Drum training session in June 2010.
The report then went on;
These included ‘‘I packed 5 or 6 coats like this [referring to a spotted cat pelt coat], but [customs] took them all’’ and ‘‘they confiscate some but I hide it really well’’ [referring to turtle carapace and coral], and reports from military police in Afghanistan in July 2010 of a Colonel who had purchased a coat apparently made from Eurasian wolf. Our experience indicates that education and raising awareness works to reduce at least some of the demand, although not eliminate it
We are not just looking at culture here in the Asian world as some people think or even “get rich quick” we are looking at lack of education, awareness, other problem areas, and general purchase coupled with “demand, culture and get rich quick”
This report along with the survey has continued on from the Snow Leopard report and we will continue this environmental report in five “parts” of the main chapter. We now all need to devise a plan and awareness session for all military bases as only the Americans where investigated by te survery.
Thank you
Dr J C Dimeri, V.M.D, B.E.S, Ma, PhD , MEnvSc
http://www.savetherhino.org/rhino_info/threats_to_rhino/poaching_for_traditional_chinese_medicine
To be continued ……..
Sadly the video above fails to mention the real issue and that’s what we are getting to.. The Tiger will be extinct in 1-2 years not a decade due to massive demand, lack of awareness, lack of education.. Where not here to write book’s or talk about it on social media were here to stop it..
Environmentalism Chapter 7 - Special Report - Snow Leopard
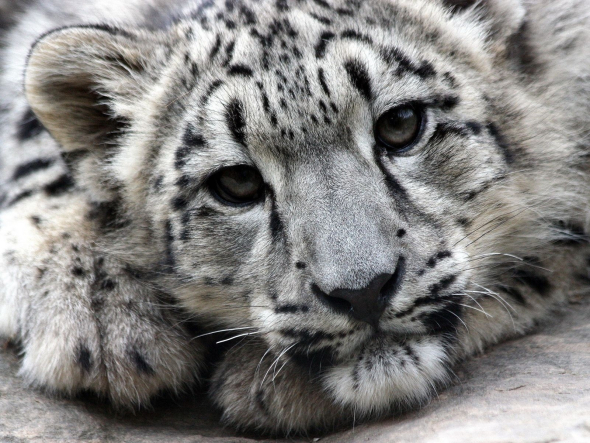

Located deep within the mountainous regions of Eastern Asia there lurks a shy predatory cat that’s so incredibly rare that locating this stunning this stunning magnificent mammal can take some days to even weeks or months in the snowy foot hills of Asia where their numbers are decreasing steadily.
With a population left of around 3,000 to 6,000 within the solitary wild and sadly listed on the International Union for the Conservation of Nature the Snow Leopard is now facing near extinction and we must all now help this species of large cat before the this magnificent mammal vanishes for good.
The highest populations of the Snow Leopard remain in China with roughly 3,000, and with regards to the other nations from Afghanistan, India, Bhutan, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Mongolia, Nepal, Pakistan and Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan populations range from one hundred to five hundred of that.
The Snow Leopard Panthera uncia a member of the Lion and Tiger bag cat family was listed on the IUCN list of globally critically endangered species, and since then through to 2008 there has been very few sightings of prides of this relatively shy mammal that didn’t always live in the high tops of the snowy mountains of Asia.
Since 2008 there has been various wildlife and conservation expeditions showcasing this beautiful leopard however with illegal hunting and poaching rife within Asia then all numbered counts of the Panthera uncia are literally just estimated primarily due to them being very solitary mammals and due to the demand of poaching to feed the fur trade with illegally obtained skins and Traditional Medicine Market with counterfeit pharmaceuticals.
There are two subspecies of this “large wild feline” although it is not related to the domestic feline however the main species is Panthera uncial, and not Uncia uncial that live roughly at 4,000 to 6,000 feet in mountainous terrain well above sea level.
Weighing in at roughly thirty to sixty kilograms the Snow Leopard was first described by Schreber in 1775 that’s behaviour is very unique compared to other large Panthera families, only pairing during the breeding season they do not roar like Lions neither. Snow leopards are considered nocturnal, but seem to be most active in the early morning and late afternoon. They den in rocky caverns and crevices well hidden from destructive man that’s pushed contributed to them being pushed further up above sea level due to poaching and their natural habitat desolated from habitual destruction.
When the war in Afghanistan started there was an “estimated” one hundred to two hundred displaced many Snow Leopards killing some hundreds, since the war ended “still to be seen” there has been hardly a sighting, however they do still use the pass between Pakistan and Afghanistan to bed down, mate and create new bundles of fluffy snowy joy.
The snow leopard’s prey include wild sheep (such as Bharal, the blue sheep), wild boar, gazelles, hares, markhor, bobak, tahr, marmots, mice and deer. They stalk their prey and usually spring from a distance of 20 to 50 feet. The prey I have listed above in the regions of which they have been estimated as high in numbers are becoming small in population to due to the medicine market, and because their “natural habitat” is becoming rapidly wiped out due to agriculture, over grazing, and vast massive population increase that leads to vast urbanisation and hunting too of which their forced higher up into the hills to look for prey or they simply perish.
The Snow Leopard has adapted though remarkably well to these conditions that are mainly icy and snowy they discreetly hide within rock caves and crevices thus making it much harder for the poacher to locate them.
Breeding season is usually January-May, with gestation lasting 98-103 days. A female will give birth to one to four young in the spring in a rocky shelter lined with her fur. The young open their eyes at 7-9 days, eat solid food at 2 months and follow their mother on hunts at three months. Cubs remain with the mother through their first winter.
Females give birth in rocky dens lined with their fur. The young follow their mother on hunts at three months and remain with her through their first winter.
Several forces are responsible for the low numbers of snow leopards left in the wild which I have described in brief below. The cats have thick, rosette-speckled fur that makes them the unfortunate target of poachers who sell their pelts in illegal markets in China, Taiwan, and Mongolia.
The furs of the endangered cat command high prices on black markets. During the 1960s, poaching drove populations as low as 1000 individuals. Although numbers of snow leopards have recovered somewhat in recent decades, there remains concern about illegal poaching as numbers of the cat in the wild are believed to be again falling. There is also demand in China for snow leopard bones for use in traditional medicines (Cat Specialist Group, 2002).

Snow Leopard pelts can fetch between $1,000 to $5,000 with most funds going to armed terrorism fractions.
Snow leopards also face the grim threat of a declining prey supply. Widespread poisoning of marmots and pikas across the Tibetan Plateau coupled with extensive hunting of large ungulates have left the leopard population without the food supply it needs. Some leopards turn to the taking of livestock animals when faced with dwindling wild food sources.
March 2012 a news report quoted “Leopards which live in increasingly fragmented populations in Asia, are protected under Appendix I of the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora along with those in Africa too, which completely prohibits commercial trade in the animals or their body parts”
“But as is the case with tigers and other species, poaching and illegal trade along with other factors such as habitat loss places enormous pressure on leopards. All nine of the world’s leopard subspecies are listed as “Near Threatened” by the International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources due to declining populations.
Snow leopards, which are endangered, are a separate species however are not in realty obtaining the same attention as the other remaining leopards in India which we all now need to start creating massive awareness on.
August 2012 an article in the Asian times also stated that rangers and farmers were also placing these beautiful cats in severe endangerment http://prizmablog.com/2012/08/02/rangers-poacher-decimate-snow-leopards-but-kumtor-mine-gets-ngos-attention/ if we cannot trust our rangers to farmers then what chance of life does the Snow Leopard stand.
“When you play this video it sounds more like a cheap porn version of desperate Russian Housewives, however you need to look very carefully at the description. With the aid of our bilingual investigators we are able to locate these sick individuals. Within the their VIDEO they freely advertise on the description below “Tiger Skins” and anything your heart desires. It is a criminal offence under CITES and IUCN law to slaughter, hunt, poach, trade and distribute to selling of TIGER or Leopard skins as they freely advertise on the World Wide Web. Who’s it left down to though to shut these traders down? ourselves that we have been doing now since 2009. Heat breaking to view but watched with anger. CITES and the IUCN should be closing these traders down and making arrests yet they are still here in Russia”..
Their website can be located here - http://www.roskoshmexa.ru/dost/index.htm
Their detail’s that are now in the hands of Law Enforcement - as we can see they have concealed their illegal money making business quite well “to a degree” but not to our investigative team CICU http://www.ip-adress.com/whois/roskoshmexa.ru
YouTube channel here which is somewhat nauseating
http://www.youtube.com/user/roskoshmexa/videosview=0&flow=grid
28th September 2012 confirmed what we already were aware of with regards to the fur trade and this is where my blood boils badly. Celebrities that know damn well how these animals are treated to even wearing the animal skins themselves are completely oblivious to the environmental destruction that they are causing. The infamous blood skin wearers as I call them may not always be “wearing critically endangered animals” however they are aiding to the bloody demand as their “supporters” wish to follow in their footsteps, being mainly children and teenagers to young mothers and fathers.
Lady Gaga, Kate Moss, Giorgio Armani, Kourtney Kardashian, Scott Disick and their son Mason (all wearing fur) Popstar Rihanna, Chloe Green, television personality, shoe designer and daughter of Top Shop owner Sir Phillip Green wears fur without the care in the damn world of what they are causing, and Hyomin, member of South Korean pop group T-ara wearing dead skinned animals that have been electrocuted or gassed or skinned alive as it “makes the fur more subtle.
(how charming and sweet) what about the skinned animals, the caged waiting to be skinned losing control of their bowls as they hear the cries of their caged species tortured, with their lifeless bodies thrown on to a dump of still moving dying carcasses to “keep up with demand”.
A report issued by the International Union for Conservation of Nature stated that India has only 1,700 Leopard species left, out of them species is the Snow Leopard the most sought after as of its fur colour plus price tag that can range from $6,000 to $30,000 a skin. With the Leopard at now near threatened and with more Tiger species then we can most certainly say that they will be the first pushed to extinction within the next year to two years if that.
Statistical analysis is used to estimate the additional levels of “undetected trade” and concludes that around 2294 Leopards were trafficked in India during the period—an average of four animals per week over the 10 year period.
TRAFFIC’s objective analysis has cast new light onto the sheer scale of the illicit trade in Leopard parts in India, which has hitherto been overshadowed by the trade in another of the country’s national icons, the Tiger.
Without an effective strategy to assess and tackle the threats posed by illegal trade, the danger is that Leopard numbers may decline rapidly as happened previously to the Tiger.

Uttarakhand emerged as a major source of Leopard parts in trade, while Delhi was found to be a major epicentre of the illegal trade, along with adjacent areas of Uttar Pradesh, Himachal Pradesh and Haryana.
Close to 90% of reported Leopard part seizures in India comprised solely of skins, making them the dominant body part found in illegal trade during the 10 year period. Other body parts, particularly bones, are known to be prescribed as substitutes for Tiger parts in traditional Asian medicine including Lions Panthera leo.
It is believed most Leopard parts are smuggled out of India to other countries in Asia, often via the porous border with neighbouring Nepal. Earlier investigations indicated many of the Leopard parts found for sale in northern Myanmar, northern Laos and the ethnic Tibetan regions of China originated from India.
However with such poaching epidemics the snow leopard face’s other threats so as quoted above. Panthera uncia hunts on rich alpine lands, however their prey bharal or blue sheep (Pseudois nayaur) and ibex (Capra sibirica) whose distribution coincides closely with snow leopard range plus the marmot (Marmota spp), pika (Ochotona spp.), hares (Lepus spp.), small rodents, and game birds also feed of these areas lower down the mountainous ridges.
As of natural habitual loss of the Snow Leopards prey’s food consumption being mainly alpines, scrubland, insects and green pastures from “over grazing”, climate change, longer winters, and agriculture then this see’s the prey that the farmers allow up to these areas then move on to fresh pastures, thus displacing the Snow Leopard’s prey = starvation for the adult and cubs..
The IUCN reported “A major threat to the Snow Leopard include prey base depletion, conflict with local people, and lack of conservation capacity, policy and awareness.
Within the Himalayan region (Tibetan Plateau and other southern China, India, Nepal and Bhutan) reduction of natural prey due to competition with livestock, killing of snow leopards in retribution for livestock depredation, lack of trans-boundary cooperation, military activity, and human population growth or poverty.
Within the regions of Northern range (Russia, Mongolia, and Altai and Tien Shan ranges of China) poaching snow leopards for trade in hides or bones, lack of appropriate policy and effective enforcement, lack of institutional capacity and awareness among local people and policy makers, and human population growth or poverty.
Although Snow Leopards are killed in retribution for livestock depredation, they are also killed for commercial purposes, and poaching for illegal trade does represent “a significant threat”. Pelts appear to be the main snow leopard produce in demand, but there is also evidence of demand for live animals for zoos and circuses which is VERY CONCERNING. Other body parts found in trade include bones (used especially in Chinese medicine as a substitute for tiger bone), as well as claws, meat and sexual organs of male cats.

Snow Leopard sized in a Circus Kyrgyzstan in central Asia (Critically Endangered)
Then the real news starts to emerge that we didn’t expect to hear although we knew as other conservationist’s did the United States Army are fueling the demand for endangered species without even realising that they are actually supporting more terrorism through black market sales. This is alarming and extremely concerning that’s now being addressed but to what degree we still don’t know.
A report stated by the Eco-centric wildlife press of which I have placed the extract below I have also included the link for February 27th 2012. The link is worrying as this could now give reason to believe why there are so many “endangered species part products in America and Canada”. The report reads; http://science.time.com/2012/02/27/wildlife-wars-how-u-s-soldiers-unknowingly-support-the-endangered-species-trade/
You’re a U.S. soldier, abroad on your first deployment in Afghanistan. Like any world traveler you want to bring a souvenir back home to the family, something they could never get at home. So you visit the local market on base, where Afghan vendors sell carpets, trinkets and clothing. And you pick out something really cool: a white spotted pelt, perfect for a rug. What could possibly be wrong with that purchase?
As it turns out, quite a lot—at least for endangered species. According to a study from the Wildlife Conservation Society (WCS)—an environmental non-profit that runs the Bronx Zoo in New York—a significant number of U.S. soldiers deployed overseas have purchased products made from wildlife. And in many cases, that wildlife is threatened—like the endangered snow leopard of Central Asia, which could have been killed to make that fine white pelt. Most soldiers aren’t knowingly purchasing products made from endangered species, but they are inadvertently supporting that trade, which can have serious consequences for conservation. “The wildlife trade is highly problematic,” says Heidi Kretser, the coordinator of the WCS North America Programs Livelihood. “There needs to be awareness raising in the military.”
The WCS research began back in 2007 when staff in Afghanistan noticed products made from threatened species being sold on military bases near Kabul. That led to a survey of nearly 400 soldiers at Fort Drum in upstate New York, one of the biggest military bases in the U.S., sending some 80,000 troops a year to Iraq and Afghanistan during the height of the conflicts.
WCS found that more than 40% of the soldiers surveyed had either purchased wildlife products or had seen a fellow service member buy one. They reported seeing wildlife items for sale on or off bases in 40 countries, with the greatest number by far in Afghanistan—a fact that makes sense, given that the Central Asian country is home to a number of endangered species, including the snow leopard. (The sheer number of U.S. troops stationed in Afghanistan played a role in the numbers as well.) “The most popular items were fur coat and rugs,” says Kretser. “And there you’re talking about species that do tend to be threatened.”
The problem isn’t just that U.S. service members are buying wildlife products—it’s that their presence in countries like Afghanistan and Iraq helps create a market for poaching and hunting that might otherwise not exist.
American soldiers—and even more so, the contractors and other international personnel who follow in their wake—can bring developed world purchasing power to bear in a developing world. Suddenly an Afghan who might have no one to sell that snow leopard pelt to—and therefore, no reason to participate in the trade in the first place—suddenly has a ready market with well-off customers. “You can sell a snow leopard pelt for $1000,” says Kretser. “That’s far more than the average Afghan person could make in a year.”
You can’t blame a poor person for trying to earn that kind of money—which is why it falls to the customers more than anyone else to halt the wildlife trade. There are international and military regulations that prohibit the purchase and transport of products made from endangered wildlife, That’s why Krester and the WCS have been working with the Department of Defense’s Legacy Program on educational courses for personnel who are about to be deployed overseas.
The programs underscore the illegality of purchasing endangered wildlife products, as well as the potential health threats that can come with them. (Wildlife—especially primates—are a major source of zoonotic disease, and the international trade can spread those diseases around the world.) The hope is that by educating service members early, they’ll be that much less likely to pick up a wildlife souvenir to take home with them.
This year 2013 Hilary Clinton then announced in a media report that the United States was the “SECOND” LARGEST importers of illegal wildlife products in the world to-date. More concerning is the money earned from the illegal trade of living animals and dead animal parts is roughly equal to that of illegal weapons smuggling and second only to drugs as an illegal business.
Organized crime is thought to be involved in the trade of ivory, coral, snake skins, conch shells, shahtoosh and abalone. Many smugglers who made a living in gold and narcotics now are into wildlife trading. Among the attractions are the light sentences if you get caught and the low probability of getting caught because of the low priority given to wildlife crimes by authorities.
The Internet has been a boon for the exotic animal traders and detriment to threatened species. Among the animals and animal products available on the web are young giraffes for $15,000, a black leopard for $4,000 gorilla for $8,131, baby chimpanzees for $60,000, cotton-top tamarins for $2,500, hawksbill turtle shells for $120, elephant bone sculptures for $18,000, crocodile skin boots, seahorse skeletons, ivory sculptures, and shahtoosh shawls.
Only yesterday 20th January 2013 my investigations team the CICU located our 7th illegal trader selling and distributing “Siberian Tiger skins” and bones, please view the link here - http://myworld.ebay.ca/reptilesmorpho/?_trksid=p4340.l2559 we then located his site here http://www.cougarsdentaxidermy.com/#! On locating more we then found that the Siberian Tiger that is only numbered as 500 maximum in the wild is listed for sale via two rug skins “both sold to two American’s” http://www.cougarsdentaxidermy.com/#!stuff-for-sale/vstc1=rugs-for-sale/productsstackergallery4g5=1
With the illegal animal parts trade being worth or more or less the same as the illegal market in arms and narcotics one can clearly see that it’s not just the Asian poachers to blame here its everyone that wants a piece of gold which is more easier to obtain and to ship thus making big bucks via slaughtering wanted endangered mammals and reptilians to aquatics.
With the American military purchasing endangered and critically endangered parts then the war on terrorism is in reality being “funded to a degree” by themselves without them knowing it.
The Snow leopard is in big danger of extinction within the next year to two years, and should no species recovery be achieved to slow this trade to even cease it that is not just being used for rugs, medicine and cultural beliefs but also mainly now for terrorism then we will view the Snow Leopard gone with many other species of species too.
To be continued …
Dr J C Dimetri V.M.D, B.E.S, Ma, PhD, MEnvSc
One may believe that WWW do not the rescue, well your correct. The WWF is not a rescue that are a “wild animal unit” that specializes in “WILD ANIMALS” they don’t rescue canines, felines, zoo animal’s, the don’t deal with domestic abuse. They are an environmental organisation that works to save “WILD ANIMALS” hence the name World Wildlife Fund. They are well known for their pioneering work to save and protect iconic wildlife like pandas, tigers, whales and rhinos - and have had some great achievements in those areas since we started in 1961.
THE ILLEGAL WILDLIFE TRADE STOPS HERE - PLEASE REPORT ANY CONSERVATION CRIME YOU WITNESS OR LOCATE TO US AS THE ADDRESS BELOW - OR CONTACT YOUR LOCAL INVESTIGATIONS / CUSTOMS UNIT
[email protected] Conservation Investigations Crime Unit C.I.C.U.
WARNING
You are breaking the law if you poach, illegally hunt, sell, distribute, purchase or smuggle any CITES or IUCN prohibited animal contraband. Should we locate/know off/ you breaking this law you will be punished with a maximum prison sentence of up to life imprison -
All information that we obtain from ground to online we share with third parties too.. Don’t be a fool and put the gun down.
Environmentalism chapter 6 - Bee Decline - An Environmental Nightmare

What’s happening to our bees? Since 1990 the population of bees has declined dramatically to date for 2013 the population of European and American honey bees has now declined by 50% which is extremely concerning for many agriculturists, horticulturists, environmentalists, but most importantly our natural wildlife that depend on such insects to pollinate some millions of flowering nectar plants that then continue the growing process of wildflowers, trees, maize, corn, to critically endangered species of flowering plants such Alliaceae Agardh endangered in Czech Republic, to the Colchicum autumnale one of the most endangered species of Crocus bulbs in the world.
There are no theories or stories regarding the decline of the honey bee, and the fact stands at this with evidential proof that the honey bee is now moving up to becoming a “vulnerable” species of insect that should we lose then we will be viewing some catastrophic agricultural and economical loss and failure that will have a knock on effect within the hypermarkets from grains, barley’s to cereal crops and even florists and more.
History of the Bee - Apis mellifera
Firstly before I give a brief history on the common European/Western American Apis mellifera please remember that the Apis genus has no relation to “manmade” (agricultural-botanical) deterrent “species” called Encarsia Formosa which is the wasp. Although the other species’s of Encarsia are natural the parasitic friendly Formosa breed in labrotories for pest control is nethier related to both wasp nor bee. This glass house agricultural friend is “a genetically grown and adapted pest controller”
The common wasp is named as this specimen however the deterrent that is used like the lady bird that is of no harm to humans at all, is specifically used for inside crop and glass house control of Aphids from black fly, green fly, red fly, and other succulent pests that wreak havoc in the botanical world.
There was a recorded 20,000 species of known bees that spanned the entire globe apart from the much colder climates which have many different behavioural patterns. There are now an estimated 18,000 species of bee from exactly nine “generic” families of which the honey bee makes up one of them the mellifera family.

The larger family of bee colonies is Apoidea, bees are known in the conservation world as arthropods, an amazingly complex species of “multi” family animals on our planet to date. An arthropod is invertebrate animal having an exoskeleton a segmented body, and jointed appendages.
Arthropods are members of the phylum Arthropoda (from Greek ἄρθρον árthron, “joint”, and ποδός podós “leg”, which together mean “jointed leg”), and include the insects, arachnids, and crustaceans. Arthropods are characterized by their jointed limbs and cuticles, which are mainly made of α-chitin
Bees are closely related to the wasp, ant, and cockroach. It’s truly impossible to determine the actual number of bee’s on the planet as they are almost microscopic and live in their “billions” which may sound “a vast quantity” however it’s not and the noticeable effects of decreasing numbers have been recorded as explained clearly below;
Destruction of the bee and bee colonies
- Colony collapse disorder (CCD) phenomena of which the worker bee the most important of them all just vanishes leaving the queen bee to die within the hive.
- Intensive farming methods that use more pesticides “although this was primarily dismissed” what some conservationists forgot to understand that pesticides are also sprayed with insecticides and fungicides, and new chemical fertilisers that are more potent today than they were back in 1070’s.
- Air and noise pollution.
- Habitat destruction that see the bee’s natural source of botanical nectar plant life destroyed to make way for buildings, and other construction activities.
- Nosemosis - Nosemosis is a parasitic disease affecting adult bees, due to the evolution and proliferation of the specific protozoan Nosema apis in the midgut epithelial cells. It causes digestive disorders (diarrhoea or constipation) and may impair the ability to fly bees have been hit hard by this parasitic disease that wipes thousands of bee’s out
- Fipronil - a broad spectrum insecticide that disrupts the bee’s central nervous system by blocking the passage of chloride ions through the GABA receptor and glutamate-gated chloride (GluCl) channels, components of the central nervous system. This causes hyperexcitation of contaminated insects’ nerves and muscles. Specificity of fipronil on insects may come from a better efficacy on GABA receptor, but also because GluCl channels do not exist in mammals. Fipronil is widely banned now in many countries as of dangers being caused to human health to.
- Carbon emissions.
- Seasonal weather disruption
- Excessive agriculture.
These nine points are what have amounted to such a vast decline in the number of bee populations falling worldwide and it’s now worrying many agriculturists, botanists and environmentalists as many plants require “insect” pollination and with the bee being one the best pollinators due to its furred body and size and location then seeing natures friend banished will have disastrous and detrimental effects on the planets ecological system that in turn will then have “knock on effects” to other species both plant, insect, avian reptilian and mammal.
From the beginning of the seventies to mid-2005-07 there was a vast decline in the number of honey bees then recorded that then had a knock on effect on the farming industry thus increasing cereal and crop prices. What was also evident to was the now almost banished bee from bee keeping within man controlled colonies of which there are few honey bee populations left in in most parts of the sates.
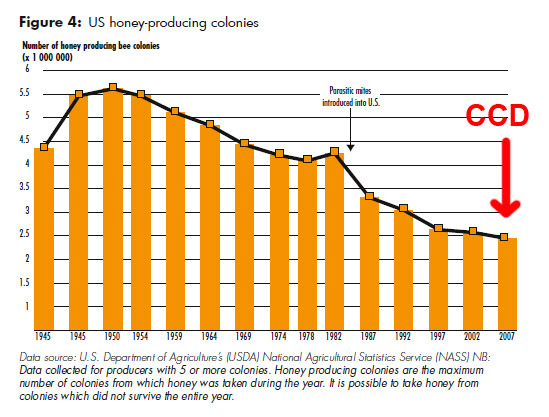 2007 saw the population of Honey bee decline in the United States and Europe
2007 saw the population of Honey bee decline in the United States and Europe
Urbanisation and the Varroa mite a genus of parasitic mites associated with honey bees that have infected many thousands have been partly blame to the decline, sadly the Varroa mite is also a major reason why the domestic bee hive population has decreased rapidly too.
In 2010 after a recent study looked at many thousands of deceased bees within hives, a parasite named as Nosemosis was located, this parasite coupled with urbanization, pollution, insecticides, pesticides, fungicides and herbicides with massive over usage of glyphosate has been a contributing factor to the loss of the bee on an international scale never seen before.

Pic off the Varroa or Nosema mite that’s been killing thousands of bee’s of within hives to date
The parasite Nosema apis AKA Varroa and a IIV6 a Deoxyribonucleic acid virus is better explained below in formation.
Deoxyribonucleic acid virus & Nosema apis control
RNA viruses in insects are targets of an RNA interference (RNAi)-based antiviral immune response, in which viral replication intermediates or viral dsRNA genomes are processed by Dicer-2 (Dcr-2) into viral small interfering RNAs (vsiRNAs).
Whether dsDNA virus infections are controlled by the RNAi pathway remains to be determined. Here, we analyzed the role of RNAi in DNA virus infection using Drosophila melanogaster infected with Invertebrate iridescent virus 6 (IIV-6) as a model.
We show that Dcr-2 and Argonaute-2 mutant flies are more sensitive to virus infection, suggesting that vsiRNAs contribute to the control of DNA virus infection. Indeed, small RNA sequencing of IIV-6-infected WT and RNAi mutant flies identified abundant vsiRNAs that were produced in a Dcr-2-dependent manner.
Graph above indicates VIRUS CONTROL that’s aimed at “controlling Nosemosis” a type Encarsia Formosa parasitic wasp was used within scientific studies as they are closely related to the bee.
We observed a highly uneven distribution with strong clustering of vsiRNAs to small defined regions (hotspots) and modest coverage at other regions (cold spots). vsiRNAs mapped in similar proportions to both strands of the viral genome, suggesting that long dsRNA derived from convergent overlapping transcripts serves as a substrate for Dcr-2.
In agreement, strand-specific RT-PCR and Northern blot analyses indicated that antisense transcripts are produced during infection. Moreover, we show that vsiRNAs are functional in silencing reporter constructs carrying fragments of the IIV-6 genome. Together, data indicates that RNAi provides antiviral defence against dsDNA viruses in mammals. Thus, RNAi is the predominant antiviral defense mechanism in insects that provides protection against all major classes of viruses.
Please note “Thus, RNAi is the predominant antiviral defence mechanism in insects that provides protection against all major classes of viruses in insects and animals ” So in reality one would believe that the bee’s numbers would increase, however we simply don’t know if this is true even with scientific analysis we still cannot establish the actual cause nor “starting indicator” for Colony collapse disorder (CCD) to the infection of Nosemosis within the colonies.
However we have managed after taking ten hives apart in the late Autumn early and Winter of 2011-12 and then examining them along with deceased bees that Nosemosis although not yet “fully understood” has been surveyed in many hives which if the defense DNA virus did work and was successful then putting that to instant practice would help to save bee populations dramatically.
Regrettably with their being little known within this “area” of hive contamination and CDC phenomena then it’s difficult to establish if this is the actual main cause or just a “generic” infestation that is “contributing” along with all nine points to the destruction of the bee and colony factories as listed above.
International Animal Rescue Foundation Botanist Dr J Williamson ND, PhD, MEnvSc and Chief Executive Officer Dr J C Dimetri V.M.D, B.E.S, Ma, PhD, MEnvSc are working extensively on this subject along with international environmentalists and botanists to apiarists to conclude studies of which the nearing conclusive reports shall be sent to the Royal Horticultural Society, arboriculture scientists and botanists and universities in America with regards to this in-depth field study and whether extensive furthering field analysis should be resumed or whether they themselves have any furthering data to helping to preserve the bee and cease copiously dropping numbers.
Quote –
“Colony collapse disorder is significant economically as vast agricultural crops internationally are pollinated by bees and ecologically, due the major important role that bees play in the reproduction of plant communities in the wild through insect pollination with the bee being the world’s largest pollinator ”…. “Should no sufficient and conclusive study be located to cease this phenomenon then our bees will eventually vanish causing massive agricultural failure and rising cereal and crop prices thus forcing nations to import = more carbon emissions, and use of alternative (genetically modified crops and insects) = total Mother Nature destruction from manmade interference and lack of scientific understanding of arable and melittology and entomology species”..
— J C Dimerti International Animal Rescue Foundation
To think that one single species of insect that is 1.2 cm in length “could” cause such catastrophic economical failure is mind-boggling but extremely worrying economically and environmentally.

Dr J C Dimetri V.M.D, B.E.S, Ma, PhD , MEnvSc International Animal Rescue Foundation
The video above from Dr Elizabeth Ele, is “moving away from the problem” and this really is wrong education and sloppy science. Native bees that now America doesn’t have would of been able to sustain the crops of the almond and fruit trees that Dr Ele was describing. By simply keeping them in a hive and then “transporting them” to outer town agricultural districts may sound all good however if the bees have “infections” then they are or could contaminate other insects to plants life to. This is NOT how Mother Nature works and it’s also BAD management and science. To describe this is just the same as “artificial insemination” more or less as Americas “native bees” have practically vanished. So to see this is very concerning, however the Doctor seems more concerned with regards to the “crop and pollination factor” not “why” the native bees are in reality drastically reduced and how we should bring them back. - Poor management and BAD science.